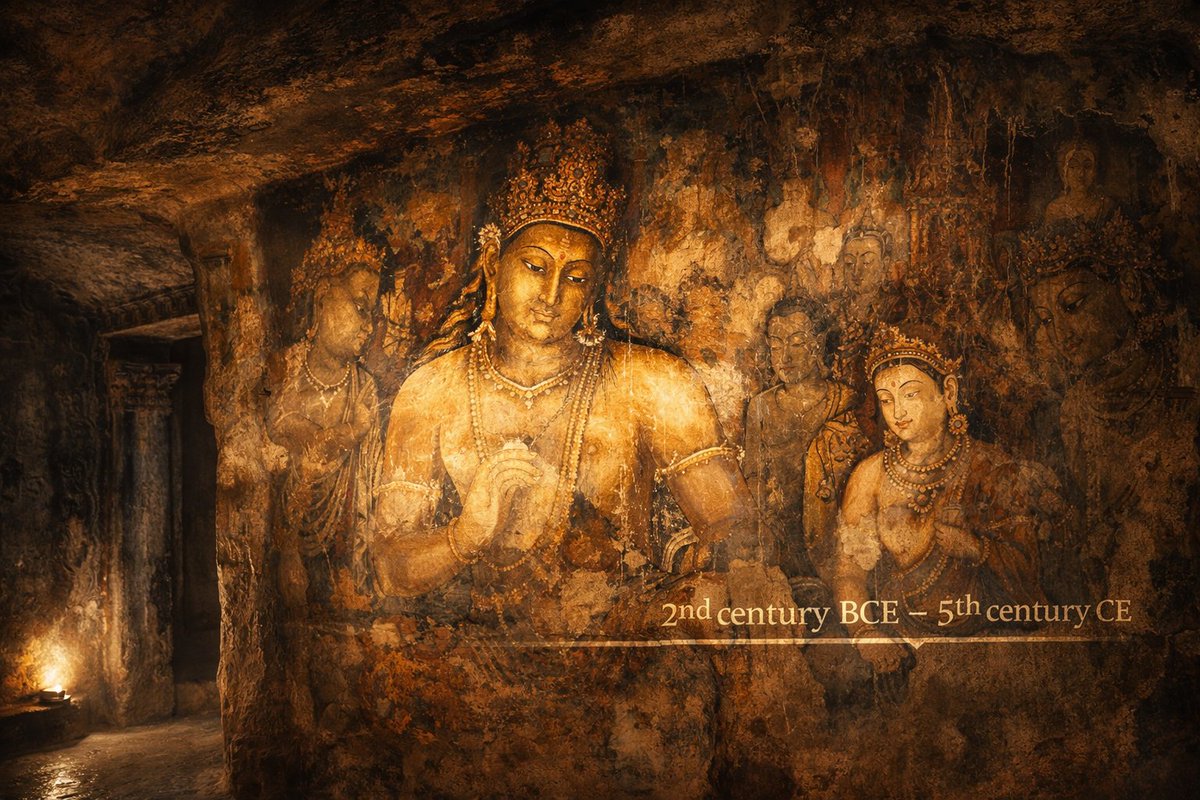
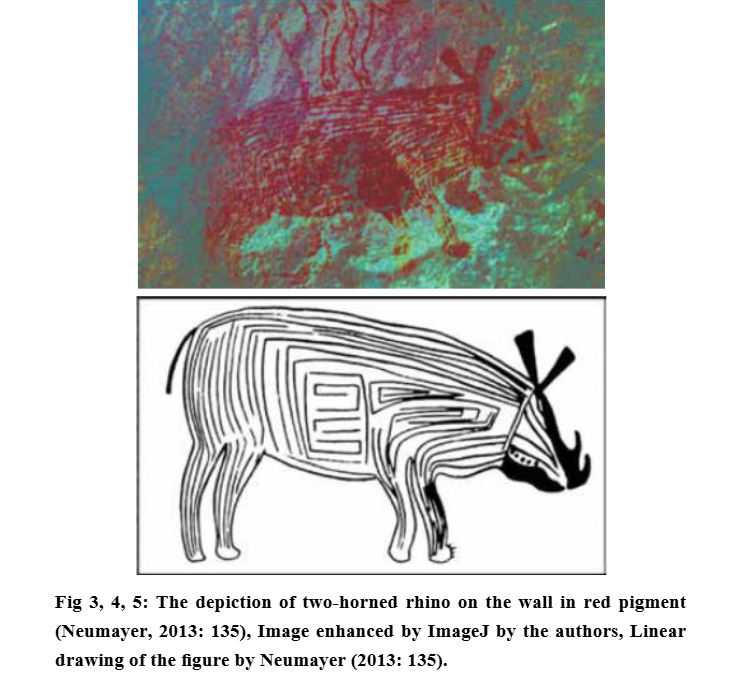
#Thread Indus Gadd 1932 Seals found in UR, a Sumerian city in ancient Mesopotamia, at the site of modern Tell el-Muqayyar in south Iraq's
Impressive Professional quality Pic by @britishmuseum. @NationalMissio1 & @ASIGoI should learn from British Museum.
#Archaeology
1/14
Impressive Professional quality Pic by @britishmuseum. @NationalMissio1 & @ASIGoI should learn from British Museum.
#Archaeology
1/14
A palm-tree with humped bull (zebu), serpent, scorpion and recumbent human figure at the top in this Dilmun Period seal found in 1930 in UR
#Archaeology
2/14
#Archaeology
2/14

Circular stamp-seal of glazed white steatite; engraved with design showing a bull standing over a manger; Indus inscription along the top; top of domed reverse broken.
2500 BC-2000 BC
Babylon (Iraq)
#Archaeology
3/14
2500 BC-2000 BC
Babylon (Iraq)
#Archaeology
3/14

Circular, dark green steatite stamp seal with pierced, centrally grooved lug at top, base engraved with inscription in Indus script above a humped bull facing right; one side badly chipped.
#Archaeology
4/14
#Archaeology
4/14

Greenish-grey steatite Dilmun-type stamp seal with creamy glaze; circular with convex top; double hole pierced through top; engraved with design on base divided into quadrants of four seated figures round periphery; section of base broken away.
#Archaeology
5/14
#Archaeology
5/14

Black glazed steatite stamp seal; circular; Gulf type and/or Indus Valley style; domed handle at top with groove along centre; hole pierced through at base of handle; design deeply engraved on base of figures and animals; chipped.
#Archaeology
6/14
#Archaeology
6/14
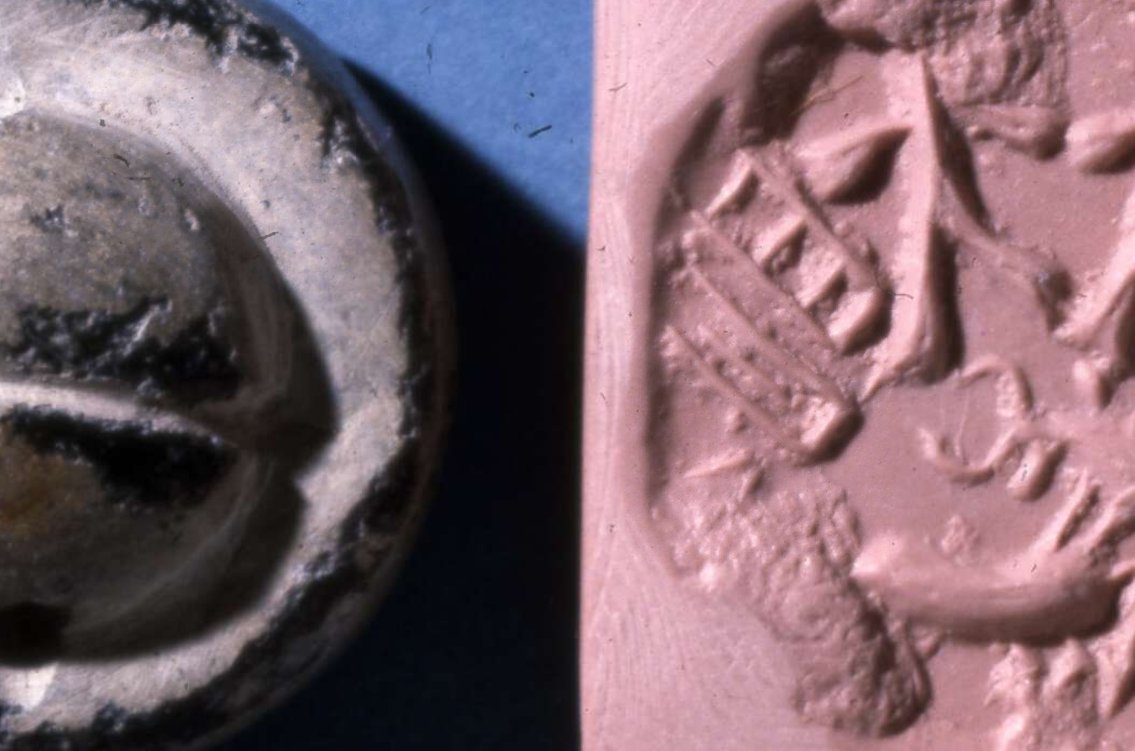
Rectangular, green-grey mottled steatite stamp-seal with pierced lug at back; front surface deeply engraved with crude design of bull standing, facing left; single line inscribed line above; Indus style seal with Sumerian inscription.
#Archaeology
7/14
#Archaeology
7/14

Fragment of a circular greenish-grey steatite stamp seal; part of an inscription and incised design on base; button boss top.
#Archaeology
8/14
#Archaeology
8/14

Circular light grey glazed steatite seal; base engraved with design of a bull facing right, with single-line inscription in Indus script above; roughly conical grooved button boss on top; hole pierced through base of button bosson; broken one side with section missing
9/14
9/14

Dark grey glazed steatite stamp seal; circular with domed top; Gulf-type; hole pierced through top; design engraved of scorpion and bull on face; complete.
#Archaeology
10/14
#Archaeology
10/14

Fragment of a pale brown glazed steatite stamp seal; circular with domed handle at top; hole pierced through base of handle; inscription and illegible design on base; lower and left hand part broken away.
#Archaeology
11/14
#Archaeology
11/14

Circular stamp-seal of black steatite, partially covered with a kind of glaze, Dilmun type; with face incised on top; hole pierced through top; geometric or animal design engraved on base.
#Archaeology
12/14
#Archaeology
12/14

Circular, light grey steatite stamp-seal; hole pierced through back; Dilmun type; face shows engraved design of two men, each dressed in a long skirt, walking left and clutching a jar between them; left figure grasps a leaping gazelle by the neck.
#Archaeology
13/14
#Archaeology
13/14

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh