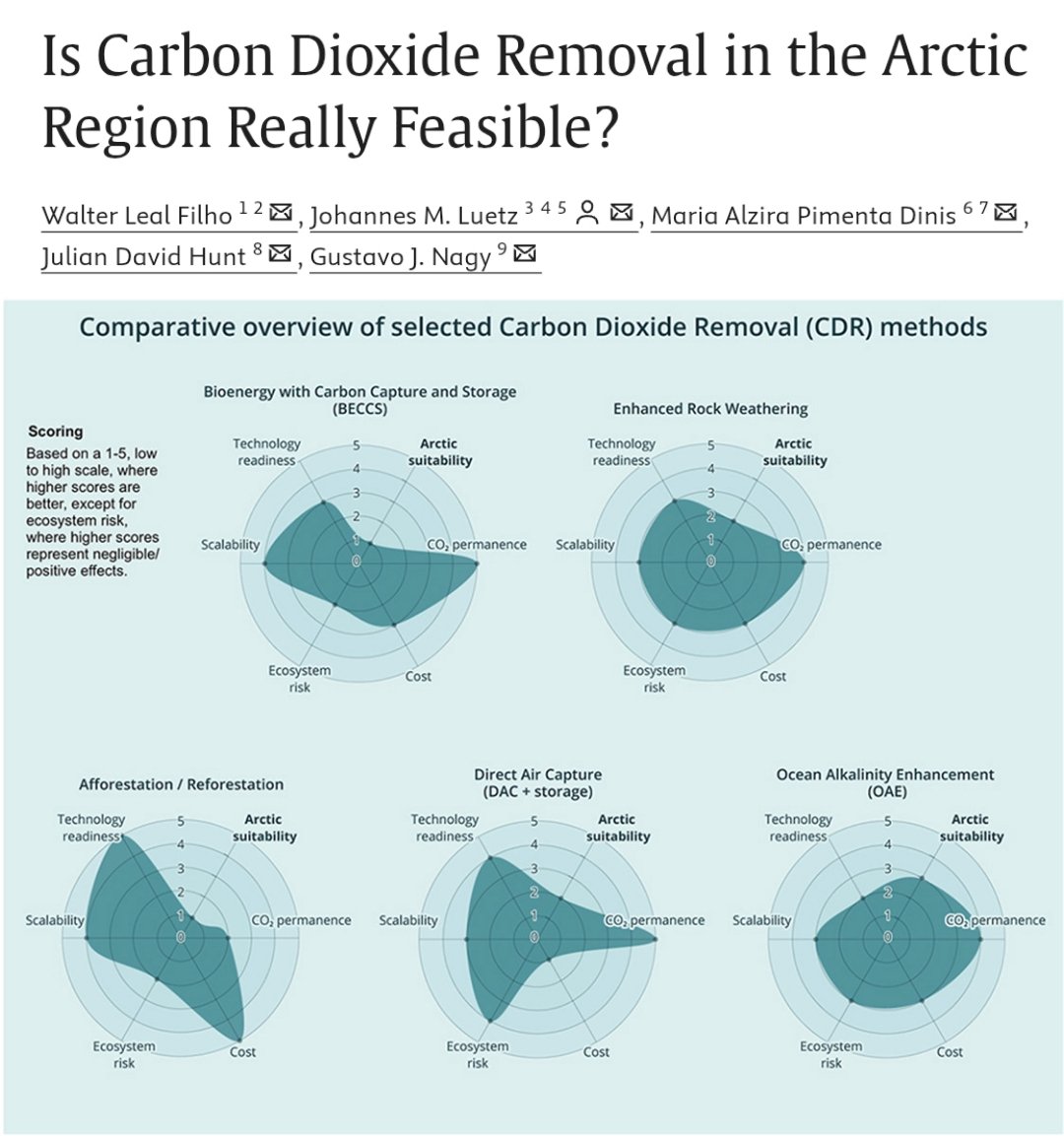
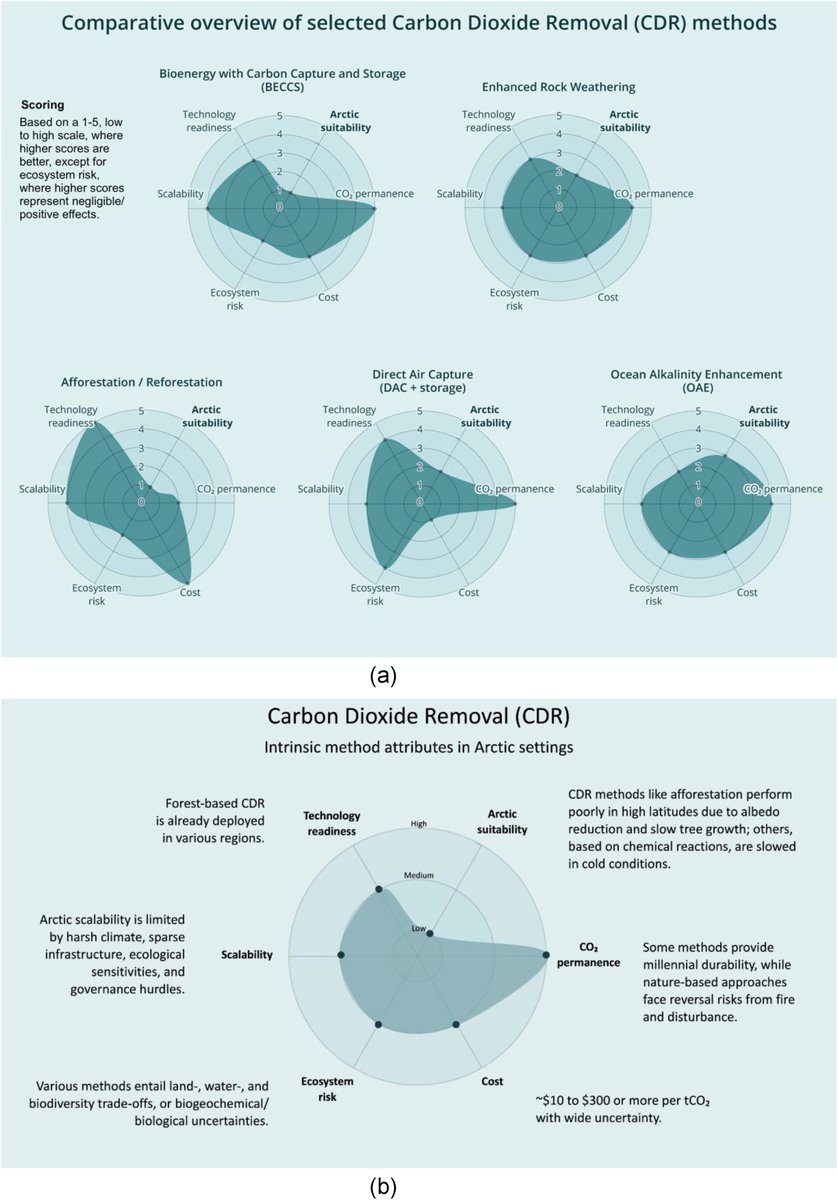
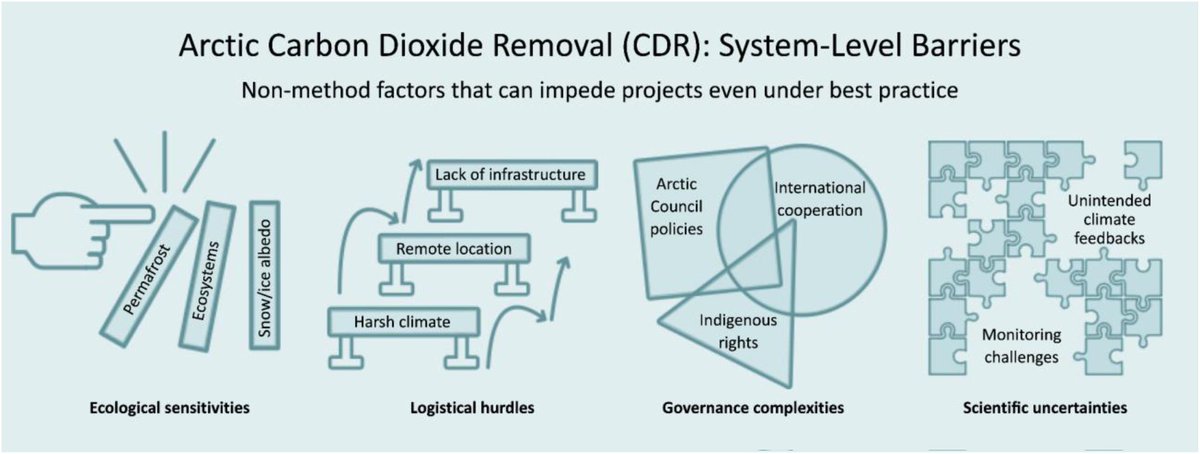
🚨PAPER🚨
The newly published article focuses on the physical & chemical aspects of #CO2 #storage via liquid & solid chemical carriers & sorbents & gives an overview of the energetics around their use & options for their future development.
#CarbonRemoval
#CarbonStorage
🧵
1/7

The newly published article focuses on the physical & chemical aspects of #CO2 #storage via liquid & solid chemical carriers & sorbents & gives an overview of the energetics around their use & options for their future development.
#CarbonRemoval
#CarbonStorage
🧵
1/7


Research pointed that "exciting opportunities for coupling #capture and medium to high maturity multi-year #storage technologies could support #CarbonRemoval in the coming decades."
2/7
2/7

Highlights of the analysis are:
🔸"The remarkable #storage capacity of oxalic acid & formic acid (CO2-density of 1857 kg m−3 & 1152 kg m−3, compared with condensed liquid CO2 at 993–1096 kg m−3, respectively)."
3/7

🔸"The remarkable #storage capacity of oxalic acid & formic acid (CO2-density of 1857 kg m−3 & 1152 kg m−3, compared with condensed liquid CO2 at 993–1096 kg m−3, respectively)."
3/7


Cont'd...
🔸"The relative scalability and compatibility of carbonate salts for stationary storage with #DirectAirCapture, and the potential promise of multiple carriers for CO2 transportation."
4/7
🔸"The relative scalability and compatibility of carbonate salts for stationary storage with #DirectAirCapture, and the potential promise of multiple carriers for CO2 transportation."
4/7

So, results suggested that "solid sorbents do not achieve such ultra-high #storage capacities, but could improve storage over compressed gas tanks on a capacity and energetics basis."
5/7
5/7

Get insights from the article ⬇️
pubs.rsc.org/en/content/art…
#CarbonDioxideRemoval
#CarbonRemoval
#CarbonStorage
6/7
pubs.rsc.org/en/content/art…
#CarbonDioxideRemoval
#CarbonRemoval
#CarbonStorage
6/7
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh