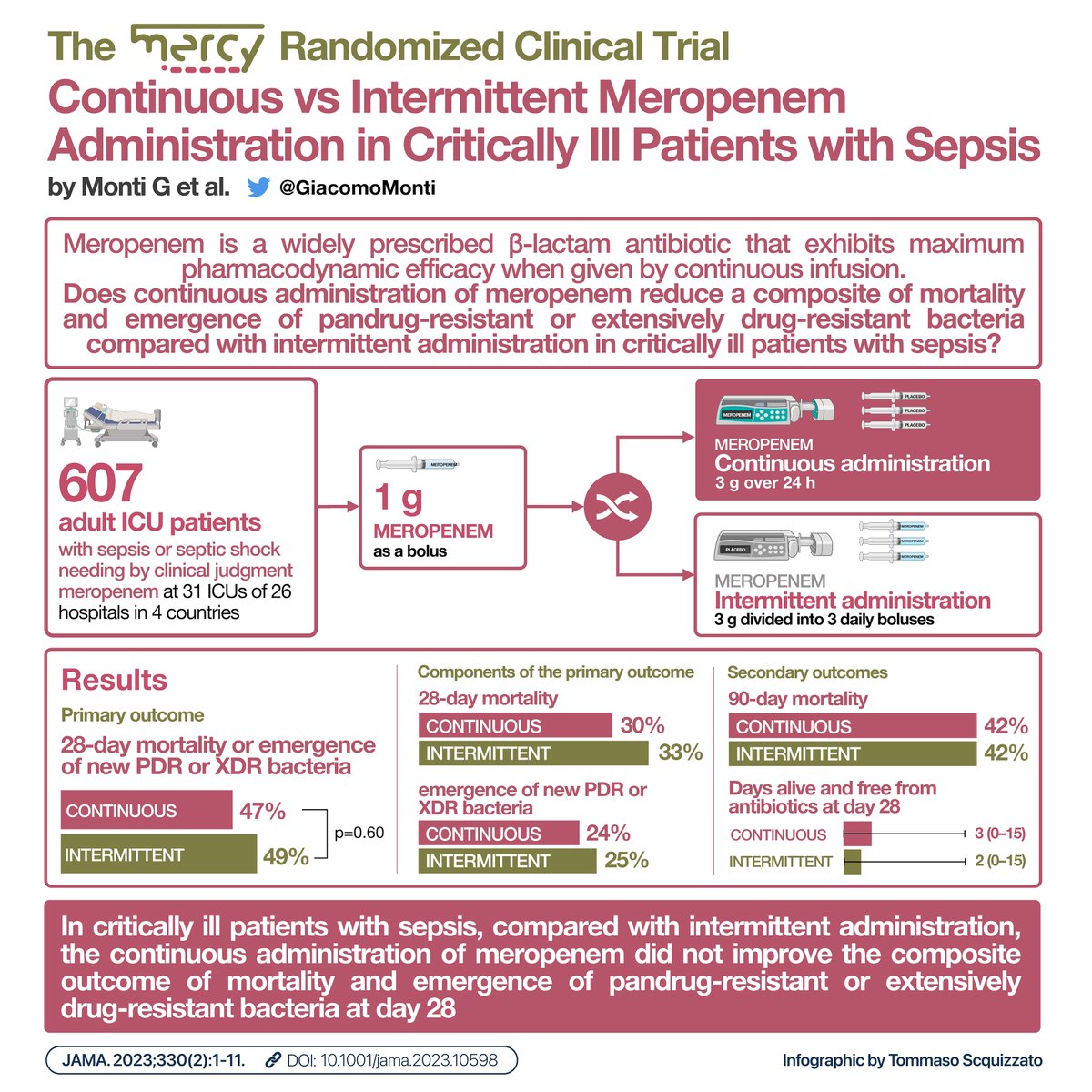
#Etomidate and mortality in critically ill patients
Etomidate is a common induction agent but controversy exists about its effects on outcomes
Our meta-analysis found a high probability that etomidate increases mortality (NNH 31)
🧵Thread 1/6 🔗sciencedirect.com/science/articl… #FOAMcc
Etomidate is a common induction agent but controversy exists about its effects on outcomes
Our meta-analysis found a high probability that etomidate increases mortality (NNH 31)
🧵Thread 1/6 🔗sciencedirect.com/science/articl… #FOAMcc

2/
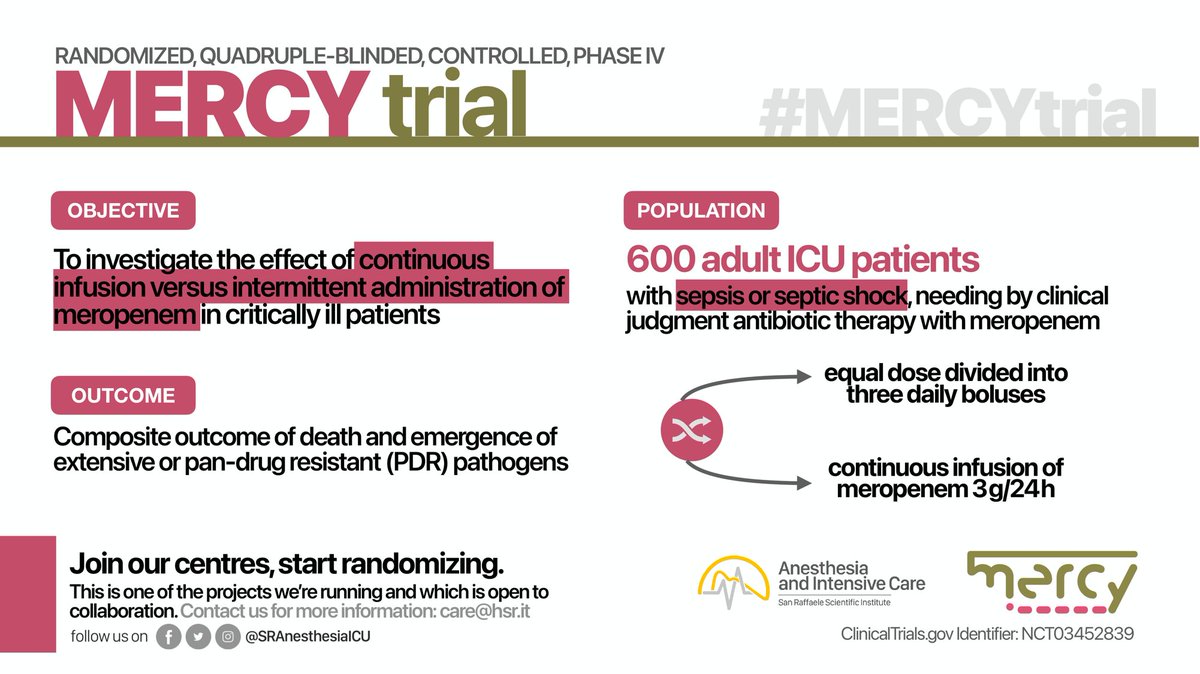
PICOS of this SR/MA
P: Critically ill patients
I: #Etomidate as an induction agent for intubation
C: Any comparator
O: Mortality at the main timepoint defined by authors
S: Randomized controlled trials
11 RCTs with 2704 patients were included
#FOAMcc
PICOS of this SR/MA
P: Critically ill patients
I: #Etomidate as an induction agent for intubation
C: Any comparator
O: Mortality at the main timepoint defined by authors
S: Randomized controlled trials
11 RCTs with 2704 patients were included
#FOAMcc

3/
#Etomidate was associated with significantly increased mortality (23% vs 20%; risk ratio = 1.16 [1.01–1.33]; P = 0.03)
The number needed to harm was 31
The probabilities of any increase and a 1% increase (NNH ≤100) in mortality were 98.1% and 92.1%, respectively.
#FOAMcc

#Etomidate was associated with significantly increased mortality (23% vs 20%; risk ratio = 1.16 [1.01–1.33]; P = 0.03)
The number needed to harm was 31
The probabilities of any increase and a 1% increase (NNH ≤100) in mortality were 98.1% and 92.1%, respectively.
#FOAMcc


4/
Sensitivity analyses confirmed main results
Direction/magnitude consistent for mortality at longest follow-up available even if statistical significance was lost (27% vs 25%; RR=1.07 [0.95–1.21]; P=0.27), corresponding to 86% probability of any harm from #Etomidate
#FOAMcc

Sensitivity analyses confirmed main results
Direction/magnitude consistent for mortality at longest follow-up available even if statistical significance was lost (27% vs 25%; RR=1.07 [0.95–1.21]; P=0.27), corresponding to 86% probability of any harm from #Etomidate
#FOAMcc


5/
#Etomidate was associated with a significantly increased risk of adrenal insufficiency (21% vs. 10%; risk ratio = 2.01 [1.59–2.56]; P < 0.001), confirming the findings of previous meta-analyses.
#FOAMcc
#Etomidate was associated with a significantly increased risk of adrenal insufficiency (21% vs. 10%; risk ratio = 2.01 [1.59–2.56]; P < 0.001), confirming the findings of previous meta-analyses.
#FOAMcc

6/
🔹Our meta-analysis showed a high likelihood that etomidate was associated with an increased risk of mortality and adrenal insufficiency
🔹Future research is warranted to investigate the optimal induction strategy for critically ill patients
#FOAMcc
🔹Our meta-analysis showed a high likelihood that etomidate was associated with an increased risk of mortality and adrenal insufficiency
🔹Future research is warranted to investigate the optimal induction strategy for critically ill patients
#FOAMcc
https://twitter.com/SRAnesthesiaICU/status/1652708942164656131?s=20
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh