One of the most important diagnostic tests in Cardiology to interpret is the EKG. Here are my thoughts and notes.
Let me know what you think!
Thread #18: Electrolyte Abnormalities #arjuncardiology #medtwitter #CardioTwitter #MedEd #IMG
Let me know what you think!
Thread #18: Electrolyte Abnormalities #arjuncardiology #medtwitter #CardioTwitter #MedEd #IMG
Hyperkalemia:
- Distinctive sequence of ECG changes affecting both depolarization (QRS) and repolarization (ST-T)
- First change: Narrowing and peaking of T-waves ('tented' or 'pinched' shape) and can become tall
- Distinctive sequence of ECG changes affecting both depolarization (QRS) and repolarization (ST-T)
- First change: Narrowing and peaking of T-waves ('tented' or 'pinched' shape) and can become tall
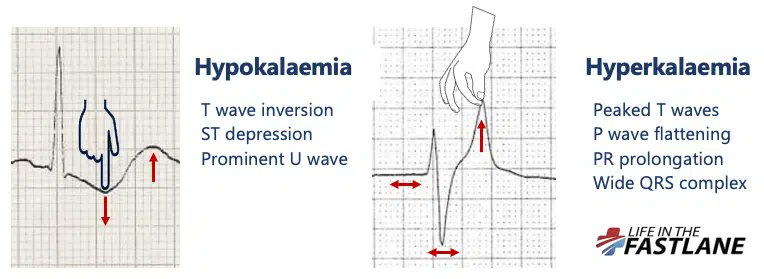
Hyperkalemia:
- Further elevation: PR intervals become prolonged, P-waves may disappear. Will have intra-ventricular conduction delay, with widening of QRS complexes.
- Can lead to large, undulating (sine wave) pattern with asystole and cardiac death
- Further elevation: PR intervals become prolonged, P-waves may disappear. Will have intra-ventricular conduction delay, with widening of QRS complexes.
- Can lead to large, undulating (sine wave) pattern with asystole and cardiac death

Hyperkalemia ECG:
- Nice example from Life in the Fast Lane (litfl.com/hyperkalaemia-…)
- Can see: prolonged PR interval, broad QRS, and peaked T-waves
- Nice example from Life in the Fast Lane (litfl.com/hyperkalaemia-…)
- Can see: prolonged PR interval, broad QRS, and peaked T-waves

Hypokalemia:
- Produces distinctive changes in the ST-T complex; most common with ST-depressions with prominent U-waves and prolong repolarization
- U-waves may even exceed the height of the T-waves
- Can be challenging to measure the QT intervals
- Produces distinctive changes in the ST-T complex; most common with ST-depressions with prominent U-waves and prolong repolarization
- U-waves may even exceed the height of the T-waves
- Can be challenging to measure the QT intervals

Hypokalemia EKG:
- Nice EKG from Life in the Fast Lane (litfl.com/hypokalaemia-e…)
- Note: Widespread ST depression and T wave inversion, Prominent U waves, Long QU interval
- Reported K~1.7
- Nice EKG from Life in the Fast Lane (litfl.com/hypokalaemia-e…)
- Note: Widespread ST depression and T wave inversion, Prominent U waves, Long QU interval
- Reported K~1.7

Hypercalcemia:
- Shortened QT interval is due to shortening of ST-segment.
- T-waves may appear to take off from the end of the QRS complex
- High Calcium can lead to coma/ death
- Shortened QT interval is due to shortening of ST-segment.
- T-waves may appear to take off from the end of the QRS complex
- High Calcium can lead to coma/ death

Hypercalcemia EKG:
- Nice EKG from Life in the Fast Lane (litfl.com/hypercalcaemia…)
- Note hypercalcemia causing marked shortening of the QT interval (260ms)
- Nice EKG from Life in the Fast Lane (litfl.com/hypercalcaemia…)
- Note hypercalcemia causing marked shortening of the QT interval (260ms)

Hypocalcemia:
- Lengthens or prolongs the QT intervals
- Example of a patient with prolonged QTc in the setting of hypoparathyoidism
- Lengthens or prolongs the QT intervals
- Example of a patient with prolonged QTc in the setting of hypoparathyoidism

Hypomagnesemia:
- Can be attributed to GI or renal losses (diuretic)
- Implicated in ventricular arrhythmias with acute MI and Torsade de Points
- Should have aggressive IV Magnesium replacement if needed
- EKG (litfl.com/hypomagnesaemi…) with an example of NSVT
- Can be attributed to GI or renal losses (diuretic)
- Implicated in ventricular arrhythmias with acute MI and Torsade de Points
- Should have aggressive IV Magnesium replacement if needed
- EKG (litfl.com/hypomagnesaemi…) with an example of NSVT

***Not to use for clinical care, just educational material**
Thanks to these websites for the amazing graphics!
litfl.com/hyperkalaemia-…
litfl.com/hypokalaemia-e…
litfl.com/hypocalcaemia-…
litfl.com/hypercalcaemia…
litfl.com/hypomagnesaemi…
Thanks to these websites for the amazing graphics!
litfl.com/hyperkalaemia-…
litfl.com/hypokalaemia-e…
litfl.com/hypocalcaemia-…
litfl.com/hypercalcaemia…
litfl.com/hypomagnesaemi…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh














