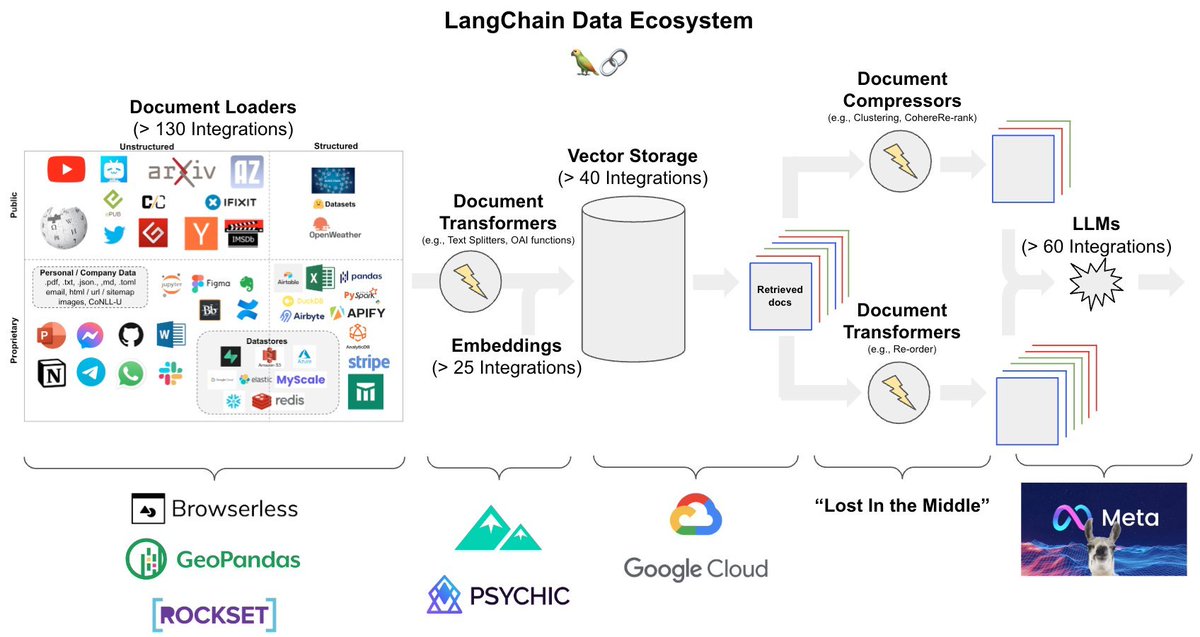
Learning data science on your own is tough...
...(ahem, it took me 6 years)
So here's some help.
5 Free Books to Cut Your Time In HALF.
Let's go! 🧵
#datascience #rstats #R
...(ahem, it took me 6 years)
So here's some help.
5 Free Books to Cut Your Time In HALF.
Let's go! 🧵
#datascience #rstats #R

1. Mastering #Spark with #R
This book solves an important problem- what happens when your data gets too big?
For example, analyzing 100,000,000 time series.
You can do it in R with the tools covered in this book.
Website: therinspark.com
This book solves an important problem- what happens when your data gets too big?
For example, analyzing 100,000,000 time series.
You can do it in R with the tools covered in this book.
Website: therinspark.com

2. Geocomputation with #R
Interested in #Geospatial Analysis?
This book is my go-to resource for all things geospatial.
This book covers:
-Making Maps
-Working with Spatial Data
-Applications (Transportation, Geomarketing)
Website: r.geocompx.org
Interested in #Geospatial Analysis?
This book is my go-to resource for all things geospatial.
This book covers:
-Making Maps
-Working with Spatial Data
-Applications (Transportation, Geomarketing)
Website: r.geocompx.org

3. Tidy Finance with #R
What tools exist in R for #Finance?
And how do I use them?
Answers to these questions are covered in this book!
P.S.- This book uses my R package, #tidyquant
Website: tidy-finance.org
What tools exist in R for #Finance?
And how do I use them?
Answers to these questions are covered in this book!
P.S.- This book uses my R package, #tidyquant
Website: tidy-finance.org

4. Text Mining with R
This is a fantastic introduction to text analysis and text mining with the #tidytext R package.
This book singlehandedly made me MORE CONFIDENT with text analysis.
Website: tidytextmining.com
This is a fantastic introduction to text analysis and text mining with the #tidytext R package.
This book singlehandedly made me MORE CONFIDENT with text analysis.
Website: tidytextmining.com

5. #Forecasting Principles and Practice
This is the best “theory” book on #timeseries analysis and forecasting.
Topics Covered:
- ARIMA,
- Exponential Smoothing,
- TimeSeries Decomposition
- A lot more!
Website: otexts.com/fpp3/
This is the best “theory” book on #timeseries analysis and forecasting.
Topics Covered:
- ARIMA,
- Exponential Smoothing,
- TimeSeries Decomposition
- A lot more!
Website: otexts.com/fpp3/

1-Dollar Bonus Book:
This is a massive value- Gives you a complete plan for EVERYTHING you need to know about learning data science.
It's only a buck.
And it will cut 2-3 years off your journey.
Website: learn.business-science.io/if-i-had-to-le…
This is a massive value- Gives you a complete plan for EVERYTHING you need to know about learning data science.
It's only a buck.
And it will cut 2-3 years off your journey.
Website: learn.business-science.io/if-i-had-to-le…

Want even more help becoming a 6-figure data scientist?
I have a free workshop that will help you become a $100K+ earner as a #DataScientist even in a Recession.
👉Register Here: us02web.zoom.us/webinar/regist…
I have a free workshop that will help you become a $100K+ earner as a #DataScientist even in a Recession.
👉Register Here: us02web.zoom.us/webinar/regist…

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh