One of the most important diagnostic tests in Cardiology to interpret is the EKG. Here are my thoughts and notes. Let me know what you think!
Thread #19: Pericarditis
#arjuncardiology #medtwitter #CardioTwitter #MedEd #IMG
Thread #19: Pericarditis
#arjuncardiology #medtwitter #CardioTwitter #MedEd #IMG
Acute Pericarditis:
- Inflammation of the pericardium
- May be caused by number of factors: viral/bacterial infection, metastatic tumors, collagen vascular diseases, MI, cardiac surgery, and uremia
- Inflammation of the pericardium
- May be caused by number of factors: viral/bacterial infection, metastatic tumors, collagen vascular diseases, MI, cardiac surgery, and uremia
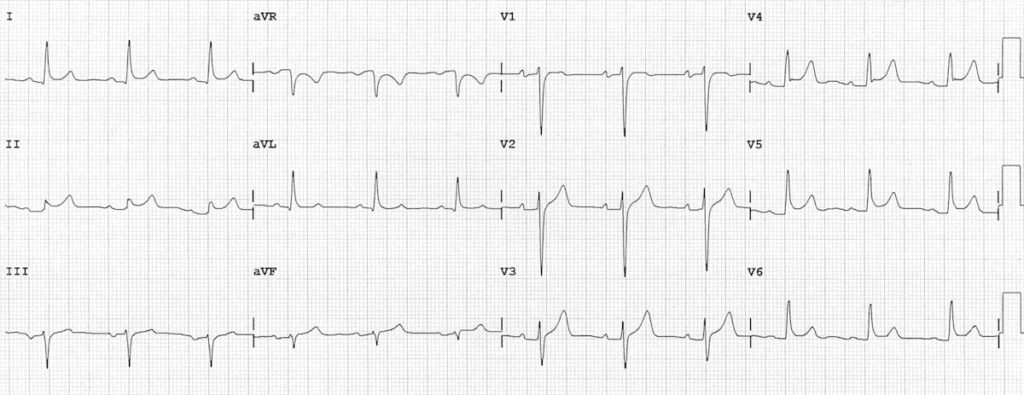
ECG Changes w/ Acute Pericarditis:
- Early phase is characterized by ST segment elevation, due to inflammation of the epicardium, which accompanies inflammation of the overlying pericardium
- Can have generalized ST-T changes in both anterior and inferior leads
- Early phase is characterized by ST segment elevation, due to inflammation of the epicardium, which accompanies inflammation of the overlying pericardium
- Can have generalized ST-T changes in both anterior and inferior leads

ECG Changes w/ Acute Pericarditis:
- Also affects the repolarization of the atria (PR segment)
- Leads to atrial current of injury with elevation in PR segment in aVR and depression of PR segment in other extremity / left-sided chest leads
- Can have T-wave inversions
- Also affects the repolarization of the atria (PR segment)
- Leads to atrial current of injury with elevation in PR segment in aVR and depression of PR segment in other extremity / left-sided chest leads
- Can have T-wave inversions

Pericardial Effusion:
- Abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pericardial sac, can be due to pericarditis
- Other causes: myxedema (hypothyroidism), or rupture of heart (VSD)
- Can lead to cardiac tamponade: drop in SBP leading to PEA activity
- Abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pericardial sac, can be due to pericarditis
- Other causes: myxedema (hypothyroidism), or rupture of heart (VSD)
- Can lead to cardiac tamponade: drop in SBP leading to PEA activity
Pericardial Effusion ECG:
- Can see low QRS voltages (<5-mm in the 6 extremity leads or < 10-mm in the chest leads V1-V6)
- Low voltage: Obesity (fat around heart), emphysema (air insulates heart), anasarca (generalized edema), pleural effusions
- Electrical alternans
- Can see low QRS voltages (<5-mm in the 6 extremity leads or < 10-mm in the chest leads V1-V6)
- Low voltage: Obesity (fat around heart), emphysema (air insulates heart), anasarca (generalized edema), pleural effusions
- Electrical alternans

Chronic Constrictive Pericarditis:
- Some conditions cause pericardial inflammation and can lead to fibrosis and calcification of the pericardial sac (cardiac surgery, trauma, infections, TB, viral infections, connective tissue diseases, sarcoid, uremia, and asbestosis)
- Some conditions cause pericardial inflammation and can lead to fibrosis and calcification of the pericardial sac (cardiac surgery, trauma, infections, TB, viral infections, connective tissue diseases, sarcoid, uremia, and asbestosis)
Chronic Constrictive Pericarditis:
- Can present with HF, elevated neck veins/ascites. Can be mistaken for liver cirrhosis.
- Treatment: Pericardiectomy ('surgical stripping' of the pericardium to decrease intra-cardiac pressures.
- Can present with HF, elevated neck veins/ascites. Can be mistaken for liver cirrhosis.
- Treatment: Pericardiectomy ('surgical stripping' of the pericardium to decrease intra-cardiac pressures.

** Not to use for clinical care, just educational material**
Thanks to these websites/journals for amazing graphics!
gfycat.com/gifs/search/ta…
litfl.com/pericarditis-e…
litfl.com/ecg-findings-i…
j-pcs.org/article.asp?is…
Thanks to these websites/journals for amazing graphics!
gfycat.com/gifs/search/ta…
litfl.com/pericarditis-e…
litfl.com/ecg-findings-i…
j-pcs.org/article.asp?is…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh














