🚨NEW STUDY🚨
Recent research analyzed "future wildfires burned areas & C emissions under #SolarGeoengineering & Shared Socioeconomic pathways (SSPs) scenarios & assessed how the different geoengineering approaches impact #fires."
Results are discussed in a 🧵 below ⬇️:
1/13
Recent research analyzed "future wildfires burned areas & C emissions under #SolarGeoengineering & Shared Socioeconomic pathways (SSPs) scenarios & assessed how the different geoengineering approaches impact #fires."
Results are discussed in a 🧵 below ⬇️:
1/13

The major conclusions and implications drawn from this study are as follows:
2/13
2/13
1️⃣ "The global total #wildfire burned A is projected to rise under the unmitigated scenario (SSP5-8.5) & drop under the 2 #geoengineering scenarios (#SolarIrradianceReduction & #StratosphericSulfateAerosols) based on a comparison of the averages of 2091–2100 as to 2021–2030."
3/
3/

2️⃣ "By the end of the century, the two #geoengineering scenarios exhibit lower burned area and fire carbon emissions than not only their base-forcing scenario (SSP5-8.5) but also the targeted-forcing scenario (SSP2-4.5)."
4/13
4/13
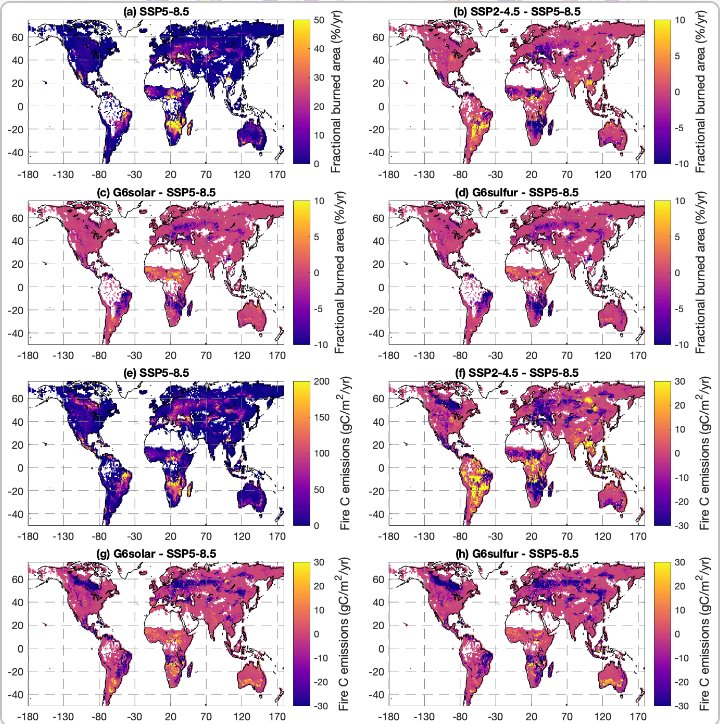
3️⃣ "The 2 #geoengineering approaches (#SolarIrradianceReduction & #StratosphericSulfateAerosols) generally lead to less wildfire activity in most regions in 2091–2100, except for Northern Hemisphere Africa & equatorial Asia."
5/13
5/13

Cont'd....
"The 40–70∘ N latitude band is the only latitude band in which the zonal mean burned area consistently increases under all of the scenarios, even the #geoengineering scenarios."
6/13
"The 40–70∘ N latitude band is the only latitude band in which the zonal mean burned area consistently increases under all of the scenarios, even the #geoengineering scenarios."
6/13
4️⃣ "Overall, changes in G6solar & #G6sulfur from SSP5-8.5 with respect to surface temperature, wind speed, and downwelling #SolarFlux at the surface are positively correlated to the changes in burned area and fire carbon emissions,....
7/13

7/13


Cont'd....
whereas their changes in precipitation, relative humidity, and soil water content are negatively correlated to the changes in burned area and fire #CarbonEmissions."
8/13
whereas their changes in precipitation, relative humidity, and soil water content are negatively correlated to the changes in burned area and fire #CarbonEmissions."
8/13

5️⃣ "Generally, the #StratosphericSulfateAerosols approach has a stronger fire-reducing effect than the #SolarIrradianceReduction approach. The impacts of the analyzed variable changes are generally larger (percent-wise) on burned area than fire carbon emissions."
9/13
9/13
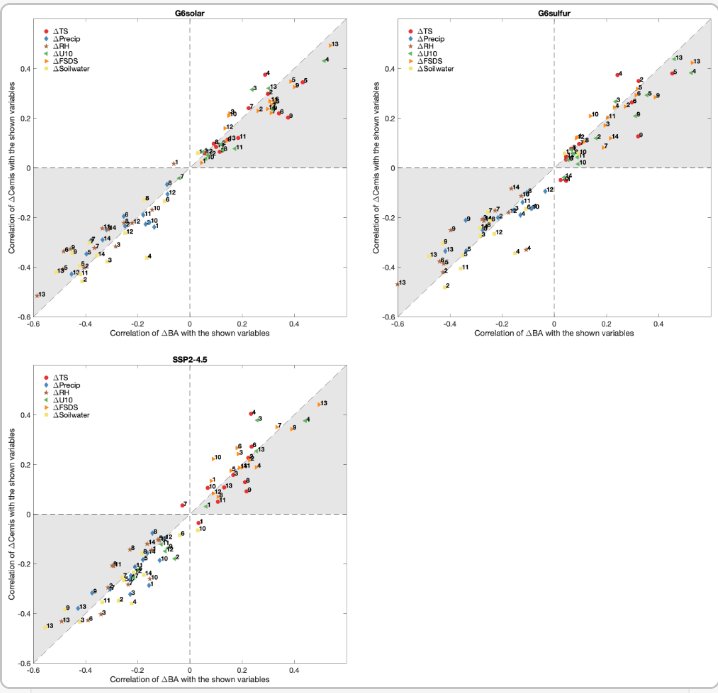
6️⃣ "#Geoengineering-imposed reductions in surface temperature & wind speed & geoengineering-imposed increases in relative humidity & soil moisture reduce fires by the end of the century."
10/13
10/13
Cont'd...
"However, the reduction in precipitation resulting from #geoengineering offsets its overall fire-reducing effect to some extent."
11/13
"However, the reduction in precipitation resulting from #geoengineering offsets its overall fire-reducing effect to some extent."
11/13
Read open-access paper entitled: "Impact of solar geoengineering on wildfires in the 21st century in CESM2/WACCM6" here ⬇️
acp.copernicus.org/articles/23/54…
#SolarGeoengineering
#Wildfires
#StratosphericSulfateAerosol
#SolarIrradianceReduction
12/13
acp.copernicus.org/articles/23/54…
#SolarGeoengineering
#Wildfires
#StratosphericSulfateAerosol
#SolarIrradianceReduction
12/13
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh