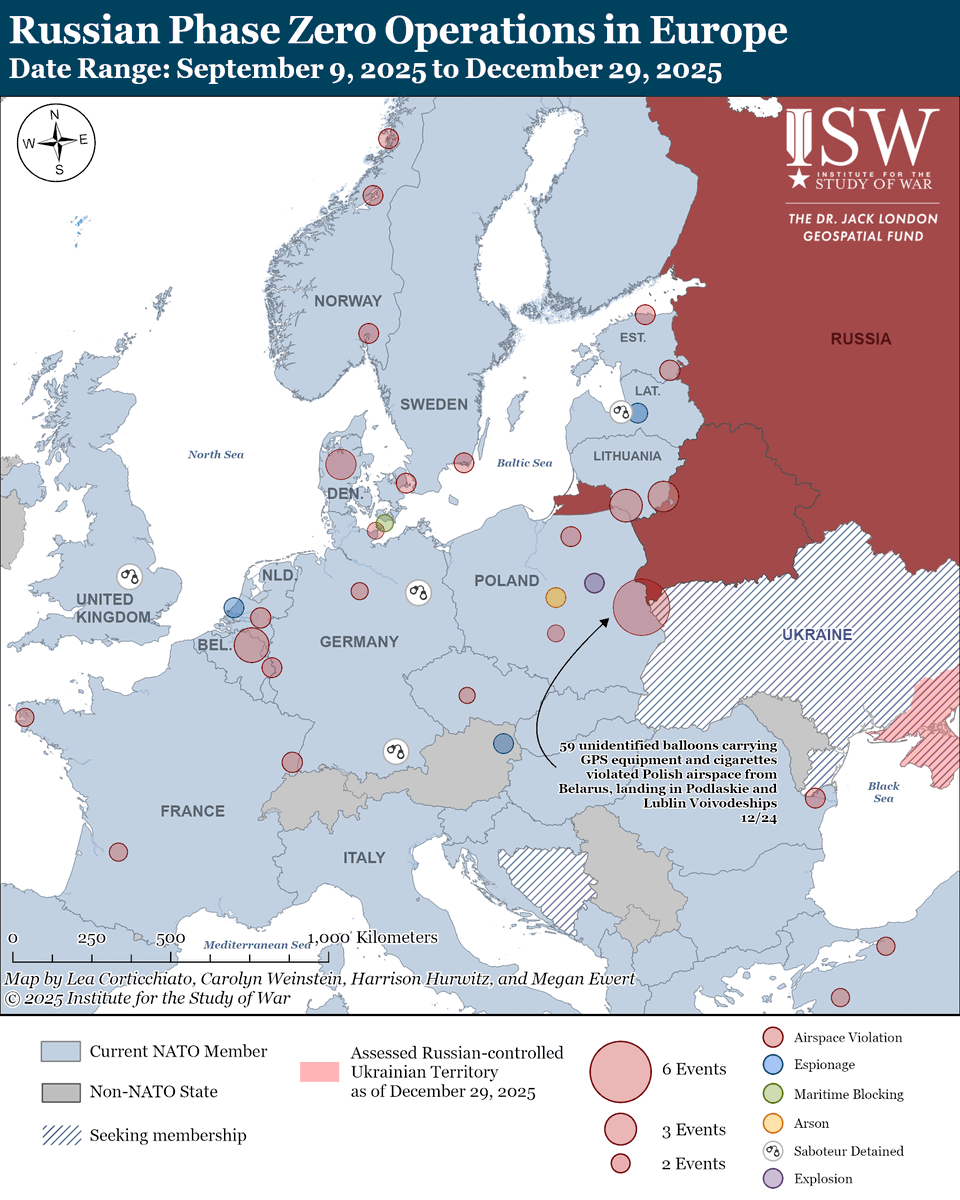
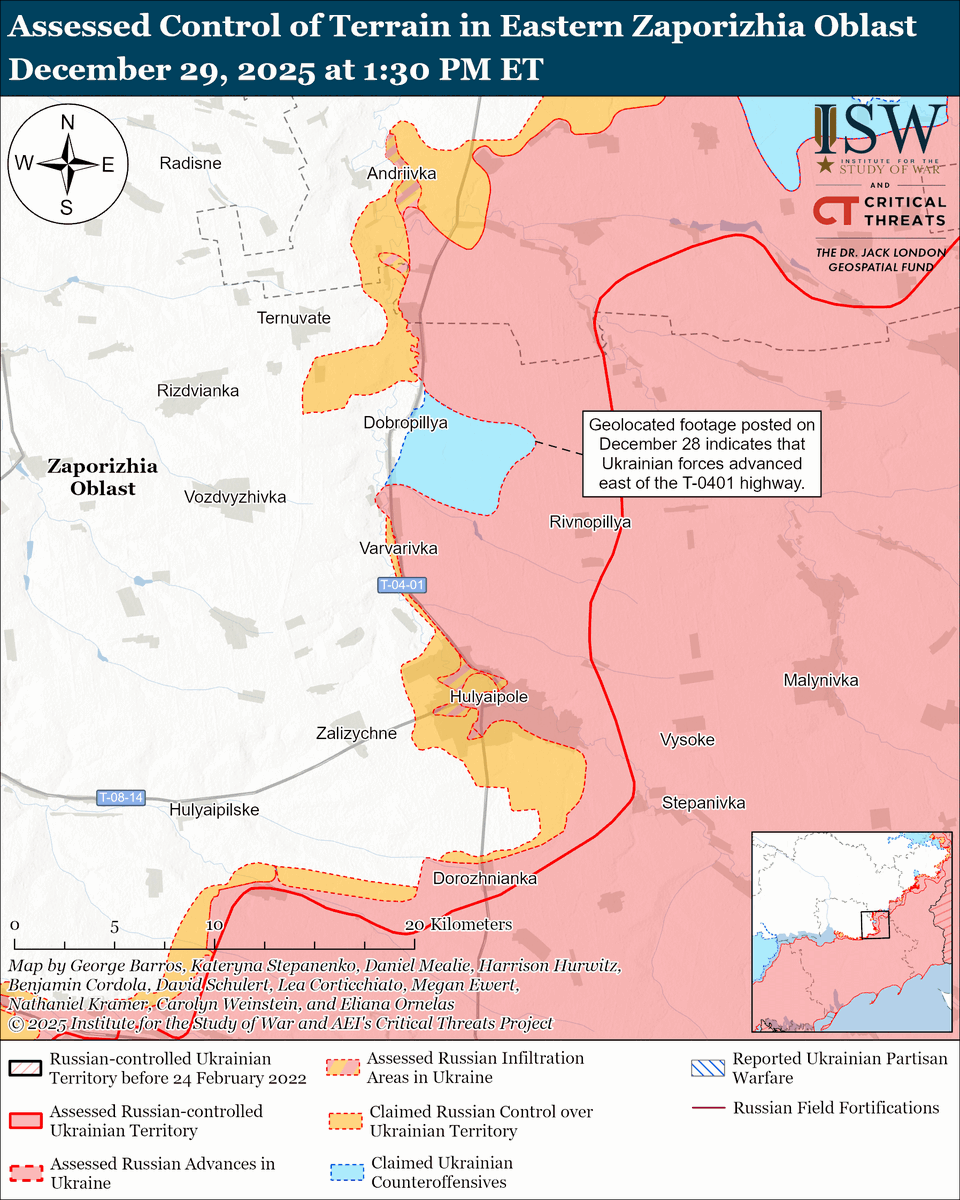
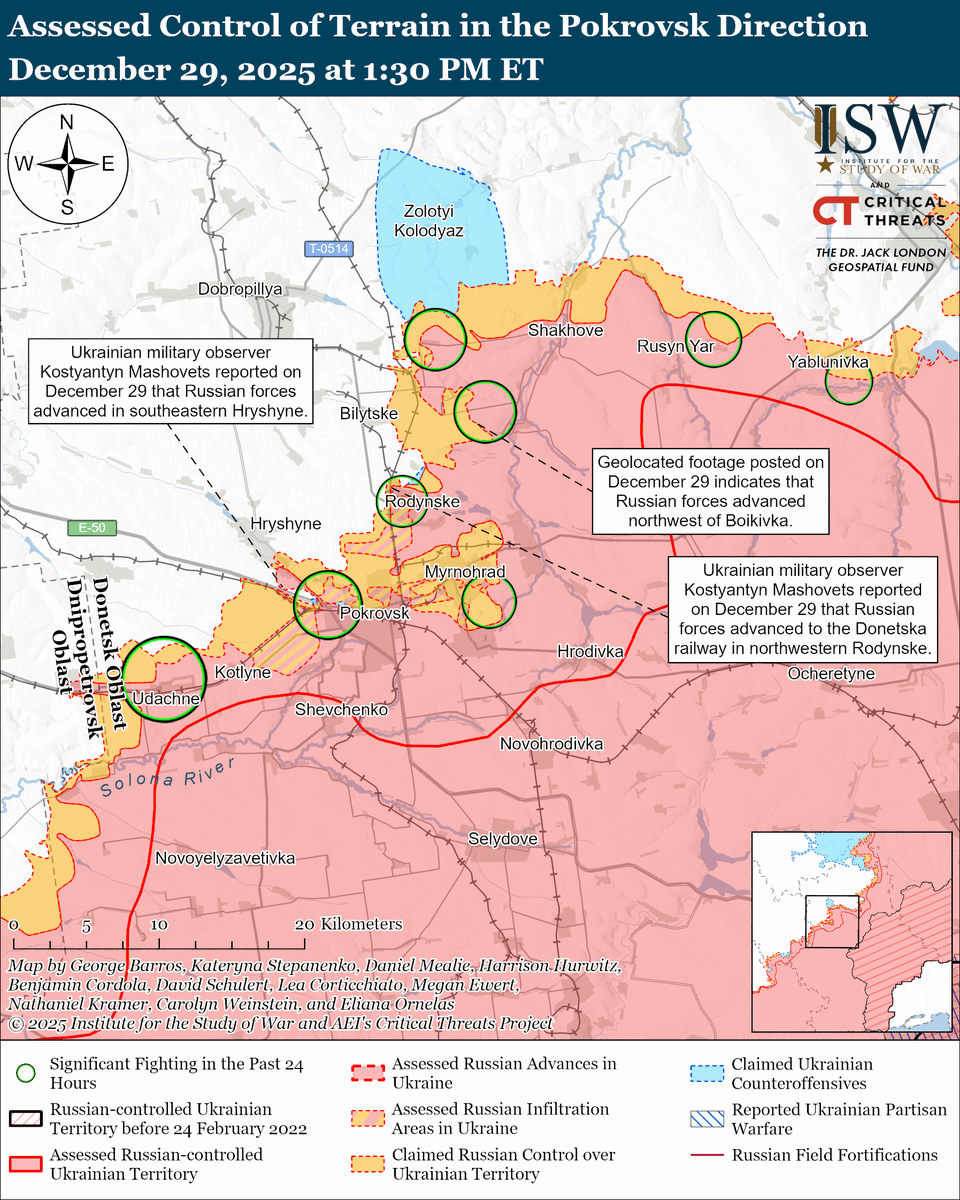
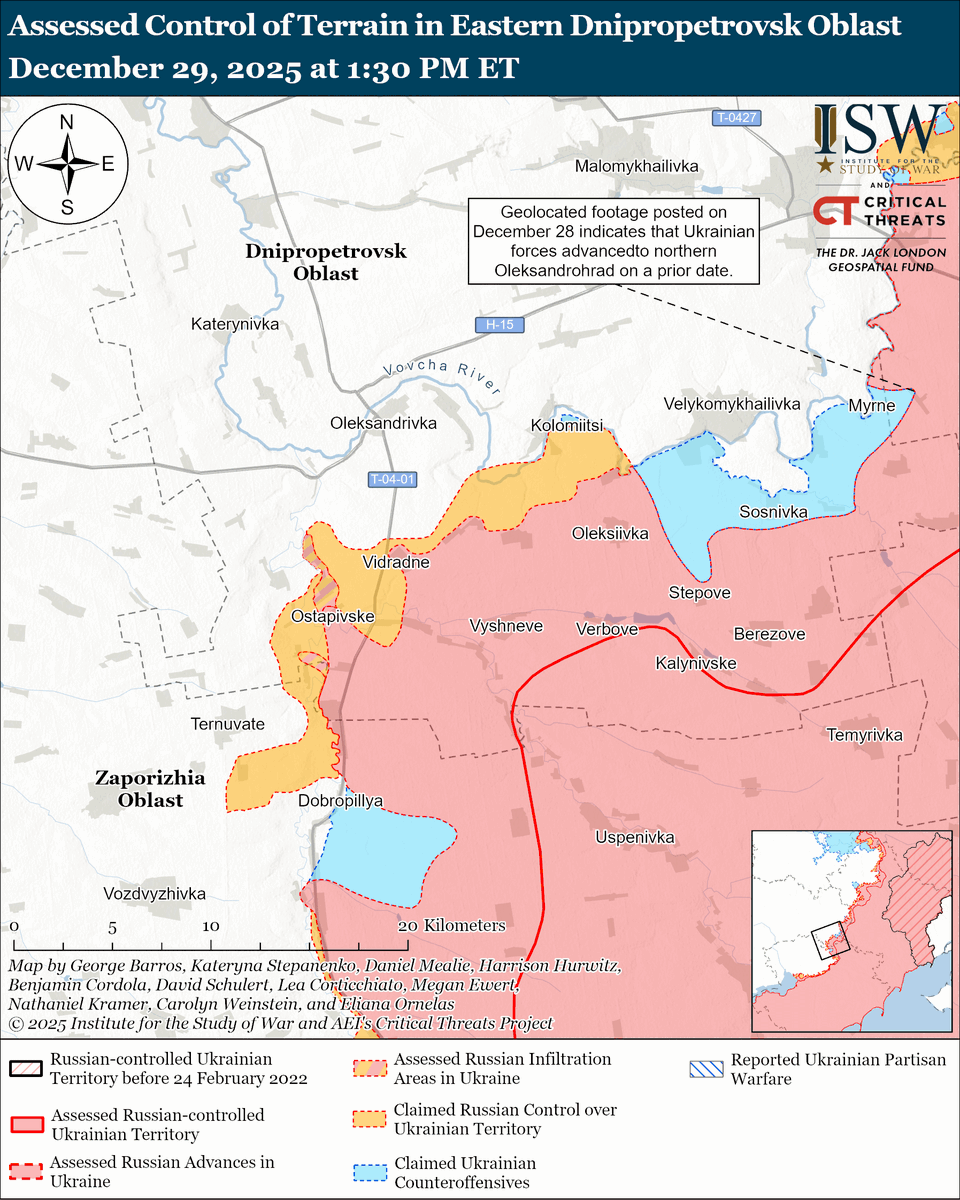
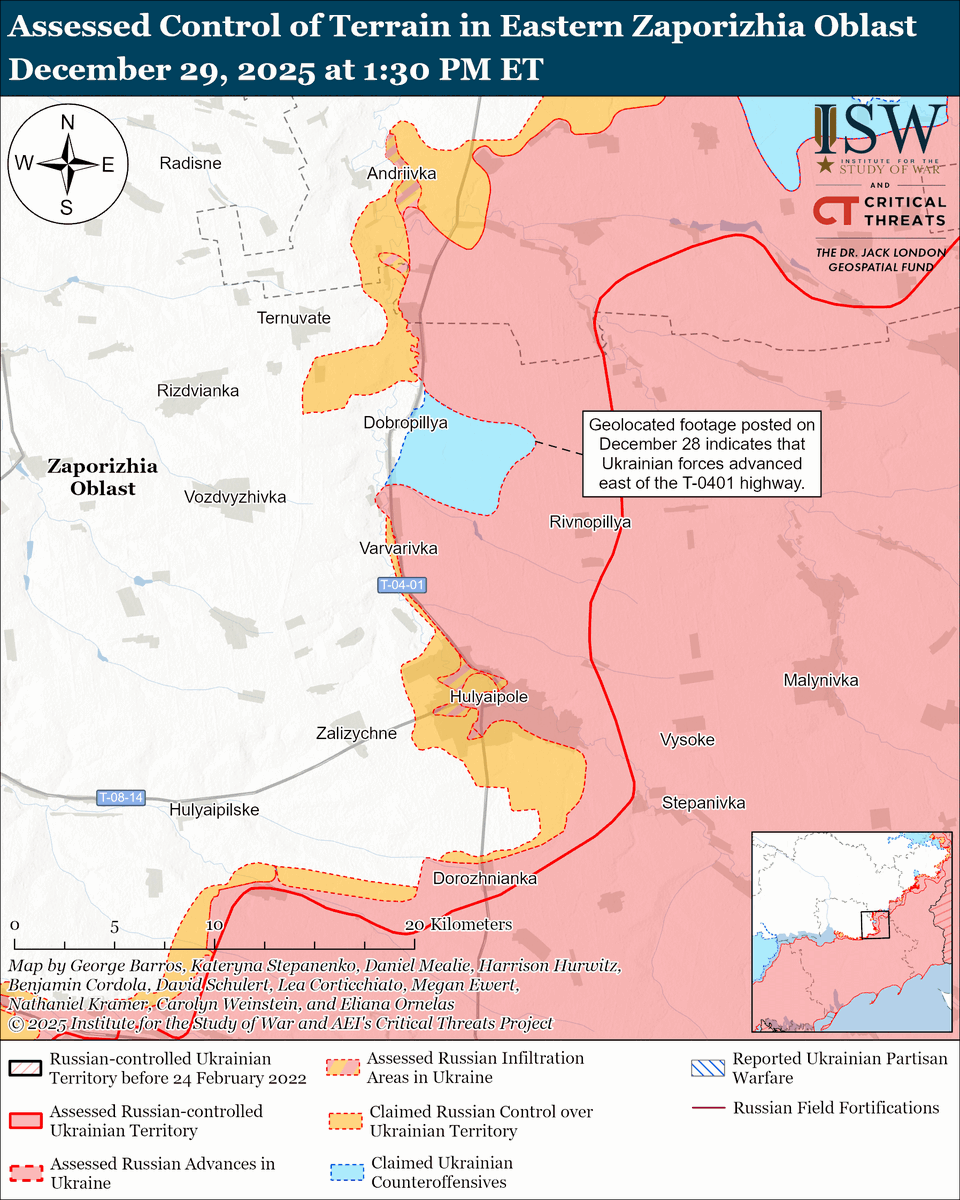
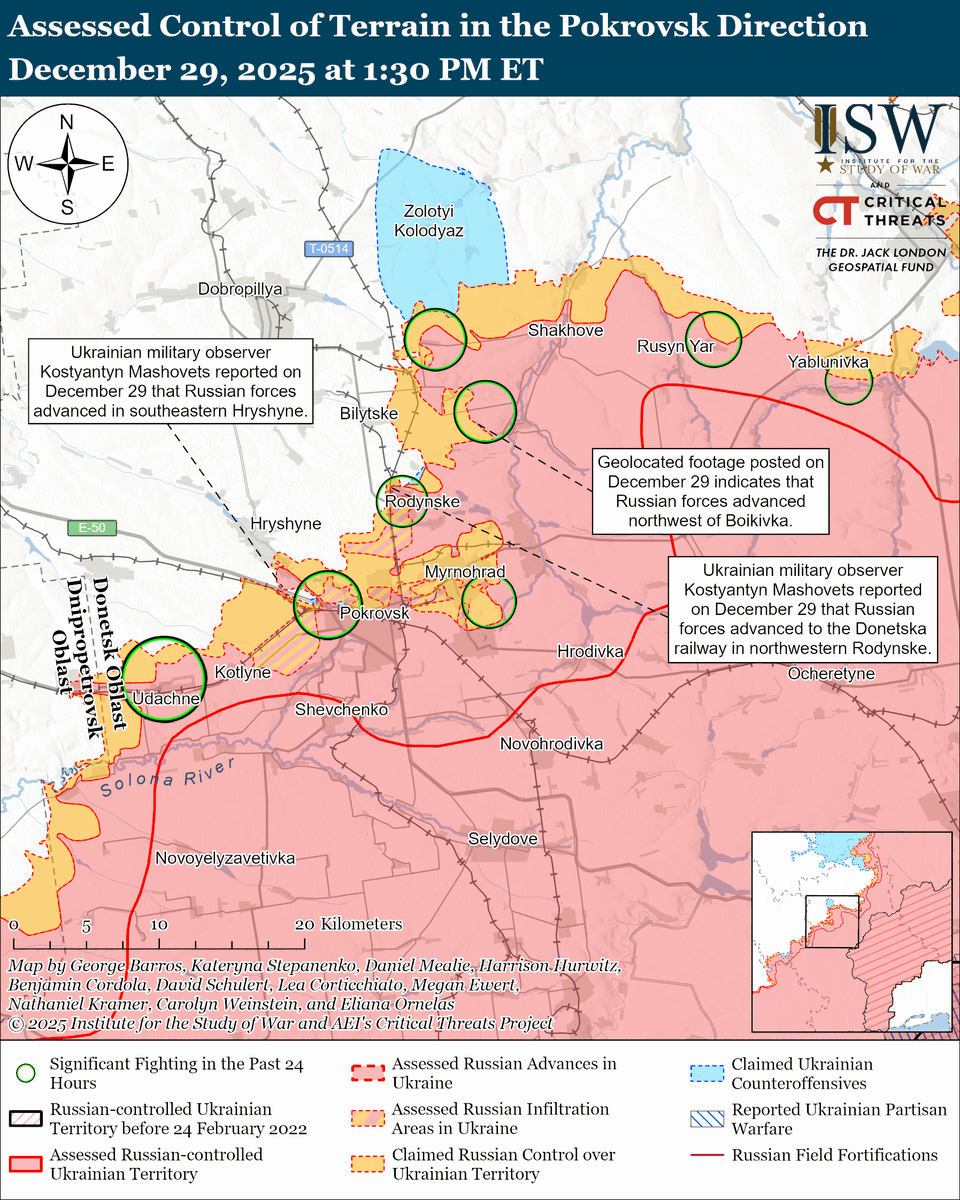
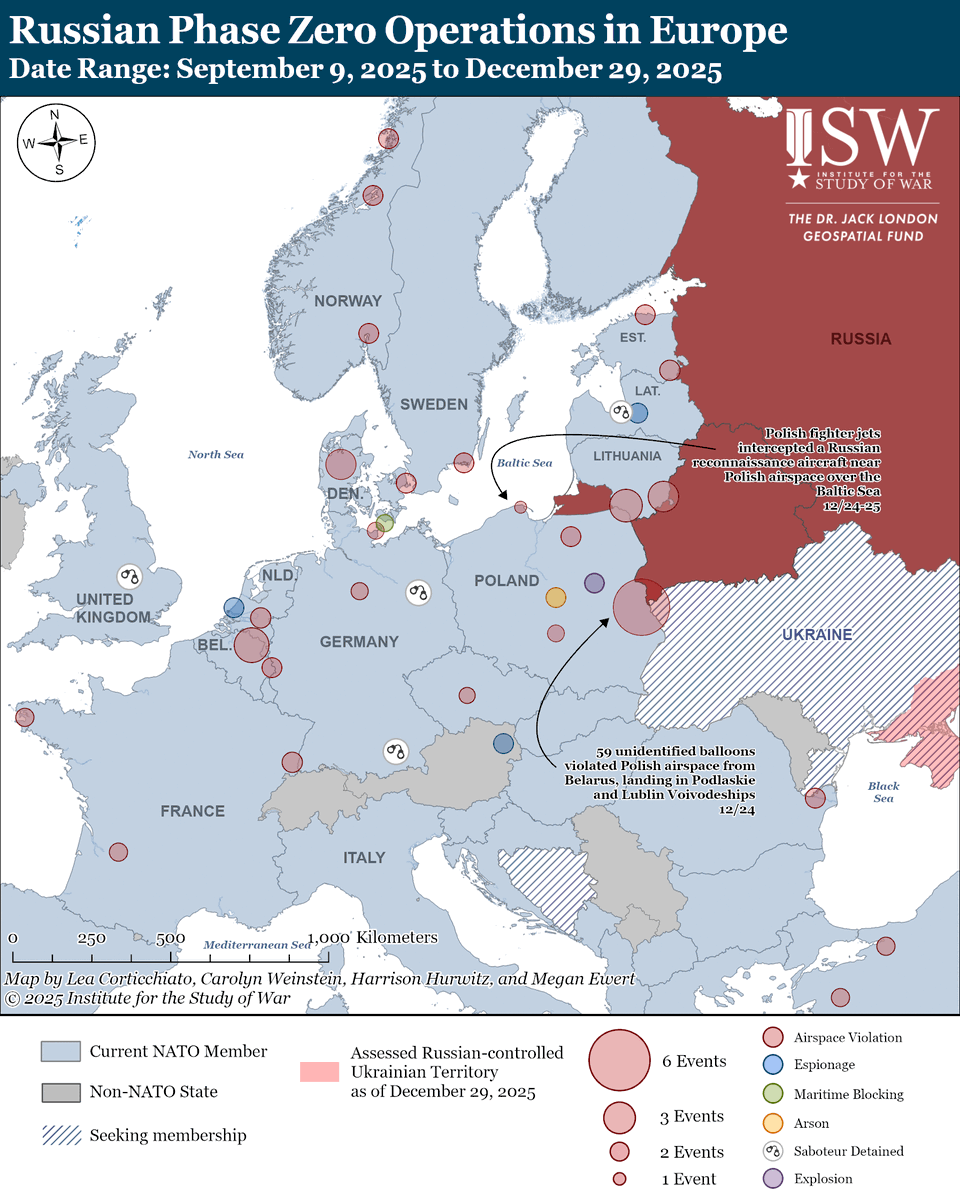
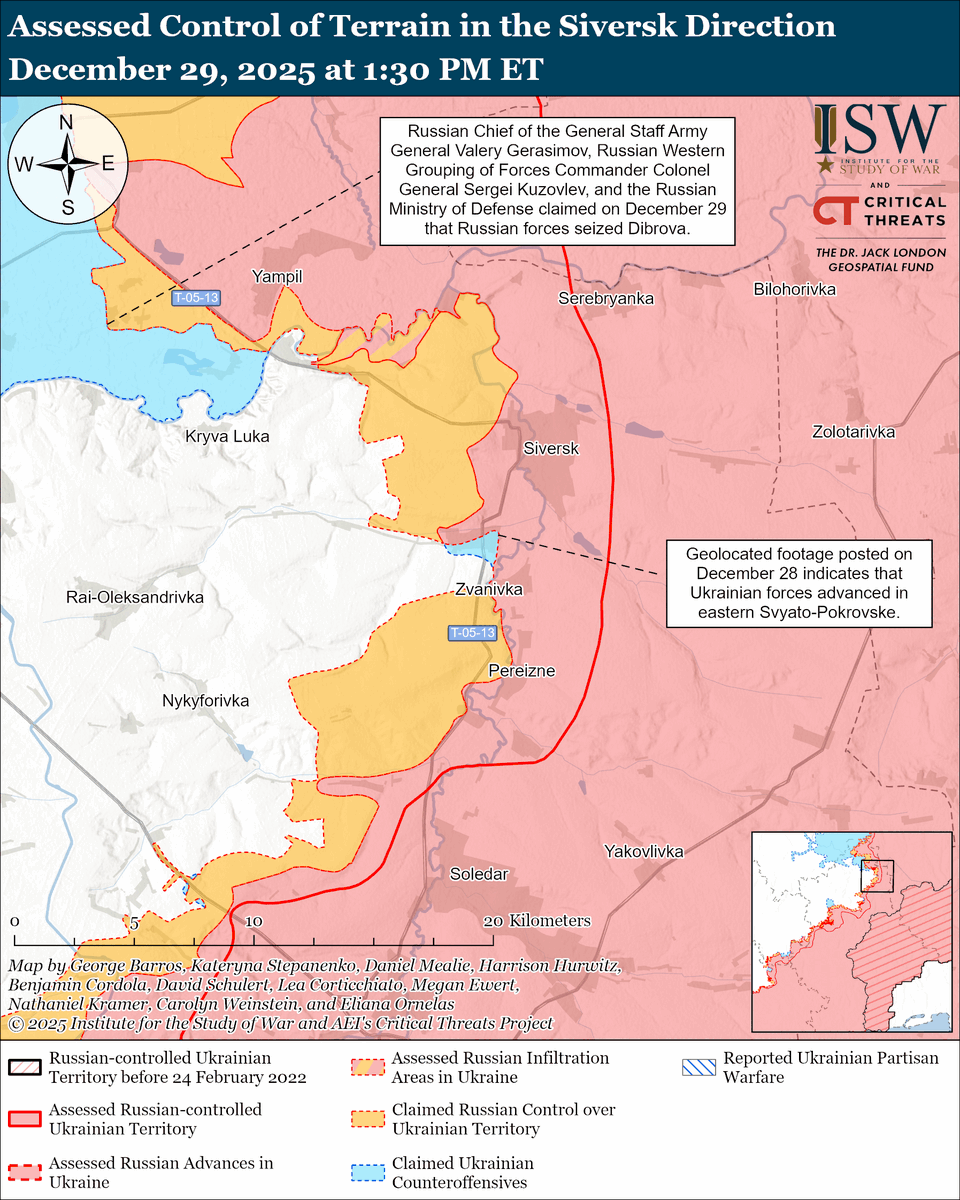
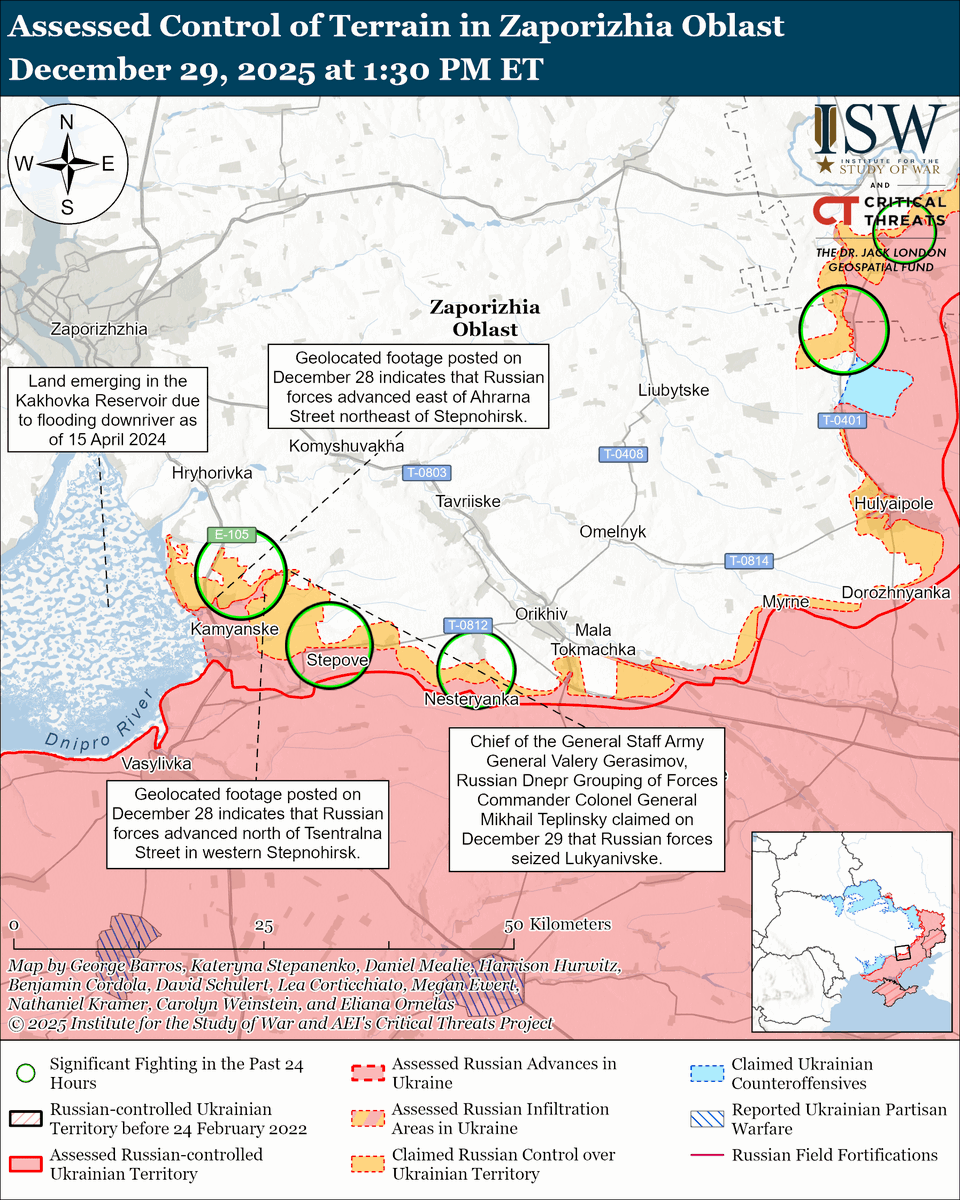
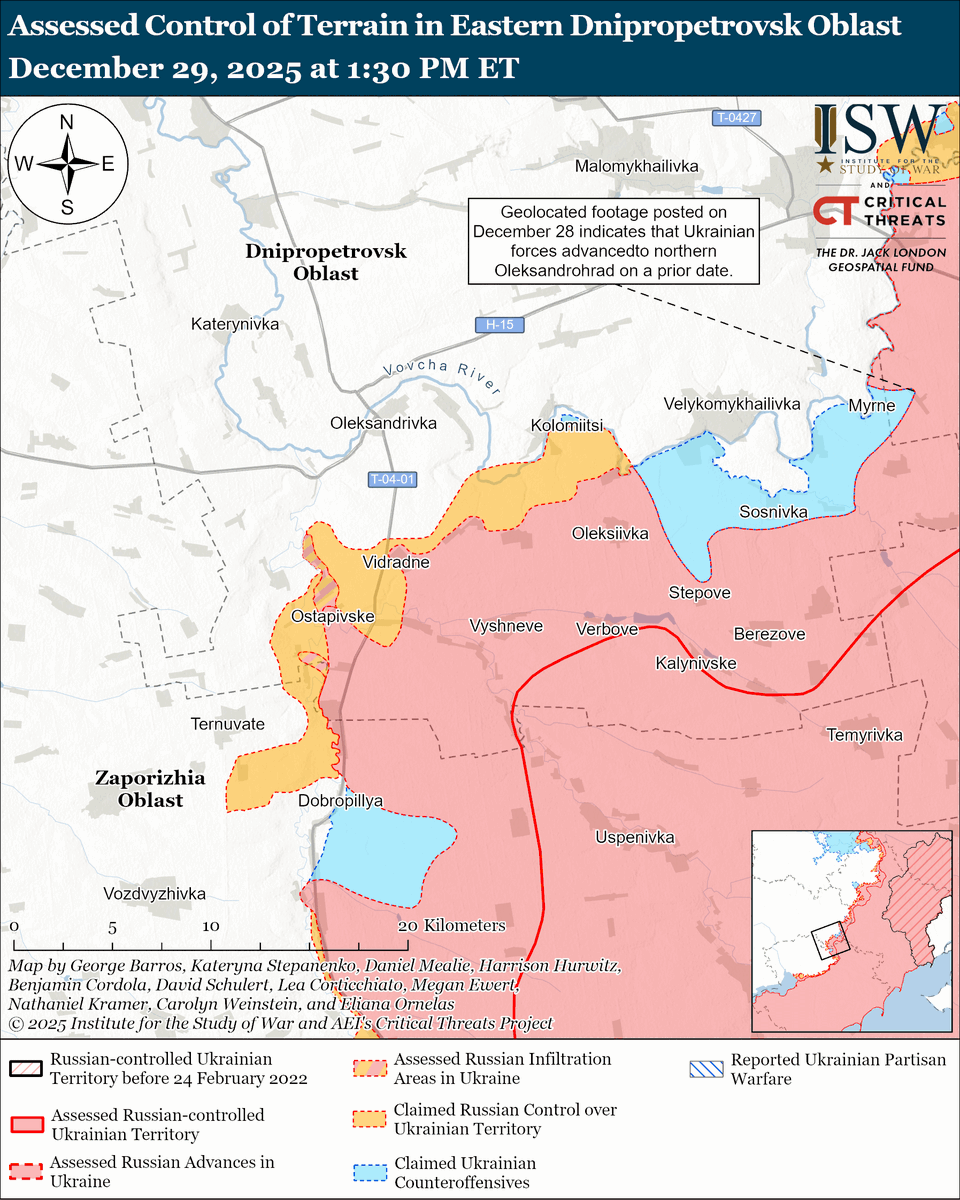
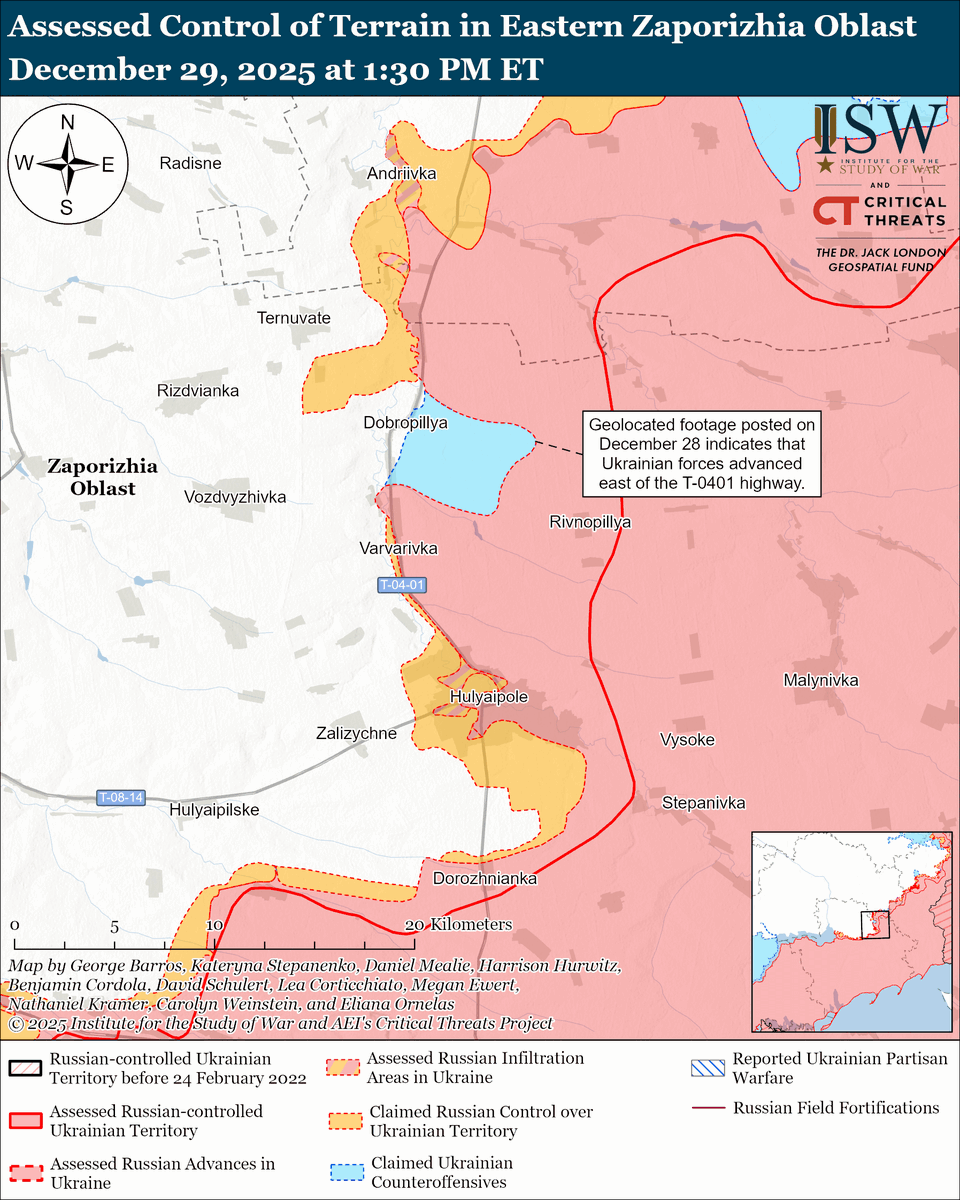
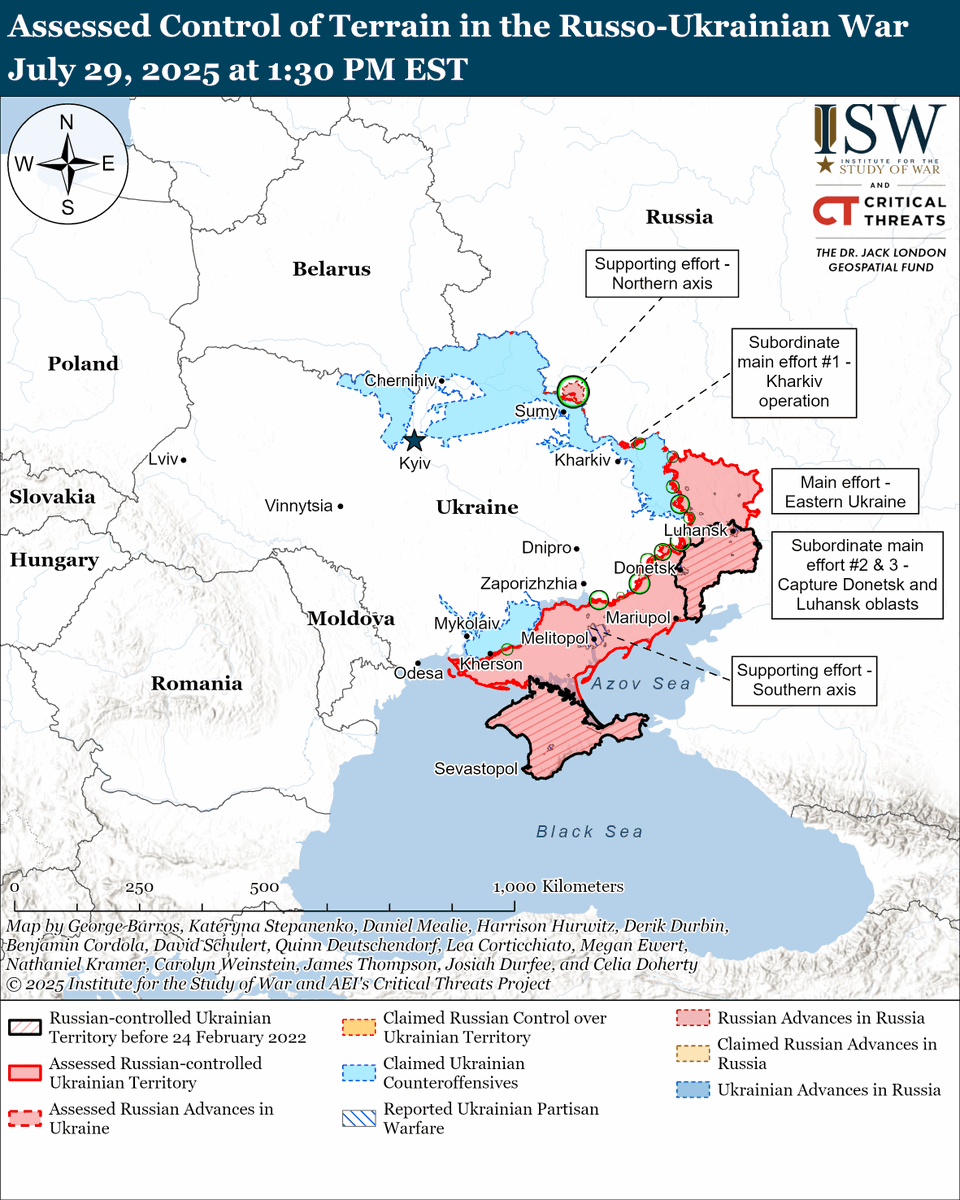
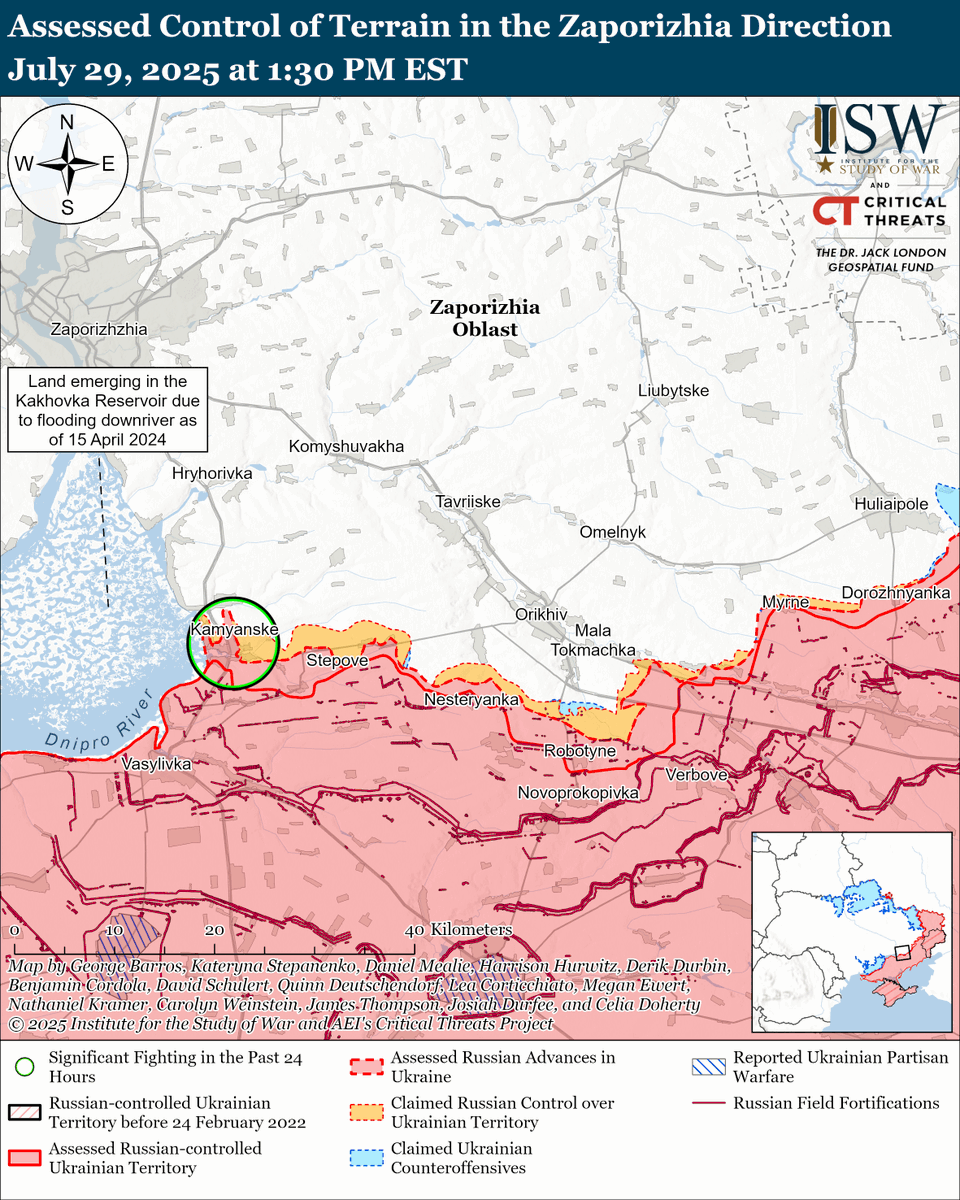
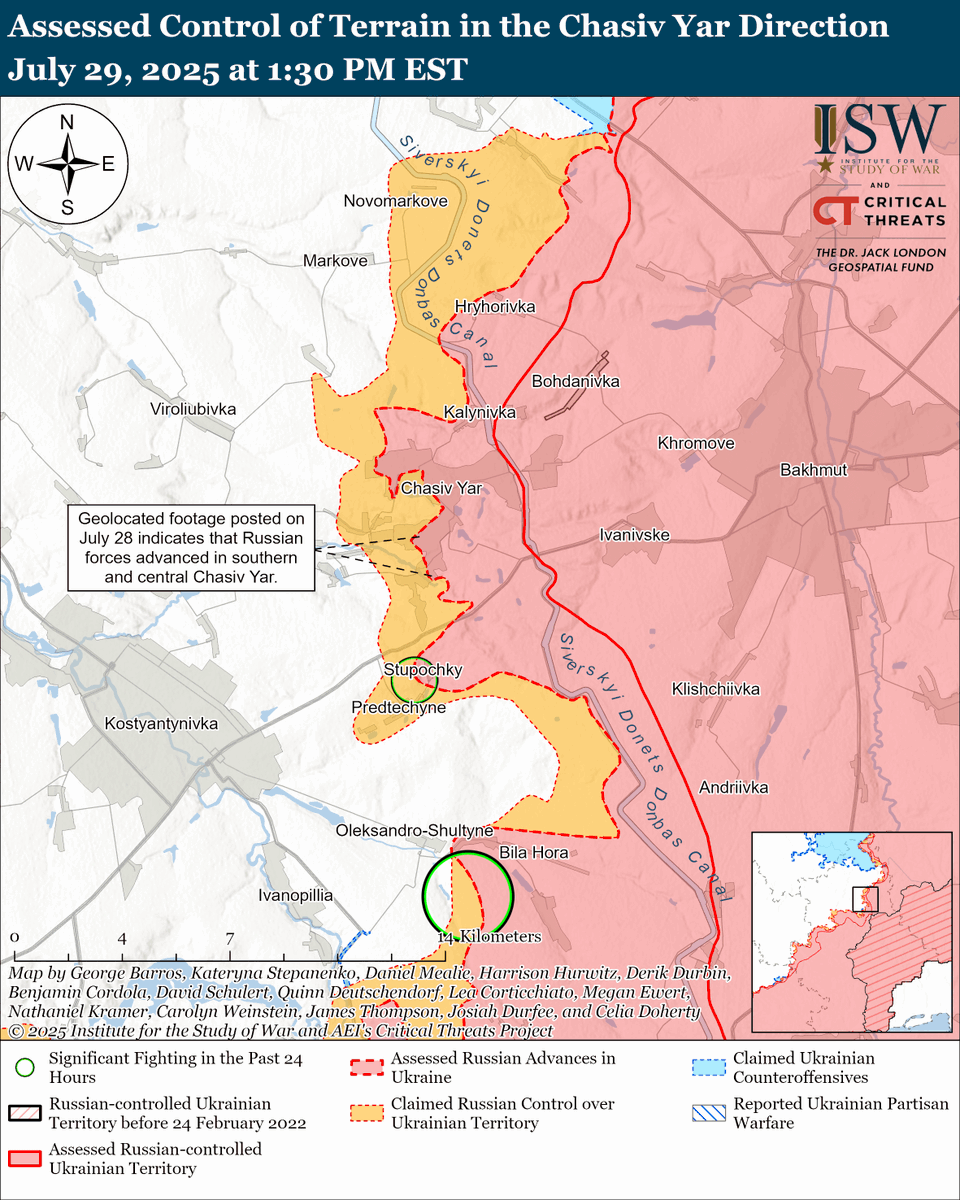
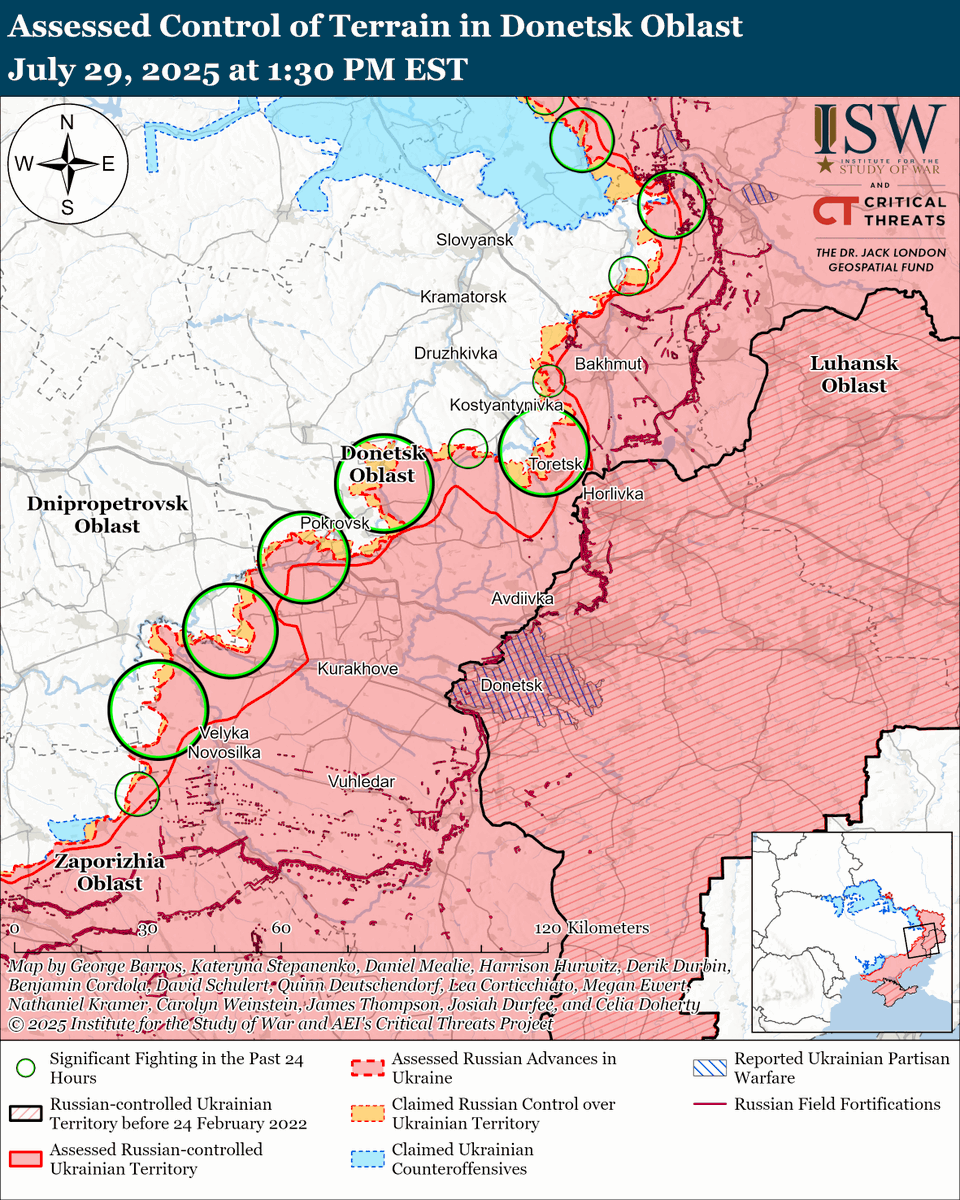
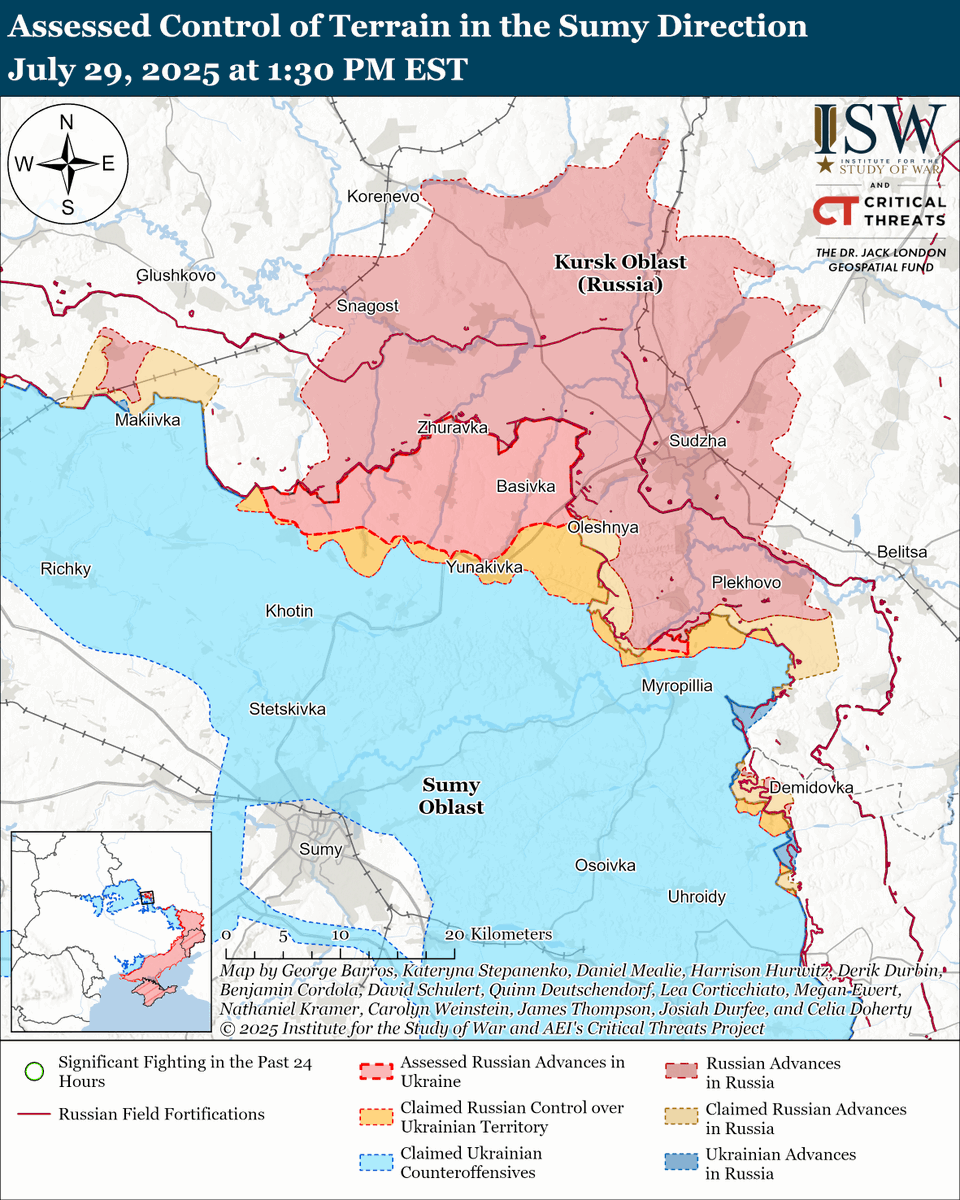
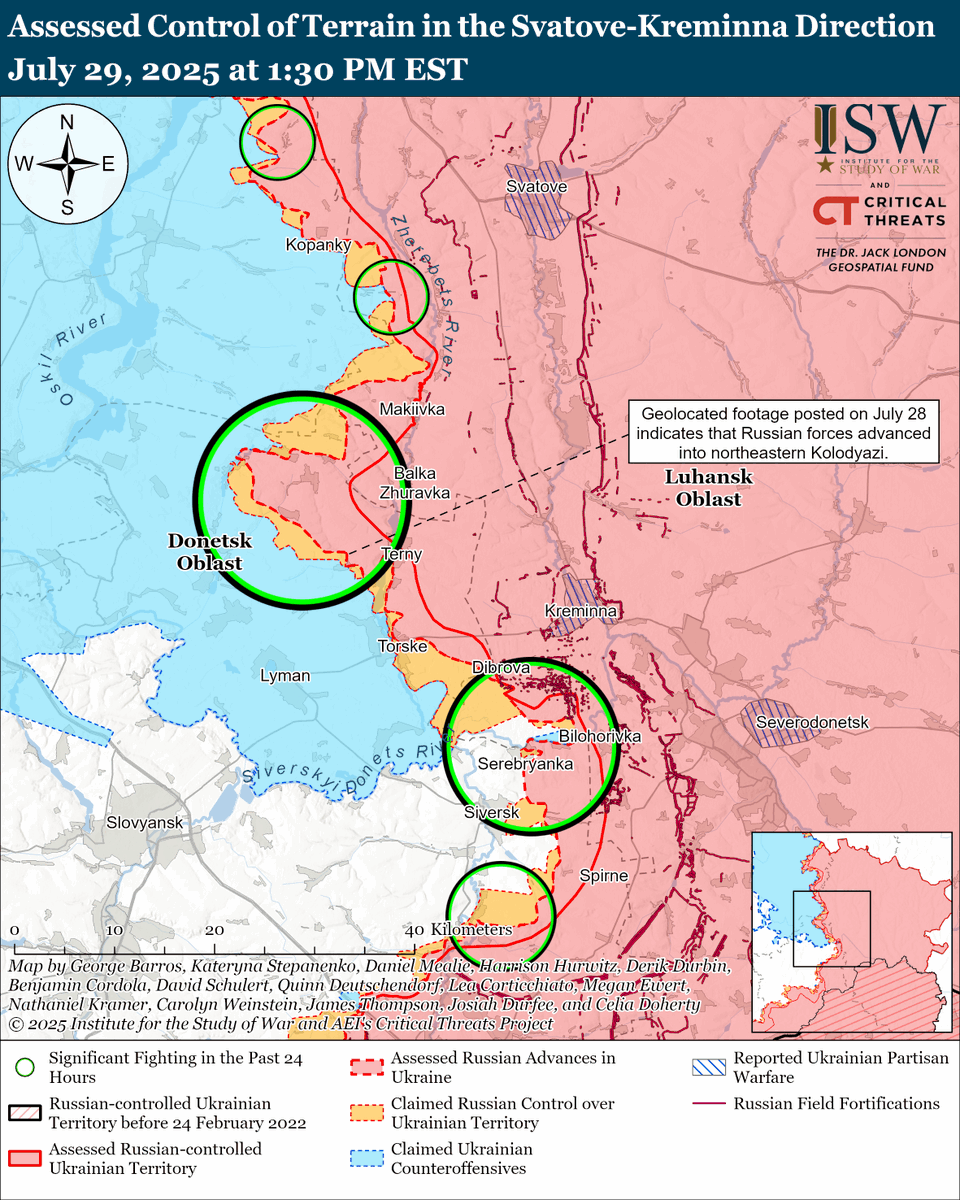
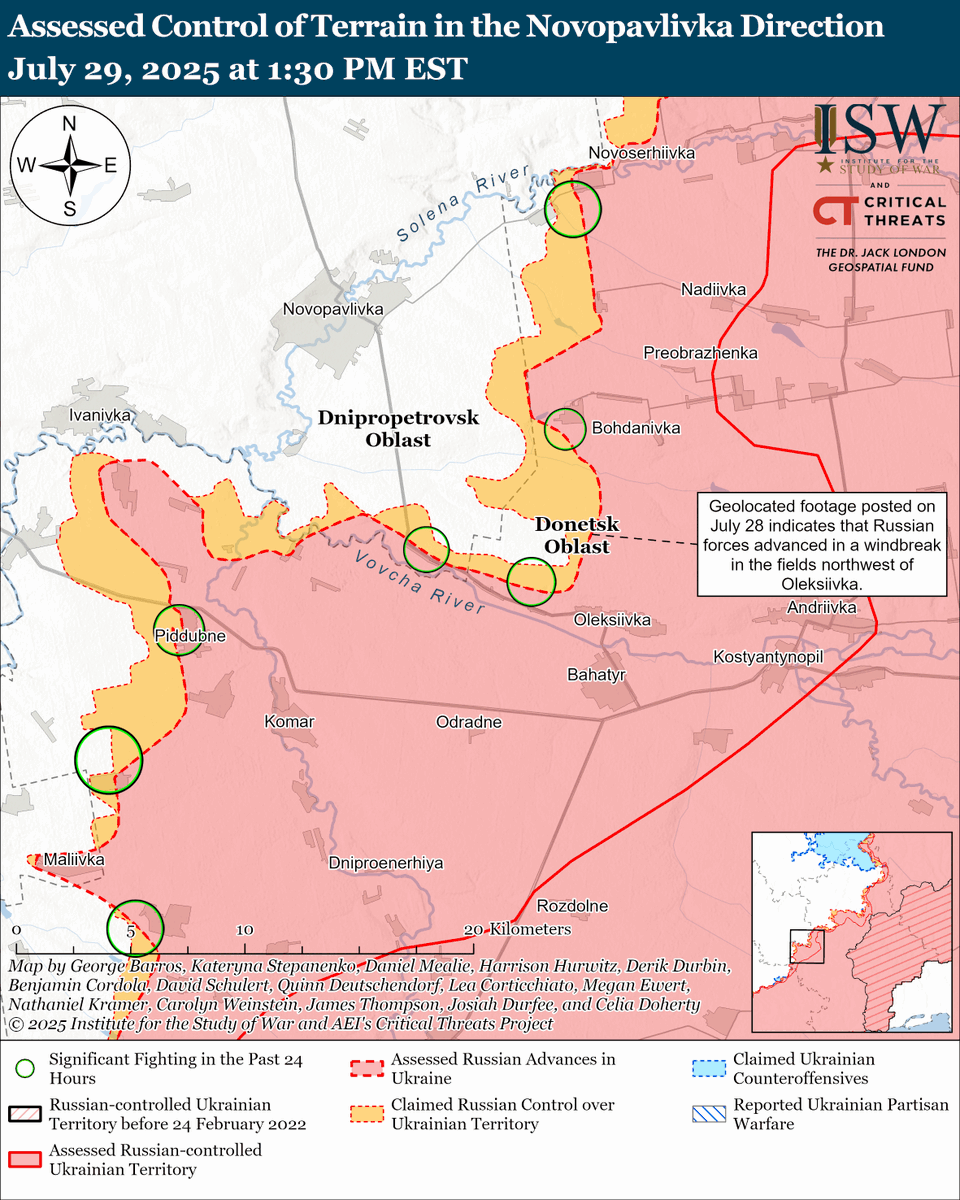
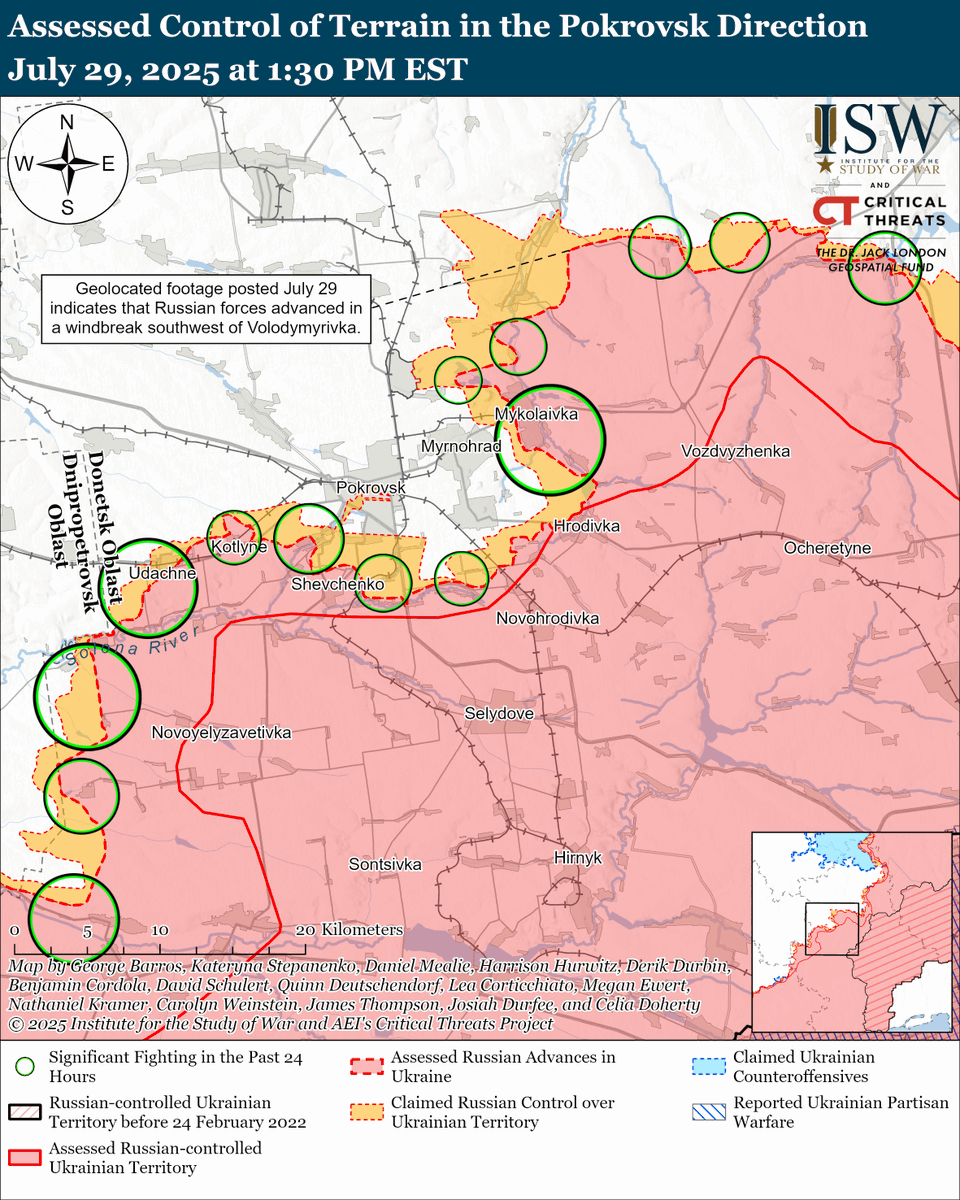
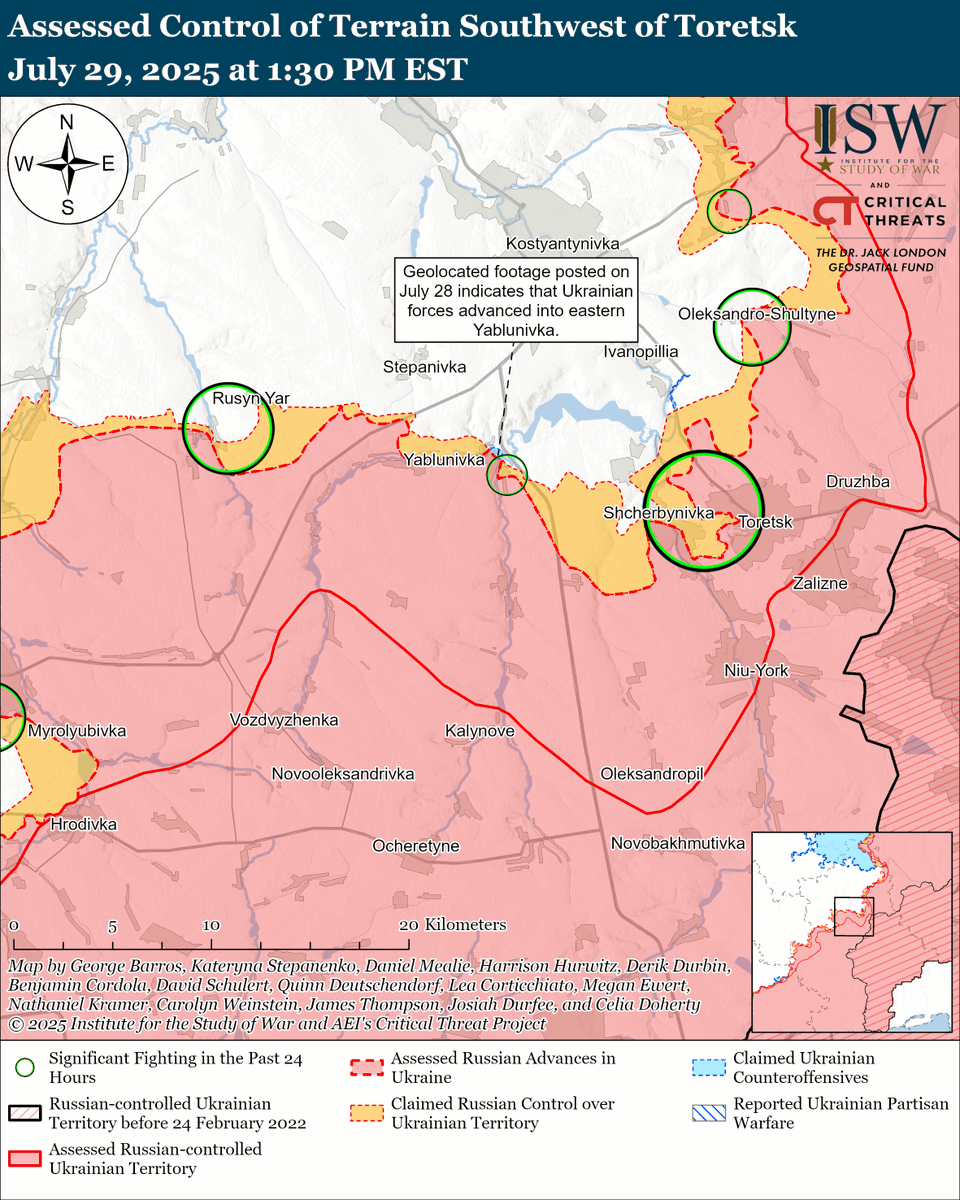
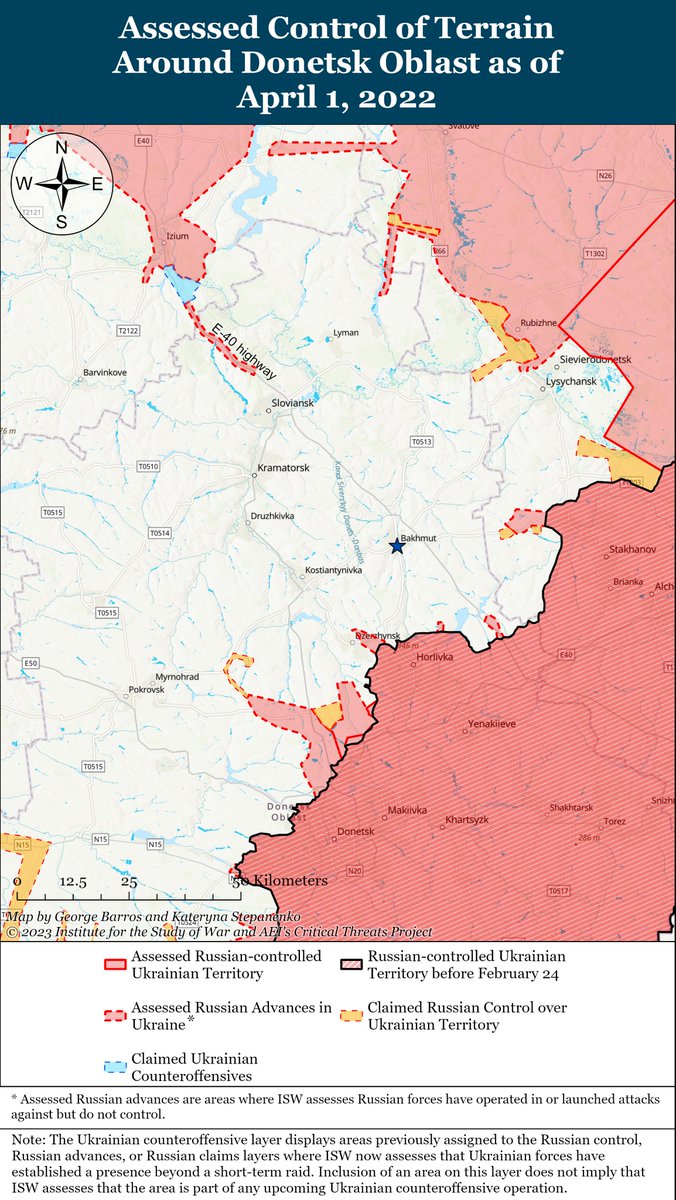
The seizure of #Bakhmut was originally intended to facilitate Russian offensives to encircle large Ukrainian forces in the east and specifically to take the large and fortified city of Slovyansk from multiple directions. isw.pub/Bakhmut052423
Key takeaways (and maps)🧵⬇️
Key takeaways (and maps)🧵⬇️
https://twitter.com/TheStudyofWar/status/1661362252593655810
2/ Russian offensive operations in Severodonetsk and Lysychansk proved extremely costly and slow, forcing the Russian military command to deprioritize the wide encirclement in #Donetsk Oblast in order to complete the seizure of those two cities. isw.pub/Bakhmut052423 

3/ #Russia reprioritized the Battle for #Bakhmut in July-August 2022, following the culmination of Russian attacks on the Severodonetsk-Lysychansk line. Wagner began assaults on settlements east and SE of Bakhmut, using Russian-occupied territories as springboards for the attack. 

4/ The successful Ukrainian counteroffensives in Kharkiv Oblast in September 2022 that liberated Izyum ended the prospect of a wide encirclement of Ukrainian forces in the east, thus depriving the attacks on Bakhmut of operational significance. 

5/ #Wagner mercenaries nevertheless intensified their offensives on #Bakhmut and fully committed to the Battle for Bakhmut in Fall 2022 likely to achieve informational and political rather than operational objectives. isw.pub/Bakhmut052423 

6/ The Russian MoD began to prepare for its own winter offensive operation in December 2022 and likely began to deprioritize support for #Wagner forces at that time. Wagner’s highly attritional offensives began to show signs of culmination by late December 2022 and in Jan 2023. 

7/ The #WagnerGroup began committing its remaining forces to #Bakhmut between February and March to threaten Ukrainian forces into withdrawing from the city so as to avoid having to fight through it. 

8/ The Ukrainian military blocked the Russian efforts to envelop or encircle #Bakhmut in March, forcing Wagner forces to fight through the city and suffer significant losses for the next two months. 

9/ ISW assessed that the Ukrainian defense of Bakhmut was a strategically sound decision as Ukrainians would benefit from exhausting Wagner forces if they were able to retain control over the two GLOCs west of Bakhmut. isw.pub/Bakhmut052423
10/ #Prigozhin has likely signaled the culmination of #Wagner forces in declaring victory in #Bakhmut on May 20 and announcing Wagner’s withdrawal from the city and plans to reconstitute on May 25, despite subsequent denials. 

11/ The #Wagner Group’s announced two-month reconstitution period could have #Wagner forces sitting out key parts of the Ukrainian counteroffensive depending on when and how it begins. isw.pub/Bakhmut052423
12/ The Battle of Bakhmut exposed several key flaws in the Russian planning and conduct of operational maneuver. It is also not even clear that the Battle of Bakhmut is yet over. isw.pub/Bakhmut052423
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh