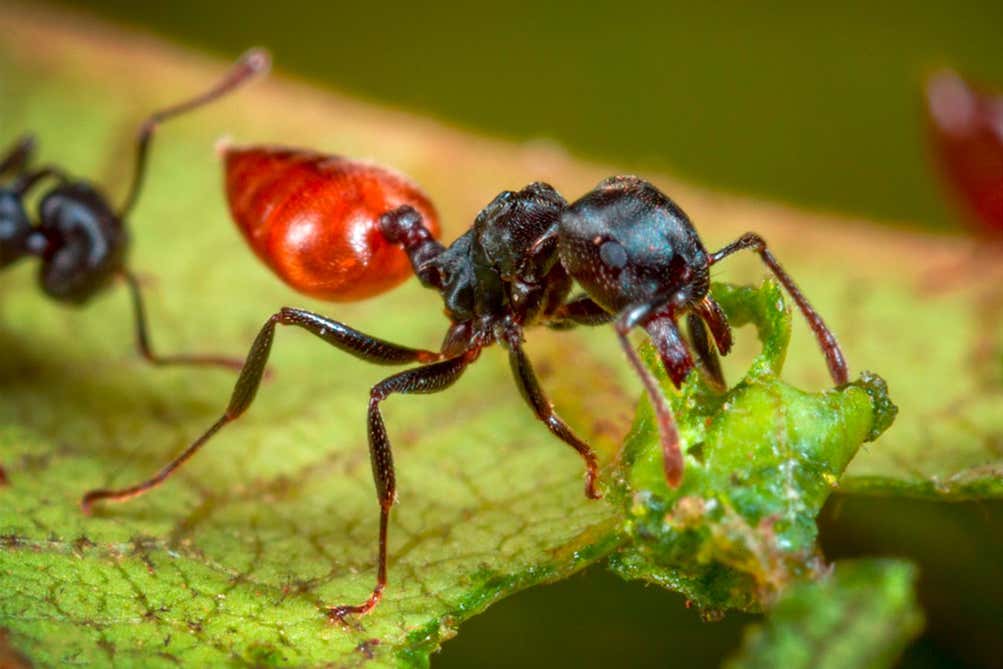
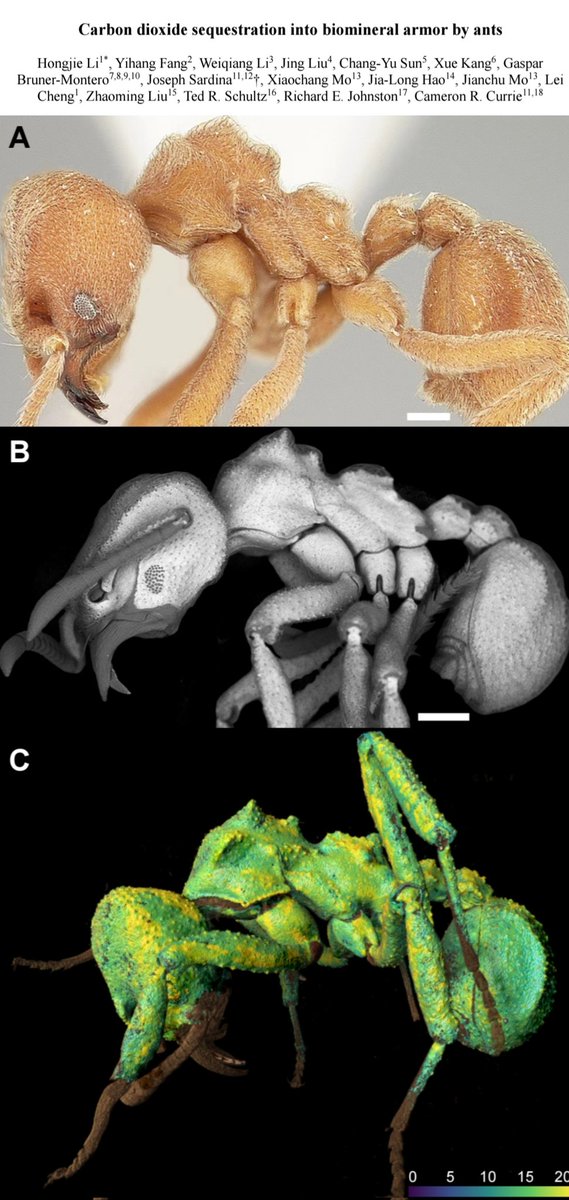
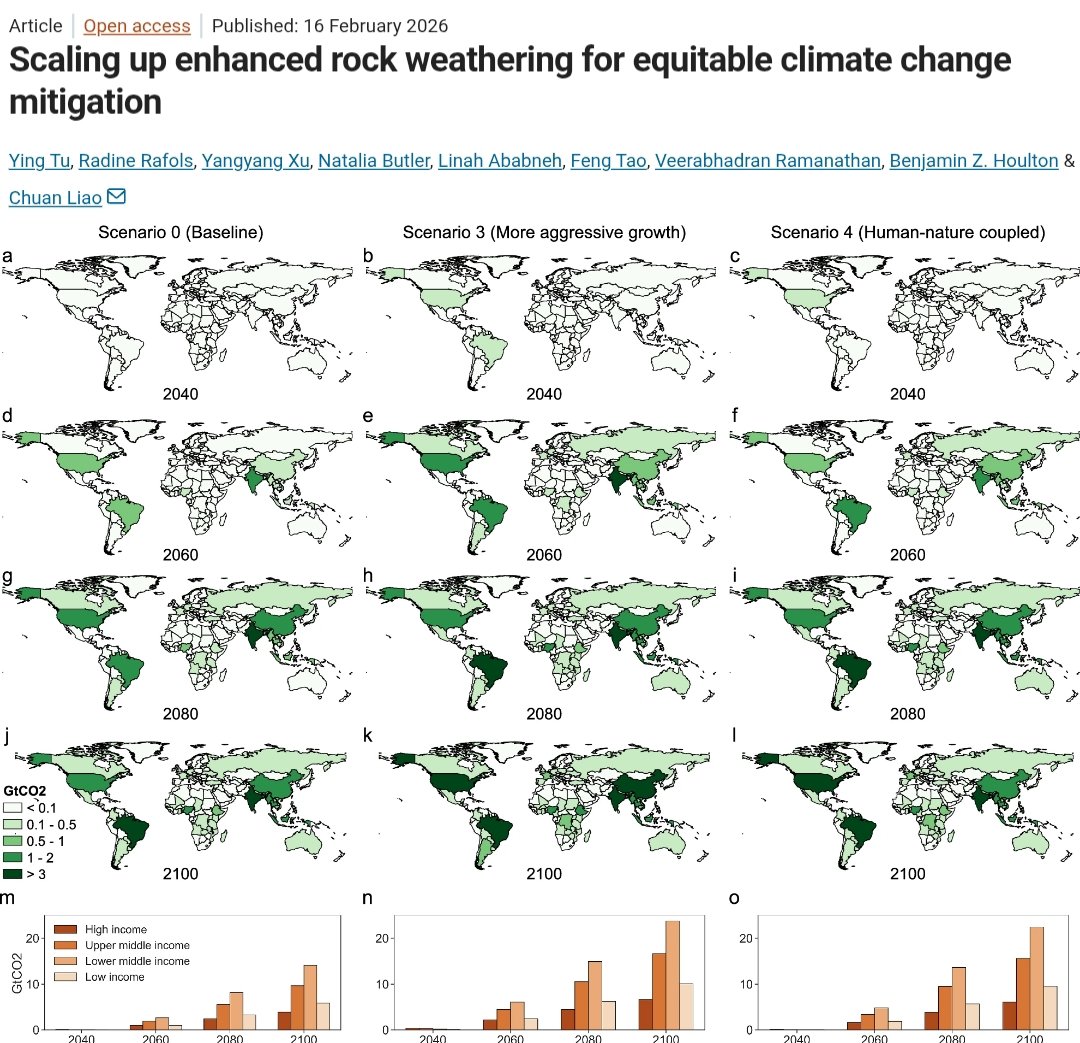
🚨NEW STUDY🚨
“Given the high expectations placed on #DAC for future #decarbonisation, recent study presents an extensive review of DAC tech, exploring a number of techno-economic aspects, including an updated collection of the current & planned DAC projects around the world.”
🧵

“Given the high expectations placed on #DAC for future #decarbonisation, recent study presents an extensive review of DAC tech, exploring a number of techno-economic aspects, including an updated collection of the current & planned DAC projects around the world.”
🧵

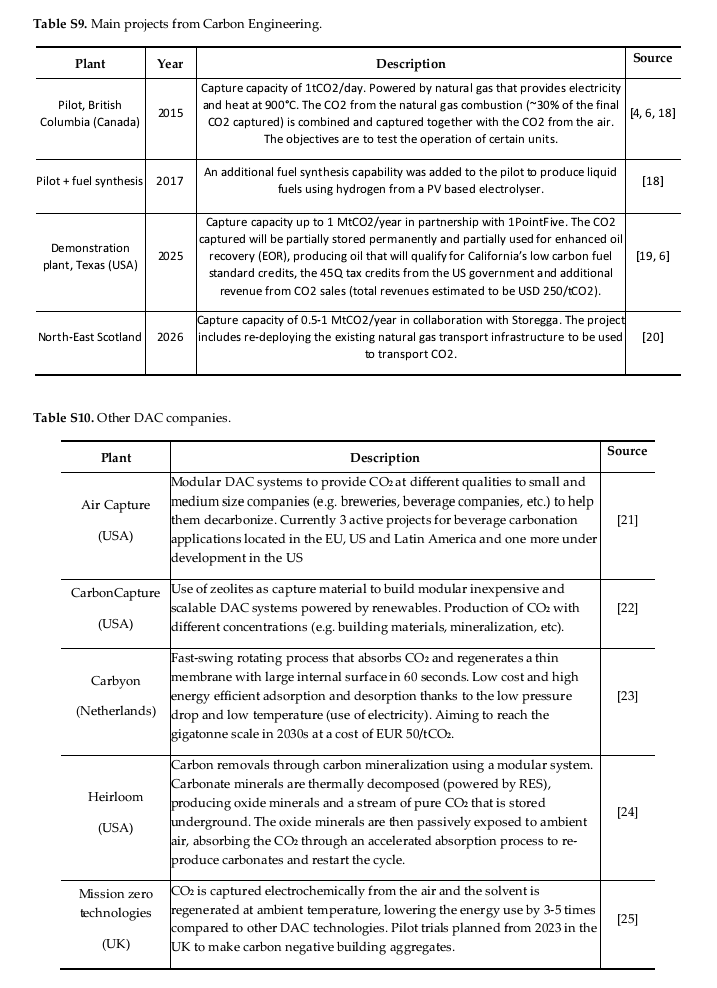
“A dedicated analysis focused on the production of synthetic methane, methanol, and diesel from #DAC and electrolytic hydrogen in the European Union (EU) is also performed, where the #carbonfootprint is analysed for different scenarios and energy sources.”
2/10
2/10

The results show that “the maximum grid carbon intensity to obtain #NegativeEmissions with #DAC is estimated at 468 gCO 2 e/kWh, which is compliant with most of the EU countries’ current grid mix.”
3/10
3/10

“Using only photovoltaics (PV) and wind, #NegativeEmissions of at least −0.81 tCO 2 e/tCO 2 captured can be achieved.”
4/10
4/10

“The maximum grid intensities allowing a reduction of the synthetic fuels carbon footprint compared with their fossil-fuels counterparts range btw 96 & 151 gCO 2 e/kWh.”
5/10
5/10
However, “to comply with the Renewable Energy Directive II (REDII) sustainability criteria to produce renewable fuels of non-biological origin, the maximum stays between 30.2 to 38.8 gCO 2 e/kWh.”
6/10
6/10

“Only when using PV and wind is the EU average able to comply with the REDII threshold for all scenarios and fuels, with fuel emissions ranging from 19.3 to 25.8 gCO 2 e/MJ.”
7/10
7/10
These results highlight the “importance of using renewable energies for the production of synthetic fuels compliant with the EU regulations that can help reduce emissions from difficult-to-decarbonise sectors.”
8/10
8/10
Read the paper entitled: "The Role of Direct Air Capture in EU’s Decarbonisation and Associated Carbon Intensity for Synthetic Fuels Production" here ⬇️
econpapers.repec.org/article/gamjen…
#DirectAirCapture
9/10
econpapers.repec.org/article/gamjen…
#DirectAirCapture
9/10

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh