Thanks to a very kind collaborator, i have some copeptin (marker of AVP) data, compared to my pre-vaccine measures👇🏻👇🏻👇🏻
Whilst not all samples were taken in ideal conditions, it is clear something funky is (or was) going on with my AVP. some thoughts🧵
#postvac #LongCovid #POTS
Whilst not all samples were taken in ideal conditions, it is clear something funky is (or was) going on with my AVP. some thoughts🧵
#postvac #LongCovid #POTS
https://twitter.com/angryhacademic/status/1526199050286120960
First a bit of background about copeptin (AVP)
AVP is part of the HPA ("stress") axis. briefly, high AVP = high ACTH = high cortisol
AVP also regulates hydration: low fluid/high salt = high AVP = kidney reabsorption of water = pee less = stay hydrated
AVP is part of the HPA ("stress") axis. briefly, high AVP = high ACTH = high cortisol
AVP also regulates hydration: low fluid/high salt = high AVP = kidney reabsorption of water = pee less = stay hydrated
https://twitter.com/angryhacademic/status/1660992171271507977
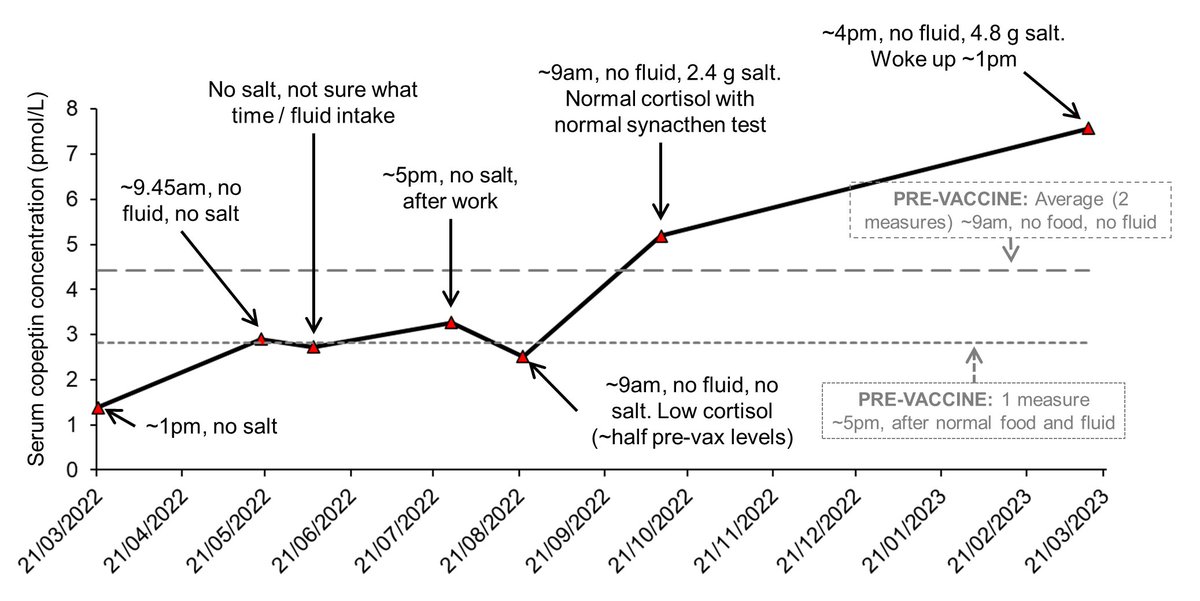
1. What i find MOST interesting is that under the most controlled conditions (9am, no fluid), my copeptin was much lower than pre-vaccine on the same day my cortisol came back much lower than pre-vaccine
https://twitter.com/angryhacademic/status/1562847108314439681
I then had a synacthen test which came back normal about 6 weeks later. this was confusing. I had just come off clopidogrel and was relapsing *HARD*.
Hypothesis 1: relapse = stress = higher cortisol
This is an expected response to illness
Hypothesis 1: relapse = stress = higher cortisol
This is an expected response to illness
Buuuut, between my low cortisol measure in August, and my synacthen test in October, we started me on salt because we learnt i wasn't producing detectable levels of aldosterone (which helps you retain salt). in essence, i was peeing out all the salt i consumed
So at my synacthen test, i had had my morning slow sodium, 2.4 g NaCl.
Hypothesis 2: salt intake was a sufficient stimulus to produce AVP = ACTH = higher cortisol
(both hypotheses could be correct ofc)
Hypothesis 2: salt intake was a sufficient stimulus to produce AVP = ACTH = higher cortisol
(both hypotheses could be correct ofc)
2. AVP is quite sensitive. Even the taste of water has been reported to reduce it. A bolus of fluid can lower AVP for several hours. This is why i put the time, salt, and fluid intake on the graph, along with a roughly equivalent measure from pre-vaccine
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29242971/
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29242971/
What we can see is that from the measures taken, regardless of the time, food, or fluid intake, prior to the synacthen test my copeptin was about the same as my pre-vaccine measure after a normal day (with food and fluid)
in other words, my copeptin was abnormally low. Essentially, my generally low salt diet wasn't enough of an osmotic stimulus to boost AVP.
Whether there's a pathological side of it is unclear.
Whether there's a pathological side of it is unclear.
3. My most recent measure was an odd one. it was semi-controlled since i had not eaten or drunk anything (except a sip to take meds), but it was also quite late in the day. my copeptin came back quite high. levels you can see in e.g. diabetes, cardiovascular disease (if chronic)
This suggests my AVP *is* responding to osmotic stimuli as it should.
Has whatever malfunction been fixed? Was the fix as simple as salt, or was there co-pathology? i don't know.
Has whatever malfunction been fixed? Was the fix as simple as salt, or was there co-pathology? i don't know.
worth noting that desmopressin (an AVP analogue) is used in #POTS treatment
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
link.springer.com/chapter/10.100…
it works by stopping you peeing so much, so you maintain your blood volume.
Yet my POTS is still very bad
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
link.springer.com/chapter/10.100…
it works by stopping you peeing so much, so you maintain your blood volume.
Yet my POTS is still very bad
https://twitter.com/angryhacademic/status/1662542550345867264
4. Most of last year/early this year, i suffered with varying levels of excessive thirst
If you read most thirst literature, it will say or hint at high AVP being a key trigger to thirst. im less convinced
explained here: hydrationforhealth.com/en/hydration-s…
and here:
If you read most thirst literature, it will say or hint at high AVP being a key trigger to thirst. im less convinced
explained here: hydrationforhealth.com/en/hydration-s…
and here:
https://twitter.com/angryhacademic/status/1283446678792609799
In brief, the most prominent #thirst idea is:
no fluid/high salt = ↑ blood osmolality (concentration) = ↑ AVP = thirst
my case above is another example of the relationship between osmolality, AVP, and thirst being complicated...
no fluid/high salt = ↑ blood osmolality (concentration) = ↑ AVP = thirst
my case above is another example of the relationship between osmolality, AVP, and thirst being complicated...
my osmolality has been normal, and my AVP low. by the dominating thirst hypothesis i should NOT be thirsty. so why was i thirsty?
1. Hypovolaemia (low blood volume): this in itself can trigger ↑ AVP (usually at losses of > ~10 %, which we can get)
1. Hypovolaemia (low blood volume): this in itself can trigger ↑ AVP (usually at losses of > ~10 %, which we can get)
https://twitter.com/angryhacademic/status/1658621833816555521
But clearly hypovolaemia did NOT trigger AVP for me. However, it may have still triggered "stretch sensitive" cells in the brain
https://twitter.com/angryhacademic/status/1335203279819730946
2. Cholinergic dysregulation: the cholinergic system regulates thirst, saliva, and drinking behaviours (see my talk/paper linked above). I am currently experimenting with choline:
https://twitter.com/angryhacademic/status/1659217769081221121
3. Neurological inflammation/damage: thirst is regulated in the brain. I have MCAS (potential neuroinflammation), platelet activation, clotting, etc. these can all cause chaos in the brain.
what is FASCINATING is that shortly after my blood test in March 2023...
what is FASCINATING is that shortly after my blood test in March 2023...
i was finally put on steroids to help the relapse. Since then, my thirst has normalised. im even having to *remember* to drink to help POTS. did steroids dampen neuroinflammation?
We can infer from my Oct 2022 (synacthen test) & March 2023 copeptin that my AVP is working again
We can infer from my Oct 2022 (synacthen test) & March 2023 copeptin that my AVP is working again
so it is (a) normal, (b) responsive to osmotic challenges
Yet my thirst is LOWER than when my AVP was abnormally low
This suggests that even if my model of thirst isnt entirely correct, the premise that thirst is (unsurprisingly) more complex than AVP & osmolality IS correct
Yet my thirst is LOWER than when my AVP was abnormally low
This suggests that even if my model of thirst isnt entirely correct, the premise that thirst is (unsurprisingly) more complex than AVP & osmolality IS correct
Anyway, there's some off the cuff, slightly jumbled thoughts... i didn't go into interactions with RAAS or other meds either. its complex!
@DeansKevin has some ideas about my thyroid, i will see if i can collate my thyroid data and correlate it to copeptin
@DeansKevin has some ideas about my thyroid, i will see if i can collate my thyroid data and correlate it to copeptin
but to summarise, my HPA axis definitely had something funky going on. it was acting distinctly different compared to pre-vaccine, and this is supported by cortisol measures.
lots of ideas why, much to learn #exciting!
lots of ideas why, much to learn #exciting!
except the living it, i do find it cool being part of my own hydration experiment. if you watch the talk i did linked above, that was during my initial "recovery" from the vac. you can see me fighting brain fog & i had to keep lying down when recording as i felt so sick & dizzy..
....the signs of POTS were there & i was completely oblivious. the irony of this illness is amazing:
1. research vaccine effectiveness: get vaccine injured
2. research hydration: vaccine dysregulates my AVP, aldosterone
3. research appetite: vaccine causes my appetite to wild
🙃
1. research vaccine effectiveness: get vaccine injured
2. research hydration: vaccine dysregulates my AVP, aldosterone
3. research appetite: vaccine causes my appetite to wild
🙃
This post in a blog, with a wee bit more elaboration and citations
dontbelievehype.co.uk/covid-%26-vacc…
dontbelievehype.co.uk/covid-%26-vacc…
@jencurtinmd you might be interested (think we discussed vasopressin and POTS a few months ago in a #TeamClots meeting)
Choline may increase vasopressin 😲
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12031853/
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12031853/
Pilot Findings on SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine-Induced Pituitary Diseases: A Mini Review from Diagnosis to Pathophysiology
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
Paper discusses cases of pituitary dysfunction post-vaccine (and COVID)
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
Paper discusses cases of pituitary dysfunction post-vaccine (and COVID)
this includes things like diabetes insipidus which many of us have symptoms of, as well as other common symptoms like weakness and headaches...sounds familiar!
authors highlight how non-specific these symptoms are so are easily dismissed and not investigated
#MedTwitter
authors highlight how non-specific these symptoms are so are easily dismissed and not investigated
#MedTwitter
there's a lot of nuance in the paper about the cases they discussed so it's unclear how well this translates to cases like mine, but they discuss inflammation, endothelial dysfunction, and ischaemia as likely causes
depending on the problem, patients were treated with desmopressin (AVP analogue) and/or steroids.
for those with hypophysitis, steroids seemed to help. this is interesting to me, since my thirst has been fixed since (low dose) steroids...
for those with hypophysitis, steroids seemed to help. this is interesting to me, since my thirst has been fixed since (low dose) steroids...
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh




