ICU stories (common): Middle-aged pt w hx of COPD was brought to the ED by EMS after SOB x 2 days. No fever or chest pain. Very quickly after ED arrival, he was intubated. CXR showed hyperinflated, “COPD” lungs. Here depicted in two images: 



BP dropped post-intubation to 55/40; propofol was started & then discontinued due to hypotension. iv fluids (2L Lactate Ringer's) were started & patient was brought to the ICU w SBP in upper 80s. Re-institution of propofol led again to hypotension. What would be the next step?
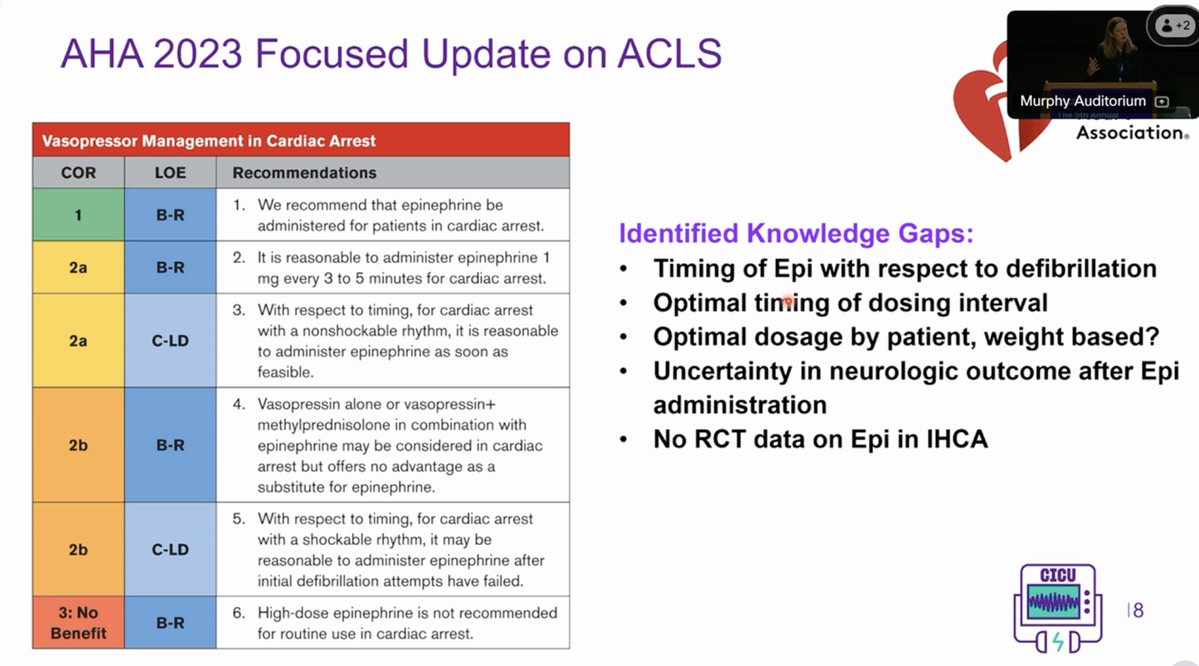
Patient came from the ED with these vent settings 👇 (RR was increased from 18 to 22 to ⬇️ the PCO2 of >100 in the first ABGs): 

There was suspicion of auto-PEEP ---> presence of expiratory flow when every new breath was given. Next step was to check lung mechanics: Pplateau was 38 and PEEPtotal 25 (revealing an auto-PEEP close to 20…) 


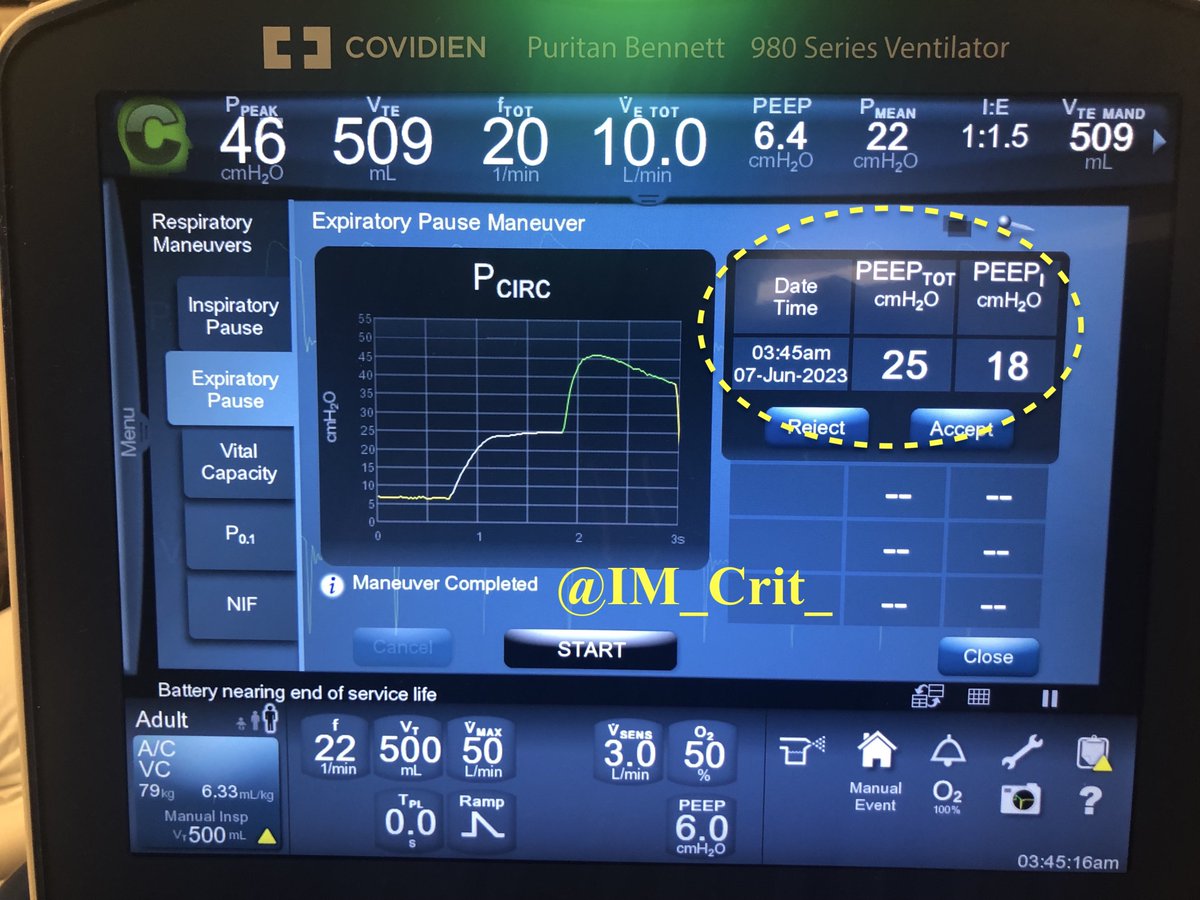
Next step?
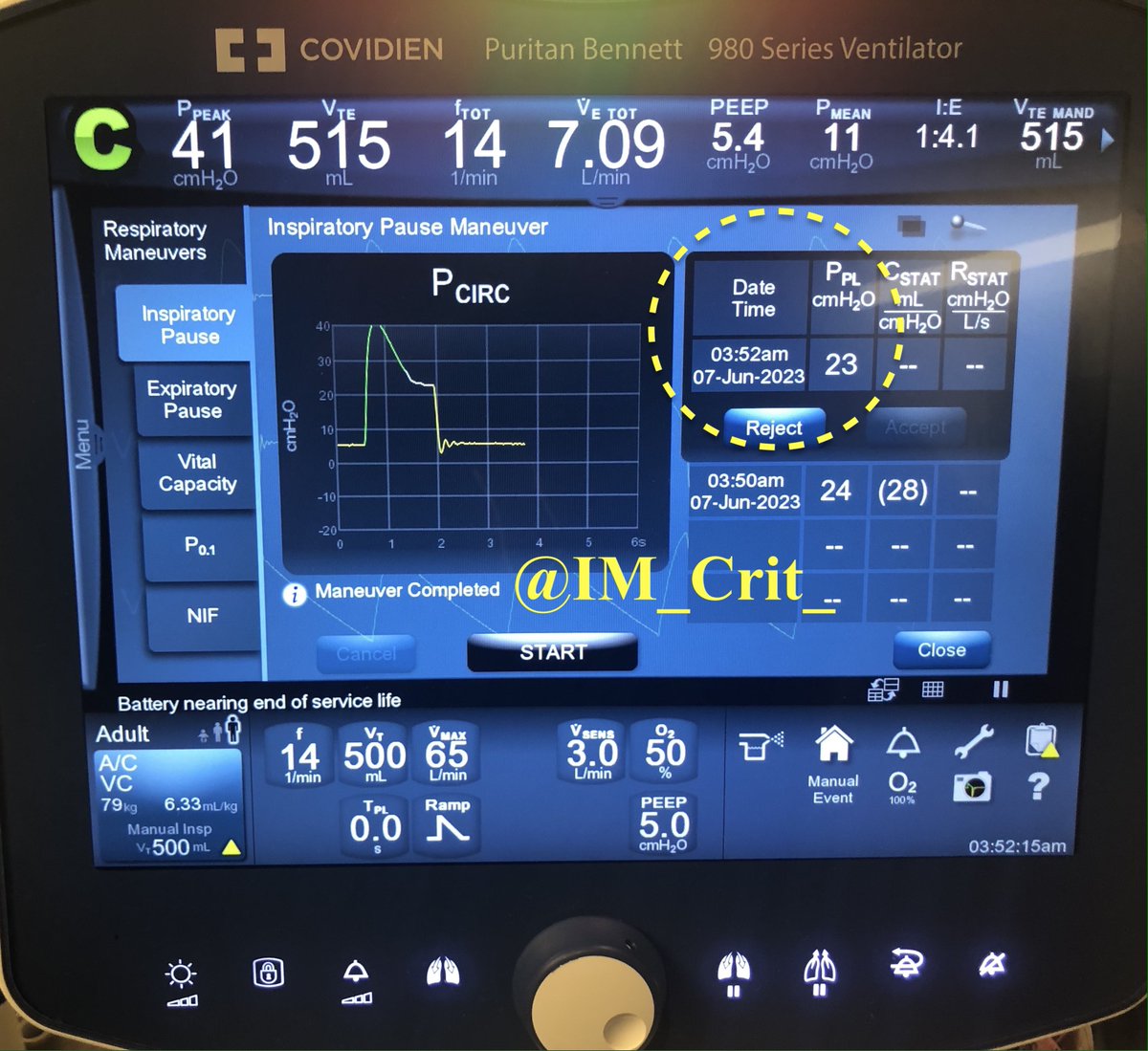
We discontinued the patient from the ventilator for 15 sec and decreased RR to 14. Five minutes later, P plateau & auto-PEEP had decreased nicely 👇. Hemodynamics improved without fluids/pressors & despite the patient being back on propofol. 


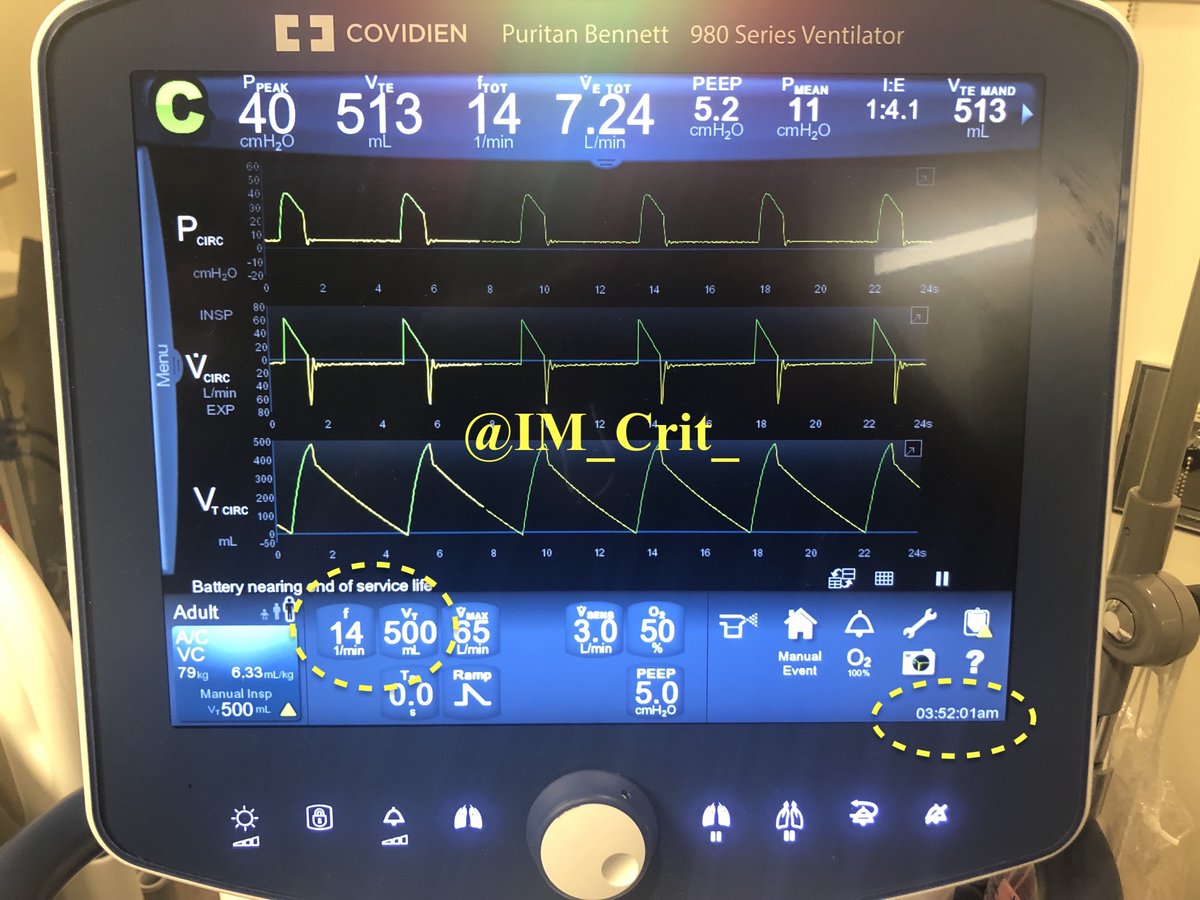

Next step to decrease auto-PEEP further?
IMHO, if you do the basic right things (⬇️ RR) and give patient time, things will continue to improve. No other change was made in the ventilator settings and, 30 min later, lung mechanics continued to improve: 



Reminder: Extrinsic PEEP is set by the clinician on a ventilator while auto-PEEP is unintentional
Pepe and Marini used the term "auto-PEEP" back in 1982 👇
Pepe and Marini used the term "auto-PEEP" back in 1982 👇

In the same paper, Pepe and Marini described the method of quantifying auto-PEEP by occlusion of the expiratory port 

I love this paper not just because it's classic and brings physiology at the bedside, but also because it gives us a chance to glimpse at the ICU practices of the times... Please take a look at dopamine use, dopamine doses and tidal volume: 



Excessive auto-PEEP can impede venous return and can also precipitate acute right ventricular failure. Volume expansion can help up to a point; the point where a dilated RV will i) be unable to eject its preload into the pulmonary circuit impair and ii) impair LV filling...
The auto-PEEP phenomenon still remains under-recognized. Sometimes, it is so dramatic that patients in PEA arrest spontaneously "recover" when they are disconnected from the ventilator circuit ("Lazarus
effect"). Especially in bad asthmatics or COPD patients that suffer PEA,
effect"). Especially in bad asthmatics or COPD patients that suffer PEA,
consideration should be given to simply discontinue ventilation transiently for 10-20 sec during CPR and observe the patient for return of circulation.
Thanks for reading!
#FOAMed #FOAMcc #MedTwitter #MedEd #EMBound @ThinkingCC @RJonesSonoEM @msiuba @siddharth_dugar @TaotePOCUS @cjosephy @MegriMohammed @emily_fri @curromir #MedStudentTwitter
#FOAMed #FOAMcc #MedTwitter #MedEd #EMBound @ThinkingCC @RJonesSonoEM @msiuba @siddharth_dugar @TaotePOCUS @cjosephy @MegriMohammed @emily_fri @curromir #MedStudentTwitter
It would be interesting to learn what the highest autoPEEP you have seen is and if there is an easy way to determine if by going to zero “set PEEP” helps with air emptying
@CCF_PCCM @Thind888 @SMHCoEMV @some4mv @Vent_Busters @AGMRRT @SCCMohio @RespiratorySCCM @ArielG_RRT
@CCF_PCCM @Thind888 @SMHCoEMV @some4mv @Vent_Busters @AGMRRT @SCCMohio @RespiratorySCCM @ArielG_RRT
Pt 1 in the Pepe-Marini paper: "it was observed that systolic BP ⬆️ to 140 mmHg within 30 s of a brief IPPV interruption, whereas wedge decreased to 10-13 mmHg. Simultaneously, mean PAP & HR ⬇️. Whenever IPPV was reinstituted, HR, BP, wedge, PAP returned to their previous values 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh