(1/n)
What are these generally white blood clots found by various embalmers, probably mainly related to COVID-19 vaccinations?
Embalmer Richard Hirschman (@r_hirschman) has now published some interesting findings about these clots ().
Here is a summary and discussion.
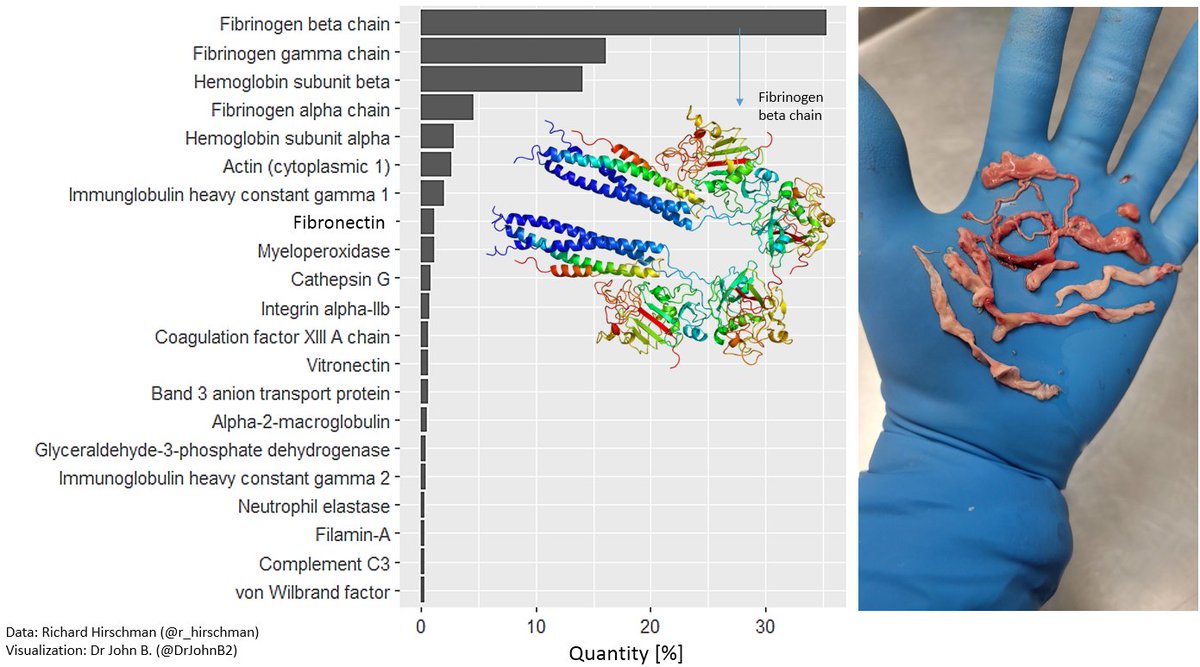
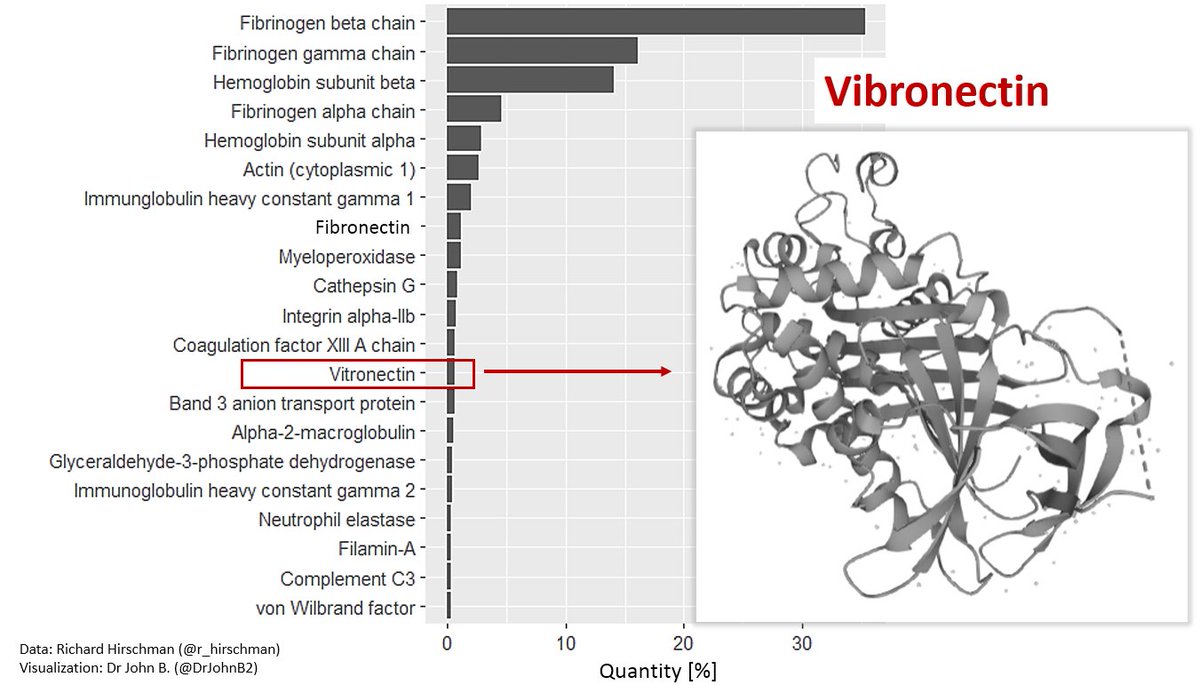
These are the proteins that were found:
What are these generally white blood clots found by various embalmers, probably mainly related to COVID-19 vaccinations?
Embalmer Richard Hirschman (@r_hirschman) has now published some interesting findings about these clots ().
Here is a summary and discussion.
These are the proteins that were found:
https://x.com/r_hirschman/status/1800562643888931174

(2/n)
The most abundant protein is fibrinogen (fibrinogen chains alpha, beta & gamma) (making 56% of total clot protein abundance). Followed by hemoglobin (subunit beta and alpha).
Fibronectin is an important protein for cell adhesion (and in a clot is normally covalently cross-linked to fibin by Factor XIII).
Fibrinogen chains are the main constituents of blood clots, and the presence of relatively large amounts of fibronectin is typical. See, for example, the study of plasma clots by Michał Ząbczyk et al. [1]:
[1] sciencedirect.com/science/articl…
The most abundant protein is fibrinogen (fibrinogen chains alpha, beta & gamma) (making 56% of total clot protein abundance). Followed by hemoglobin (subunit beta and alpha).
Fibronectin is an important protein for cell adhesion (and in a clot is normally covalently cross-linked to fibin by Factor XIII).
Fibrinogen chains are the main constituents of blood clots, and the presence of relatively large amounts of fibronectin is typical. See, for example, the study of plasma clots by Michał Ząbczyk et al. [1]:
[1] sciencedirect.com/science/articl…

(3/n)
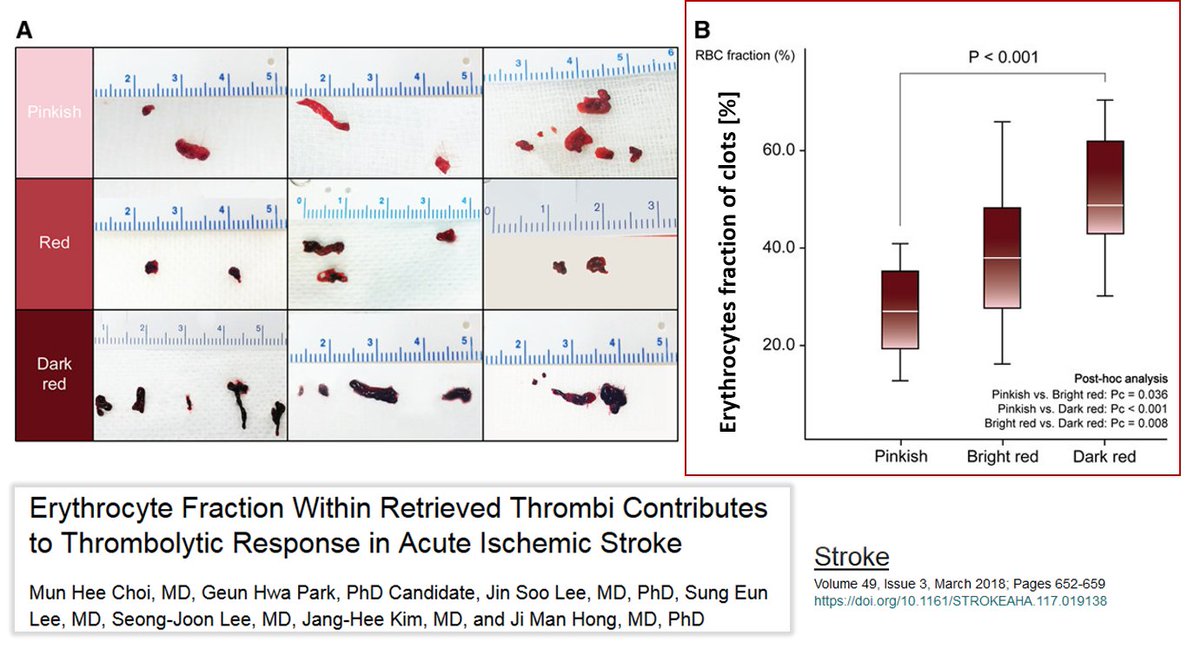
The hemoglobin proteins (beta & alpha subunits) indicate the presence of erythrocytes or the hemoglobin of the erythrocytes (free hemoglobin, Hb).
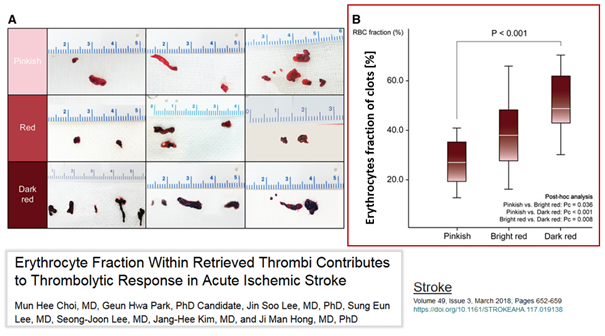
Hb is known to bind to von Willebrand Factor (VWF), inducing the formation of platelet aggregates on fibrinogen-rich surfaces [1]. The amount of erythrocytes/Hb present in clots varies. Choi et al [2] showed that the more erythrocytes there are in a clot, the more red it is:
[1]
[2] ashpublications.org/blood/article/…
ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.11…
The hemoglobin proteins (beta & alpha subunits) indicate the presence of erythrocytes or the hemoglobin of the erythrocytes (free hemoglobin, Hb).
Hb is known to bind to von Willebrand Factor (VWF), inducing the formation of platelet aggregates on fibrinogen-rich surfaces [1]. The amount of erythrocytes/Hb present in clots varies. Choi et al [2] showed that the more erythrocytes there are in a clot, the more red it is:
[1]
[2] ashpublications.org/blood/article/…
ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.11…
(4/n)
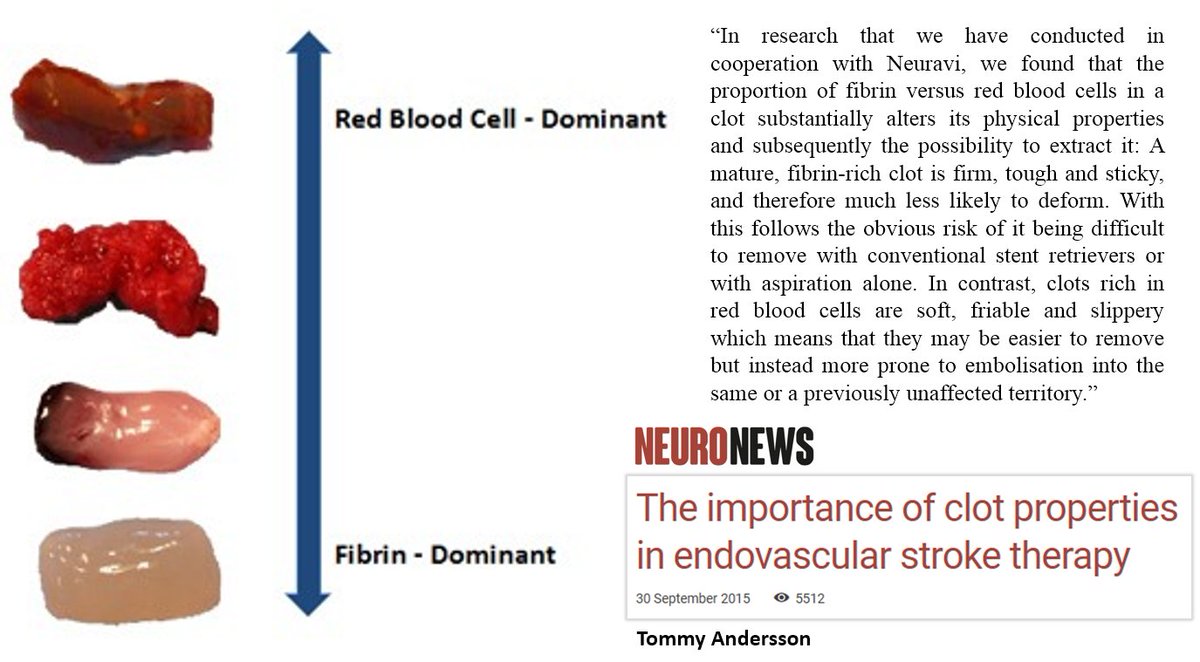
In terms of clot color, the relative abundance of erythrocytes and fibrin is related to the color of the clot and the ratio is related to the physical properties of the clot (more erythrocytes in the clot: more soft & friable clot) [1]:
[1] neuronewsinternational.com/the-importance…

In terms of clot color, the relative abundance of erythrocytes and fibrin is related to the color of the clot and the ratio is related to the physical properties of the clot (more erythrocytes in the clot: more soft & friable clot) [1]:
[1] neuronewsinternational.com/the-importance…

(5/n)
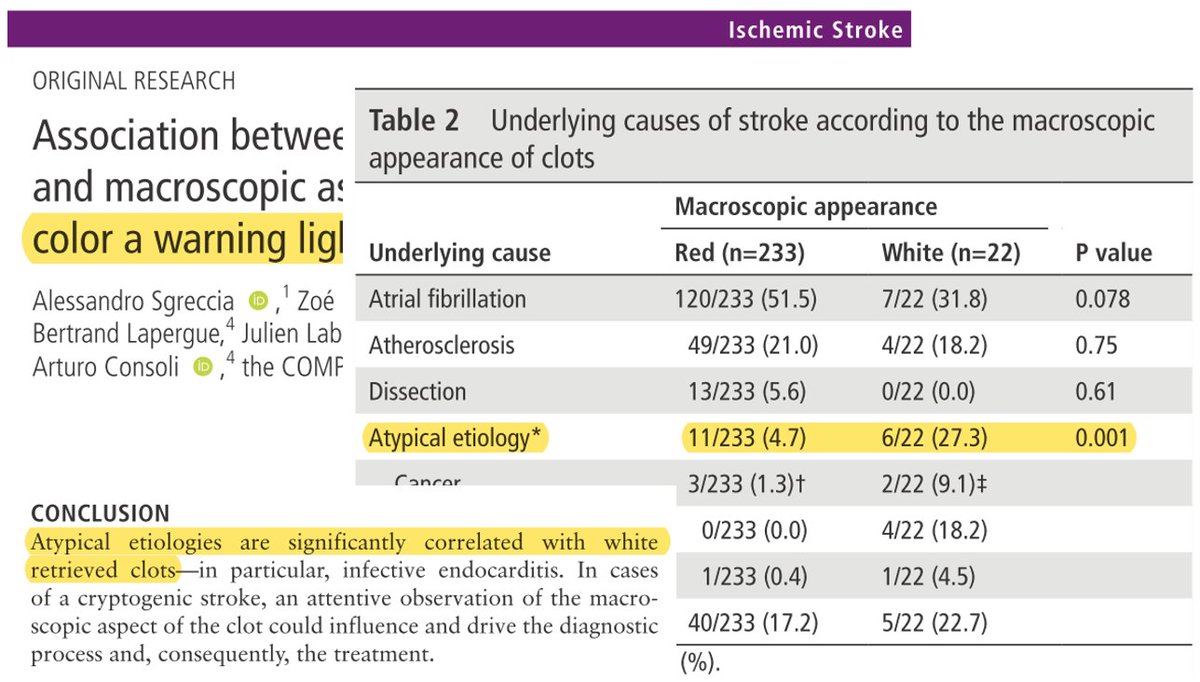
Sgreccia et al [1] concluded that the color of the clot is related to its composition and could be a „warning light for underlying pathologies“.
White clots are less common and indicate an "atypical" aetiology:
[1] jnis.bmj.com/content/11/12/…

Sgreccia et al [1] concluded that the color of the clot is related to its composition and could be a „warning light for underlying pathologies“.
White clots are less common and indicate an "atypical" aetiology:
[1] jnis.bmj.com/content/11/12/…

(6/n)
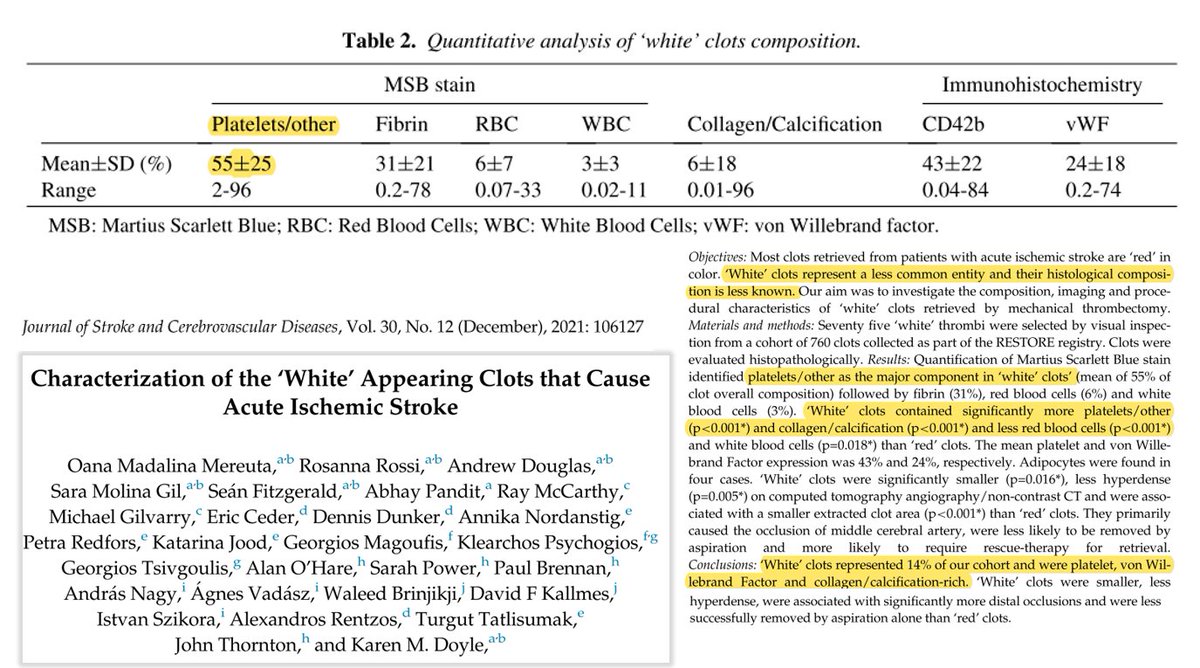
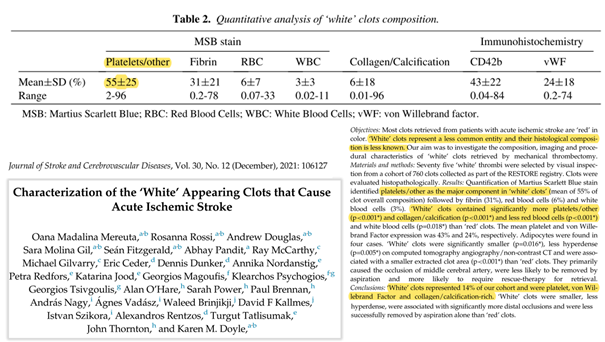
In a study published in 2021, Mereuta et al [1] examined white clots, as they "represent a less common entity and their histological composition is less known". They highlighted that these white clots „account for a small subset of thrombi and are often perplexing to the clinician regarding the etiology“.
The study found that white clots were less common than red clots (14% of the 760 clots studied) and contained significantly more platelets and collagen/calcification and less erythrocytes and white blood cells than red clots.
(White clots also contained a significant amount of von Willebrand factor (vWF). vWF was also found in Richard Hirschman's analysis).
[1] sciencedirect.com/science/articl…
In a study published in 2021, Mereuta et al [1] examined white clots, as they "represent a less common entity and their histological composition is less known". They highlighted that these white clots „account for a small subset of thrombi and are often perplexing to the clinician regarding the etiology“.
The study found that white clots were less common than red clots (14% of the 760 clots studied) and contained significantly more platelets and collagen/calcification and less erythrocytes and white blood cells than red clots.
(White clots also contained a significant amount of von Willebrand factor (vWF). vWF was also found in Richard Hirschman's analysis).
[1] sciencedirect.com/science/articl…
(7/n)
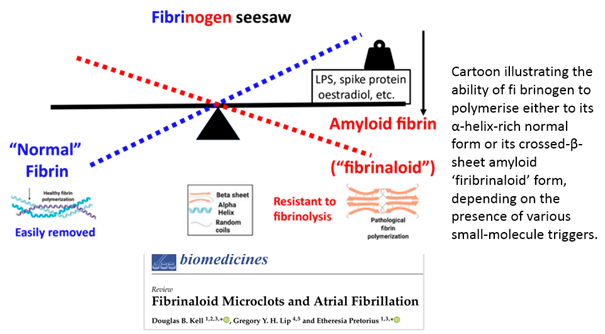
In my opinion, the discovery of "fibrinaloid" microclots by Pretorius & Kell [1] is very important in explaining the white clots observed by embalmers.
As highlighted in a recent excellent review by Kell et al [2], the polymerisation of fibrinogen to fibrin in clots can occur in different forms on a spectrum.
One end of the spectrum represents the normal fibrin polymerisation process in which "normal" (α-helix-rich) fibrin is formed.
The other end of the spectrum is characterised by abnormal fibrin polymerisation, resulting in a crossed-β-sheet amyloid 'fibrinaloid' form:
[1]
[2] pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27605168/
mdpi.com/2227-9059/12/4…
In my opinion, the discovery of "fibrinaloid" microclots by Pretorius & Kell [1] is very important in explaining the white clots observed by embalmers.
As highlighted in a recent excellent review by Kell et al [2], the polymerisation of fibrinogen to fibrin in clots can occur in different forms on a spectrum.
One end of the spectrum represents the normal fibrin polymerisation process in which "normal" (α-helix-rich) fibrin is formed.
The other end of the spectrum is characterised by abnormal fibrin polymerisation, resulting in a crossed-β-sheet amyloid 'fibrinaloid' form:
[1]
[2] pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27605168/
mdpi.com/2227-9059/12/4…
(8/n)
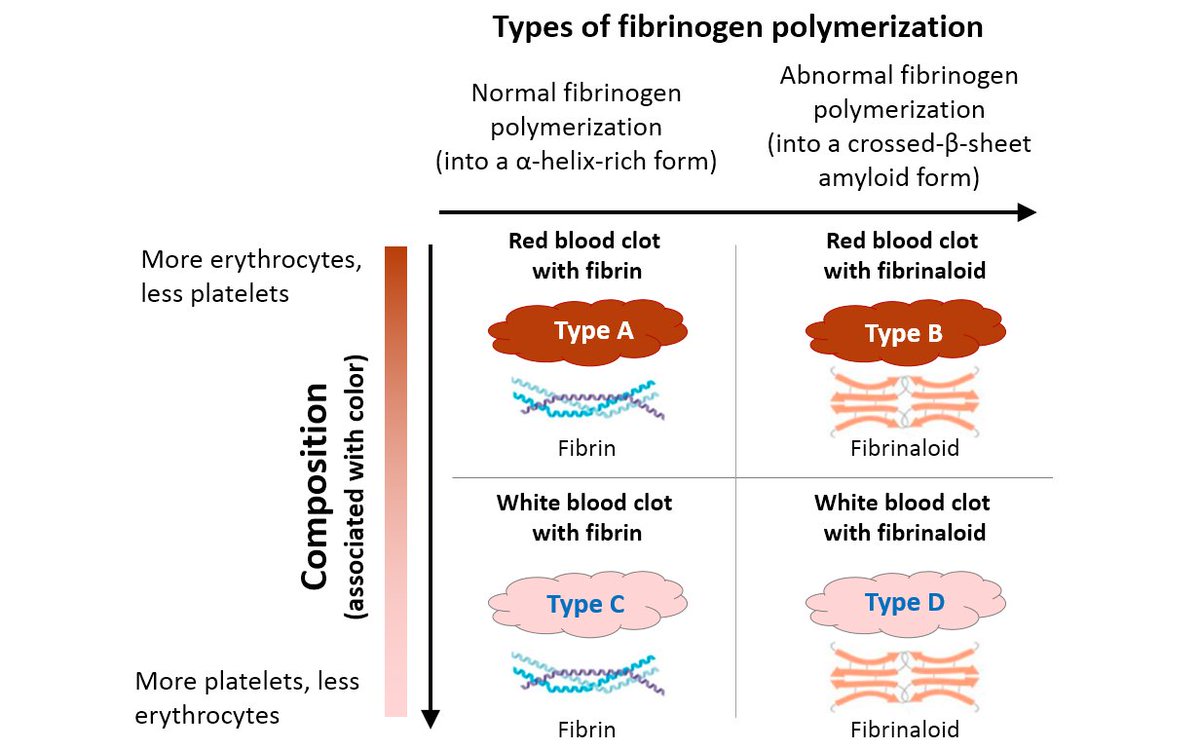
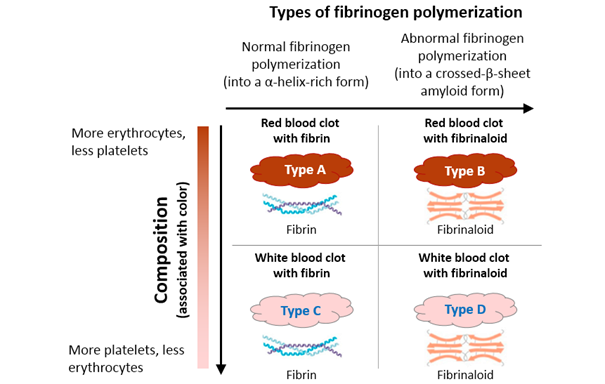
I think the different types of clots can be categorised along two dimensions: one dimension (y-axis) is the composition (more erythrocytes or more platelets?), which also correlates with the color. The other dimension (x-axis) is the type of fibrinogen polymerization (normal [fibrin] or abnormal [fibrinaloid]).
There are therefore four types of expression: Type A, B, C and D.
My hypothesis is that the clots that embalmers are now finding more of are actually type D clots (or those on the axis from type B to type D).
I think the different types of clots can be categorised along two dimensions: one dimension (y-axis) is the composition (more erythrocytes or more platelets?), which also correlates with the color. The other dimension (x-axis) is the type of fibrinogen polymerization (normal [fibrin] or abnormal [fibrinaloid]).
There are therefore four types of expression: Type A, B, C and D.
My hypothesis is that the clots that embalmers are now finding more of are actually type D clots (or those on the axis from type B to type D).
(9/n)
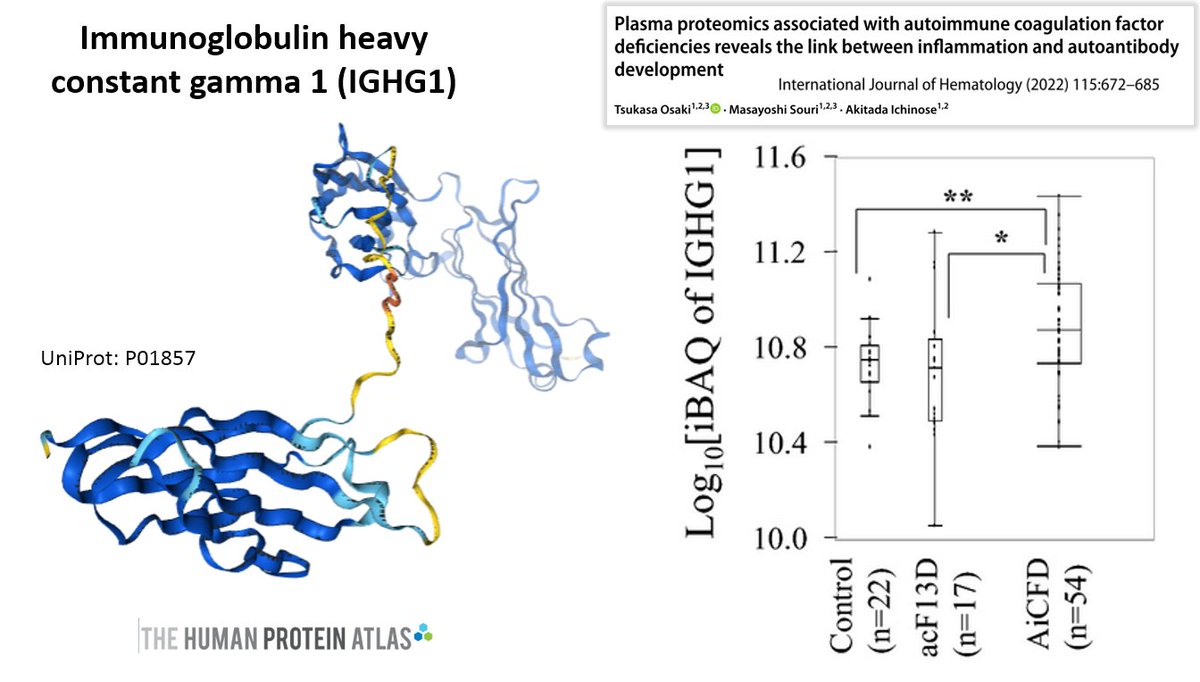
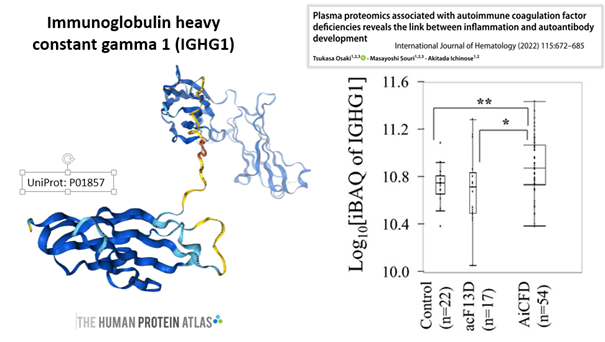
Among the other proteins found in the clots reported by Hirschman, the immunoglobulin heavy constant gamma 1 protein (IGHG1) showed a relatively high abundance.
IGHG1 is associated with an immunological and inflammatory pathway [1], is expressed in COVID-19 [2], is abundant in platelets from stroke patients (and interacts with platelet surface receptors) [3], is increased in brain tissue from Alzheimer's patients [4], is involved in cancer [5,6,7], is upregulated in autoimmune coagulation factor deficiency (AiCFD) (characterised by sudden excessive bleeding due to autoantibodies against coagulation factors) [8].
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[5]
[6]
[7]
[8] ashpublications.org/blood/article/…
cell.com/immunity/fullt…
journals.plos.org/plosone/articl…
nature.com/articles/s4159…
tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.10…
onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.11…
link.springer.com/article/10.118…
link.springer.com/article/10.100…
Among the other proteins found in the clots reported by Hirschman, the immunoglobulin heavy constant gamma 1 protein (IGHG1) showed a relatively high abundance.
IGHG1 is associated with an immunological and inflammatory pathway [1], is expressed in COVID-19 [2], is abundant in platelets from stroke patients (and interacts with platelet surface receptors) [3], is increased in brain tissue from Alzheimer's patients [4], is involved in cancer [5,6,7], is upregulated in autoimmune coagulation factor deficiency (AiCFD) (characterised by sudden excessive bleeding due to autoantibodies against coagulation factors) [8].
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[5]
[6]
[7]
[8] ashpublications.org/blood/article/…
cell.com/immunity/fullt…
journals.plos.org/plosone/articl…
nature.com/articles/s4159…
tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.10…
onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.11…
link.springer.com/article/10.118…
link.springer.com/article/10.100…
(10/n)
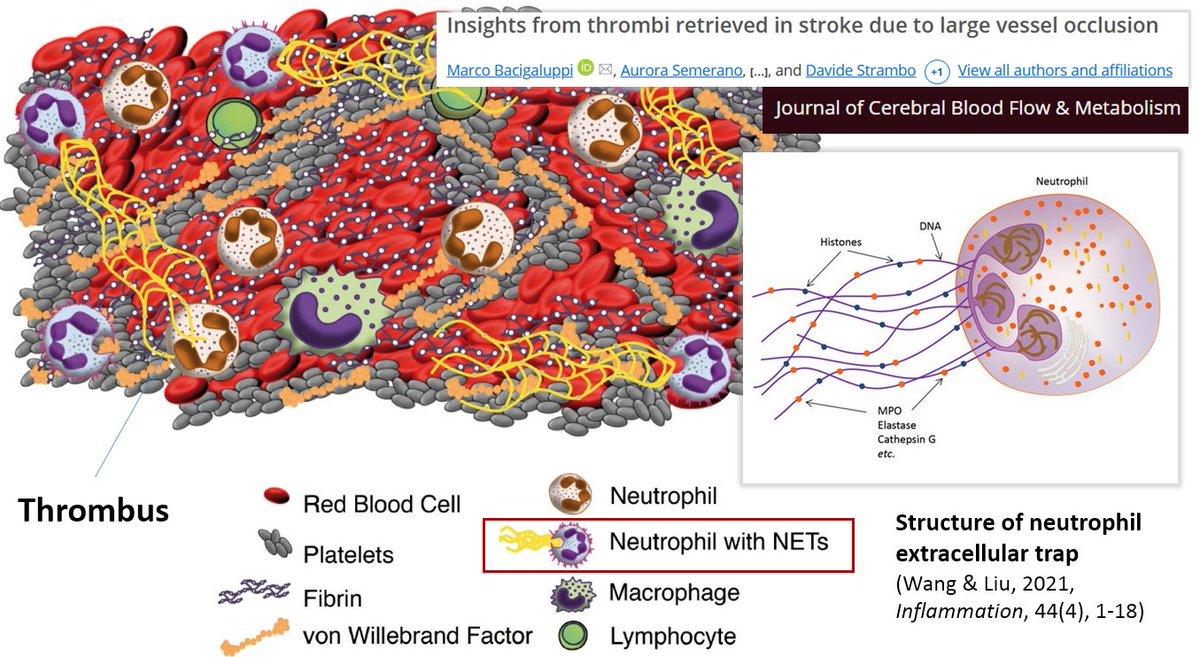
The relatively high concentration of myeloperoxidase (MPO) is also interesting.
MPO is mainly released by neutrophils and is an important component of the innate immune system.
MPO is required for the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) [1].
Circulating MPO-DNA complexes are a marker for NETs levels and are associated with cardiovascular risk factors [2].
NETs promote thrombus formation and can "abnormally activate the coagulation pathway and participate in the formation of pathological thrombi" [3].
NETs are part of blood clots (to varying degrees) [4, 5, 6].
The SARS-CoV-2 spike protein alone can induce neutrophil activation and NETosis [7,8].
The formation of NETs (NETosis) is also likely to play a role in the formation of the white clots observed by embalmers.
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[5]
[6]
[7]
[8] pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20974672/
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
journals.sagepub.com/stoken/default…
journals.sagepub.com/stoken/default…
onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.10…
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
The relatively high concentration of myeloperoxidase (MPO) is also interesting.
MPO is mainly released by neutrophils and is an important component of the innate immune system.
MPO is required for the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) [1].
Circulating MPO-DNA complexes are a marker for NETs levels and are associated with cardiovascular risk factors [2].
NETs promote thrombus formation and can "abnormally activate the coagulation pathway and participate in the formation of pathological thrombi" [3].
NETs are part of blood clots (to varying degrees) [4, 5, 6].
The SARS-CoV-2 spike protein alone can induce neutrophil activation and NETosis [7,8].
The formation of NETs (NETosis) is also likely to play a role in the formation of the white clots observed by embalmers.
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[5]
[6]
[7]
[8] pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20974672/
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
journals.sagepub.com/stoken/default…
journals.sagepub.com/stoken/default…
onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.10…
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
(11/n) A few more observations about the proteins found in the clots.
Vitronectin (VN).
This is a glycoprotein released by the liver and activated platelets.
It „acts as a biological ‘glue’ and is a key regulator of mammalian tissue repair and remodelling activity“ as well as a „master controller of the extracellular environment“ [1].
It is involved in clot formation and stabilizes clots in the arteries and arterioles [2-4] by binding to activated platelets and supporting platelet aggregation [5,6]. However, it also has anti-coagulant activity by inhibiting thrombin-fibrinogen interactions and inhibiting platelet-platelet interactions [7].
An important paper published earlier this year by Uhl et al. [8], it could be demonstrated that VN plays an important role in microvascular immunothrombotic dysregulation: „VN accumulates in the microvasculature during systemic inflammation, where this matricellular protein establishes a dense molecular network. In this manner, it supports interactions of platelets, immune cells, and endothelial cells through the platelet surface receptor GPIIb/IIIa, thus effectively promoting immunothrombosis.“
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[5]
[6]
[7]
[8] iubmb.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.10…
ashpublications.org/blood/article/…
ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.11…
sciencedirect.com/science/articl…
jci.org/articles/view/…
ashpublications.org/blood/article/…
ashpublications.org/blood/article/…
frontiersin.org/journals/immun…
Vitronectin (VN).
This is a glycoprotein released by the liver and activated platelets.
It „acts as a biological ‘glue’ and is a key regulator of mammalian tissue repair and remodelling activity“ as well as a „master controller of the extracellular environment“ [1].
It is involved in clot formation and stabilizes clots in the arteries and arterioles [2-4] by binding to activated platelets and supporting platelet aggregation [5,6]. However, it also has anti-coagulant activity by inhibiting thrombin-fibrinogen interactions and inhibiting platelet-platelet interactions [7].
An important paper published earlier this year by Uhl et al. [8], it could be demonstrated that VN plays an important role in microvascular immunothrombotic dysregulation: „VN accumulates in the microvasculature during systemic inflammation, where this matricellular protein establishes a dense molecular network. In this manner, it supports interactions of platelets, immune cells, and endothelial cells through the platelet surface receptor GPIIb/IIIa, thus effectively promoting immunothrombosis.“
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[5]
[6]
[7]
[8] iubmb.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.10…
ashpublications.org/blood/article/…
ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.11…
sciencedirect.com/science/articl…
jci.org/articles/view/…
ashpublications.org/blood/article/…
ashpublications.org/blood/article/…
frontiersin.org/journals/immun…
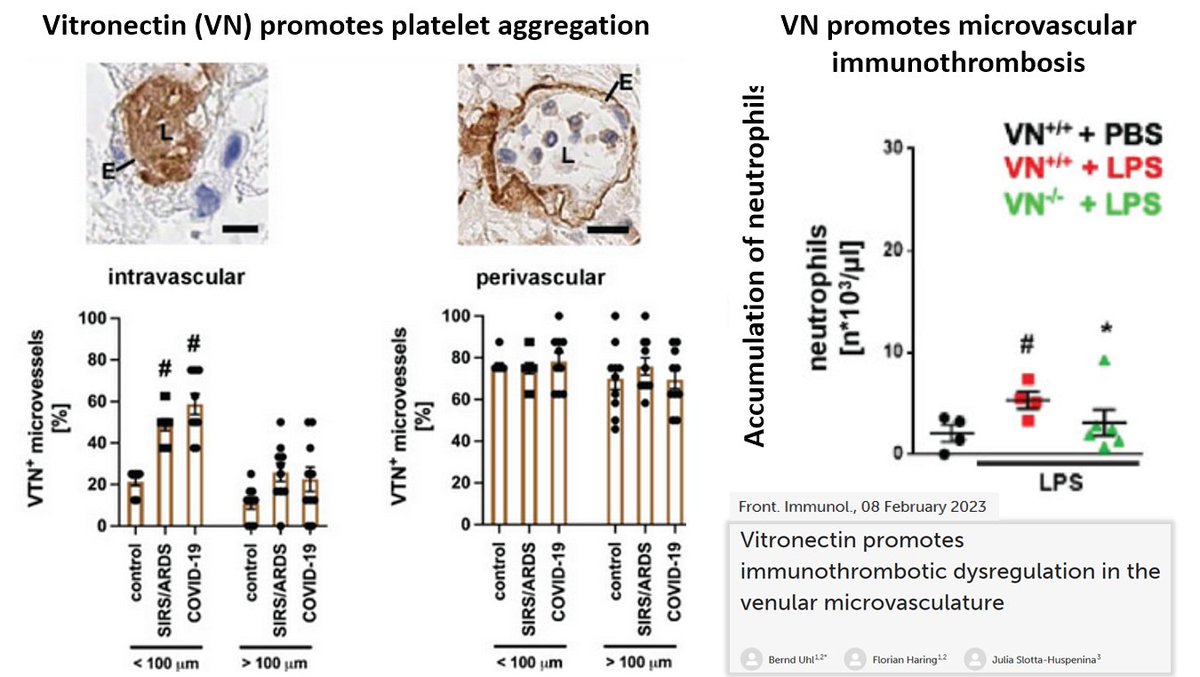
(12/n) Uhl et al. [1] showed that:
- VN accumulates in the thrombotic microvasculature during systemic inflammation
- VN promotes microvascular immunothrombosis in systemic inflammation
- Microvascular immunothrombosis is controlled by the VN receptor CD41/CD61.
- VN promotes platelet aggregation via CD41/61 in immunothrombosis of the venular microvasculature by cross-linking activated platelets through GPIIb/IIIa.
- Binding of VN to its interaction partner PAI-1 „increases the inhibitory potential of this protease inhibitor to compromise plasmin-dependent fibrin degradation elicited by urokinase-type or tissue plasminogen activator in fibrinolysis“
[1] frontiersin.org/journals/immun…
- VN accumulates in the thrombotic microvasculature during systemic inflammation
- VN promotes microvascular immunothrombosis in systemic inflammation
- Microvascular immunothrombosis is controlled by the VN receptor CD41/CD61.
- VN promotes platelet aggregation via CD41/61 in immunothrombosis of the venular microvasculature by cross-linking activated platelets through GPIIb/IIIa.
- Binding of VN to its interaction partner PAI-1 „increases the inhibitory potential of this protease inhibitor to compromise plasmin-dependent fibrin degradation elicited by urokinase-type or tissue plasminogen activator in fibrinolysis“
[1] frontiersin.org/journals/immun…
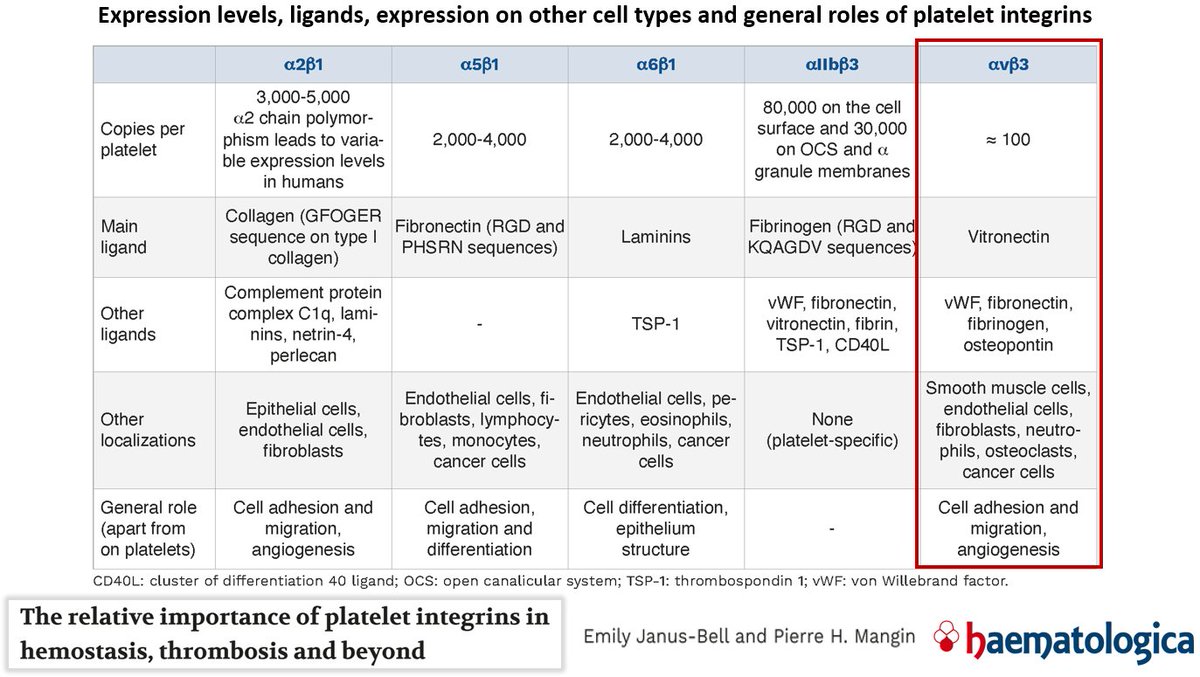
(13/n)
Interestingly, the SARS-CoV-2 spike arginylglycylaspartic acid (RGD) motif (i.e. the arginine/glycine/aspartic acid amino acid sequence) is similar to that of VN. The RGD motif enables binding to ingerins. (Note: all coronavirus predecessors lack the RGD motif, i.e. it is a specific feature of SARS-CoV-2. SARS-CoV-2 binds to ACE2 and to αVβ3).
The integrin αVβ3 is highly expressed in the endothelium and the SARS-CoV-2 protein has been shown to be able to bind to it [1]. Binding to this ingerin in the epithelium triggers significant endothelial dysregulation, resulting in loss of barrier integrity.
The αvβ3 integrin is also a vitronectin receptor [2], promotes VN gene expression [3] and mediates platelet/endothelium adhesion [4].
Activated integrin αvβ3 in combination with fibronectin also promotes clot invasion and metastasis [5].
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[5] journals.plos.org/plosone/articl…
sciencedirect.com/science/articl…
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21433063/
aacrjournals.org/cancerres/arti…
ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.11…
Interestingly, the SARS-CoV-2 spike arginylglycylaspartic acid (RGD) motif (i.e. the arginine/glycine/aspartic acid amino acid sequence) is similar to that of VN. The RGD motif enables binding to ingerins. (Note: all coronavirus predecessors lack the RGD motif, i.e. it is a specific feature of SARS-CoV-2. SARS-CoV-2 binds to ACE2 and to αVβ3).
The integrin αVβ3 is highly expressed in the endothelium and the SARS-CoV-2 protein has been shown to be able to bind to it [1]. Binding to this ingerin in the epithelium triggers significant endothelial dysregulation, resulting in loss of barrier integrity.
The αvβ3 integrin is also a vitronectin receptor [2], promotes VN gene expression [3] and mediates platelet/endothelium adhesion [4].
Activated integrin αvβ3 in combination with fibronectin also promotes clot invasion and metastasis [5].
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[5] journals.plos.org/plosone/articl…
sciencedirect.com/science/articl…
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21433063/
aacrjournals.org/cancerres/arti…
ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.11…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh