
How to get URL link on X (Twitter) App


 Primary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis can be diagnosed in patients with:
Primary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis can be diagnosed in patients with:
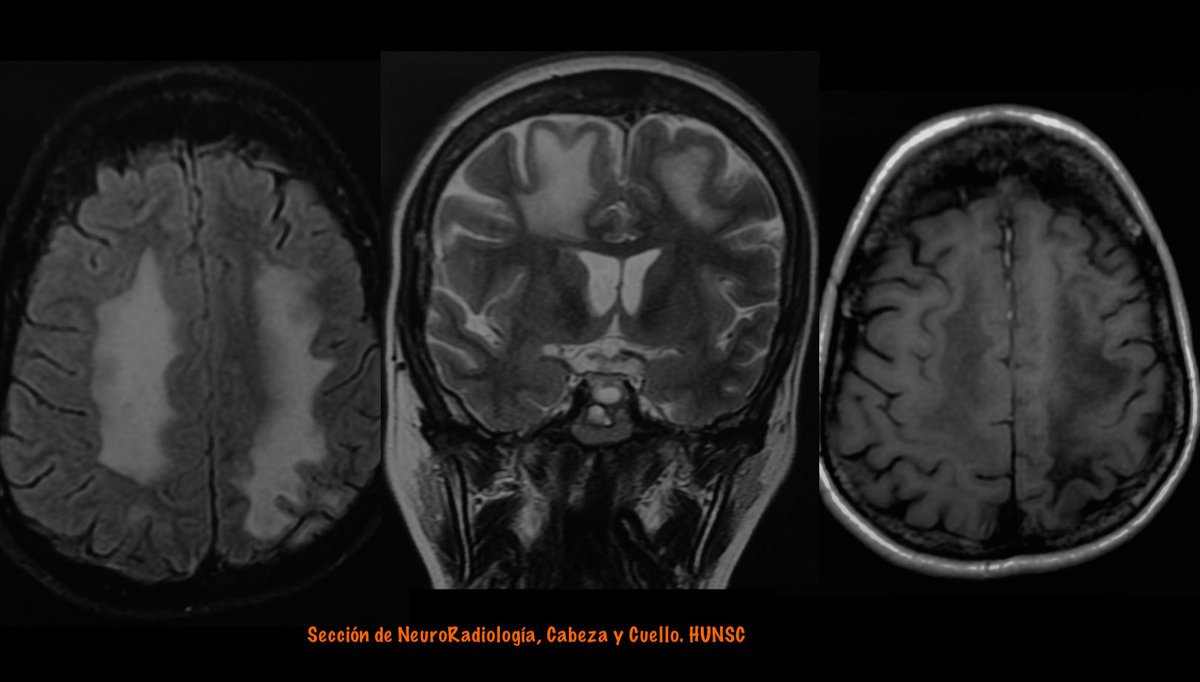
 Right side:
Right side:

 Usually have no clinical significance.
Usually have no clinical significance.


 A: Meningioma
A: Meningioma


 Cytotoxic edema
Cytotoxic edema

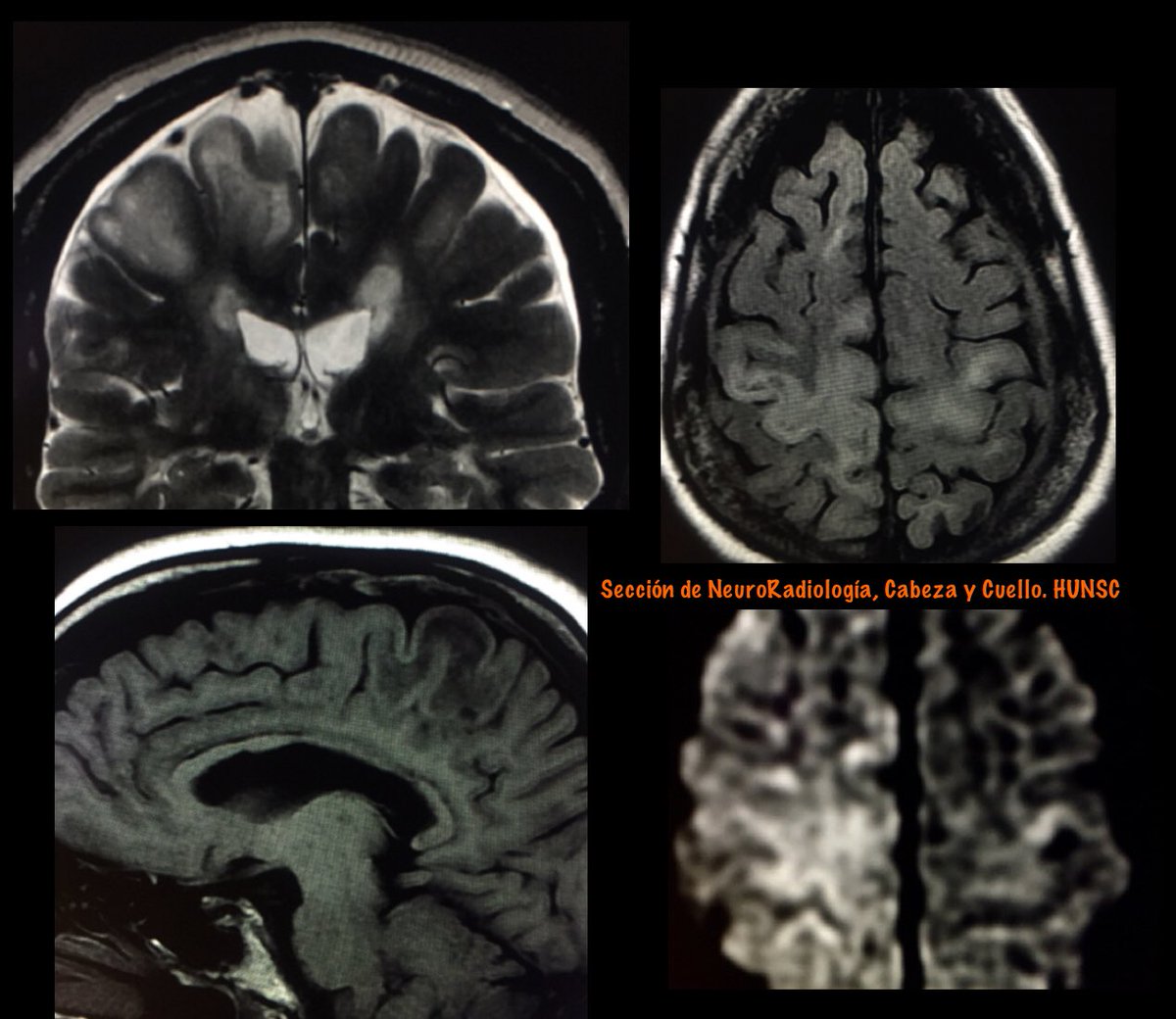
 Features favoring PML over MS (as proposed by Yousry et al) are the following:
Features favoring PML over MS (as proposed by Yousry et al) are the following: 