Short Thread - Not farmers but water management causes cropfires
Public Health Emergency declared in #Delhi due to #AirPollution
It's not just Delhi but many parts of #NorthIndia are affected by it as shown by Himawari Satellite
#DelhiAirQuality #DelhiChokes #DelhiPollution
Public Health Emergency declared in #Delhi due to #AirPollution
It's not just Delhi but many parts of #NorthIndia are affected by it as shown by Himawari Satellite
#DelhiAirQuality #DelhiChokes #DelhiPollution
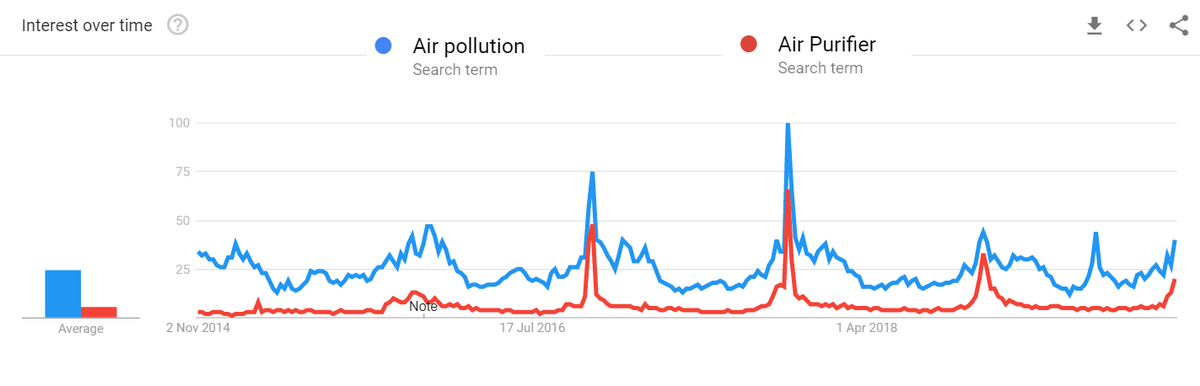
Like always Air Pollution becomes a topic of discussion when Delhi is facing it during crop fire season and it's eventually forgotten. Interestingly people also search for #AirPurifiers when #AirPollution also trends as shown in Google Search Trends 
Along with private transport, industrial (including construction), power plants, Crop fires also play an important role in Delhi's pollution spikes.
Animation shows crop fires in #Punjab, #Haryana this season (VIIRS Data)
But are farmers to blame?
Animation shows crop fires in #Punjab, #Haryana this season (VIIRS Data)
But are farmers to blame?
Crop fires' root cause is with our water management and crop selection practices (which themselves go back to green revolution era). Ever since green revolution, we have been planting more and more water intensive crops all over India. Punjab, Haryana are no different. 

In order to prevent water depletion, government adjusted irrigation practices. This led farmers to plant these water intensive crops in quick succession. To clear the land, farmers are resorting to crop fires.
Satellite images from @CopernicusEU @sentinel_hub
Satellite images from @CopernicusEU @sentinel_hub

Hence to address the #cropfires issue, we have to address our irrigation and water management issues which have been plaguing our country in different forms.
Companies like @Flipkart , @amazonIN @amazon can procure the stubble for packaging and reduce the burden a bit too.
Companies like @Flipkart , @amazonIN @amazon can procure the stubble for packaging and reduce the burden a bit too.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh




















