In India, We need to work on #PoliceReform asap, #Police being a key player to ensure #socialjustice
The population is rising rapidly, yet we are facing acute shorts of Police personnel in all states of India.
I'll try to summarize issues being faced by every state police here
The population is rising rapidly, yet we are facing acute shorts of Police personnel in all states of India.
I'll try to summarize issues being faced by every state police here

Shortage of Staff
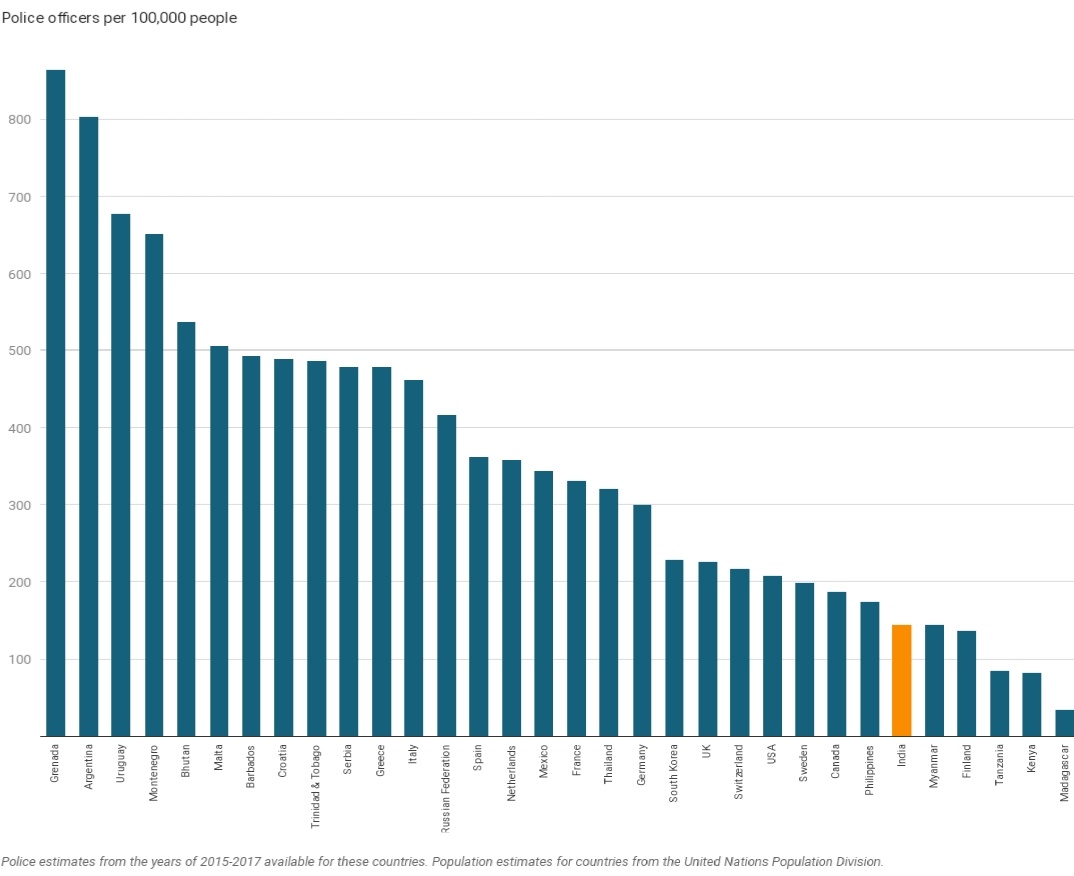
The sanctioned strength of the police across states is around 2.8 million, but only 1.9 million police officers are employed
UN recommended standard is 222 police per lakh persons v/s 137 in India
#Tweet4Bharat #socialjustice
The sanctioned strength of the police across states is around 2.8 million, but only 1.9 million police officers are employed
UN recommended standard is 222 police per lakh persons v/s 137 in India
#Tweet4Bharat #socialjustice
Faulty Promotion Policy
Max of the state police comprises of constabulary (80-85%)
The Police functioning rest on their Shoulders, are typically promoted once during the Service, normally retiring as head constables.
This weakens their will to perform well.
Max of the state police comprises of constabulary (80-85%)
The Police functioning rest on their Shoulders, are typically promoted once during the Service, normally retiring as head constables.
This weakens their will to perform well.

Crime/lakh population has increased multifold. The convictions however have been low.
Law Commission observed that a major reason behind this is the poor quality of investigation.
Why poor quality because the Police is understaffed and each member has to perform several jobs
Law Commission observed that a major reason behind this is the poor quality of investigation.
Why poor quality because the Police is understaffed and each member has to perform several jobs

Encroachment
2 ARC noted the Politicians have used police forces for personal & political reasons. Which in turn affects the L&O duty of police.
It is necessary that the scope of the political executive’s control must be limited under law.
2 ARC noted the Politicians have used police forces for personal & political reasons. Which in turn affects the L&O duty of police.
It is necessary that the scope of the political executive’s control must be limited under law.

primary role of Police is to uphold & enforce laws, investigate crimes & ensure security for people.
In a large country like India, police needs to be well-equipped, in terms of
Personnel
Weaponry
Forensics
Communication &
Transport Support, to perform their role well
In a large country like India, police needs to be well-equipped, in terms of
Personnel
Weaponry
Forensics
Communication &
Transport Support, to perform their role well

Funds
The CAG found shortages in weaponry with police across India.
Rajasthan and West Bengal had shortages of 75% and 71% in required weaponry with the state police
@BPRDIndia noted a 30.5% deficiency in stock of required vehicles (2,35,339 vehicles) with Police forces
The CAG found shortages in weaponry with police across India.
Rajasthan and West Bengal had shortages of 75% and 71% in required weaponry with the state police
@BPRDIndia noted a 30.5% deficiency in stock of required vehicles (2,35,339 vehicles) with Police forces

Underutilisation of Funds
The Reports have highlighted that the funds dedicated for modernisation of infrastructure of Police forces are typically not utilised fully.
On an act of the total funds only 15-20% of such funds were used by the states.
The Reports have highlighted that the funds dedicated for modernisation of infrastructure of Police forces are typically not utilised fully.
On an act of the total funds only 15-20% of such funds were used by the states.

Environment
In it's 1st Report, National Police Commission (1979) highlighted the Importance of providing housing to the constabulary & others as well to improve their efficiency & also as an incentive to accept remote postings
Condition of Police housing however is not hidden

In it's 1st Report, National Police Commission (1979) highlighted the Importance of providing housing to the constabulary & others as well to improve their efficiency & also as an incentive to accept remote postings
Condition of Police housing however is not hidden
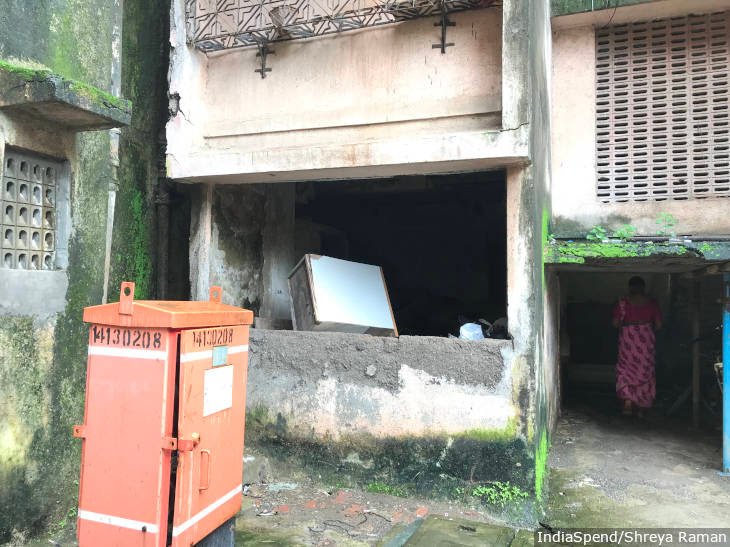
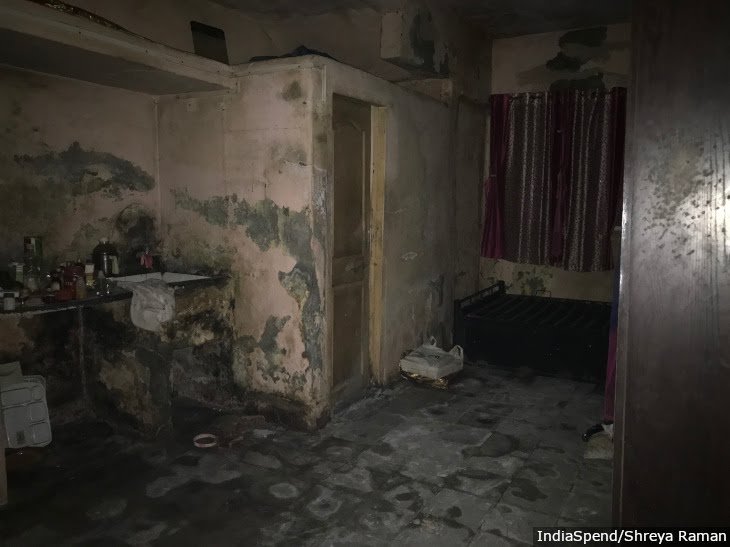


In the Urban areas, house rent is high and adequate accommodation may not be available in the immediate vicinity of the police stations, which affects their operational efficiency
With already being underpaid & overburdened with work, a few become what we call 'rotten apple'
With already being underpaid & overburdened with work, a few become what we call 'rotten apple'

Crime investigation requires special skill & training along with adequate forensic capabilities & infrastructure
Report No. 239 of the Law commission highlights state police are understaffed and overburdened with task other than their primary responsibility.
Report No. 239 of the Law commission highlights state police are understaffed and overburdened with task other than their primary responsibility.

The 14th Report (Vol 2) of the Law Commission has suggested the states to have their own specialized investigation units & at all costs, these units should not ordinarily be diverted for other duties. 

During a 2010 study by the MHA while preparing the Forensic Perspective Plan 2010, it was found,
1. The forensic labs are short of funds & qualified staff
2. There is indiscriminate referencing of cases to these labs resulting in high pendency
1. The forensic labs are short of funds & qualified staff
2. There is indiscriminate referencing of cases to these labs resulting in high pendency

Another big concern that emerged by the Audit Report (Social, Economic, Revenue and General Sectors) of the CAG were,
1. There were 40%-50% vacancies in key segments such as radio operators, technicians
2. Non-installation of essential infrastructure (RSU & gen sets)
1. There were 40%-50% vacancies in key segments such as radio operators, technicians
2. Non-installation of essential infrastructure (RSU & gen sets)

Community Policing
Police needs the confidence, cooperation & support of the community to prevent crime.
It rely on members of the community to be informers & witnesses in any crime investigation.
Police needs the confidence, cooperation & support of the community to prevent crime.
It rely on members of the community to be informers & witnesses in any crime investigation.

The 2nd ARC report however States that the police-public relations are in an unsatisfactory state because people view the police as Corrupt, Inefficient, Politically partisan and Unresponsive.
It clearly highlights a wide Communication gap between the Police & Public.
It clearly highlights a wide Communication gap between the Police & Public.

Community policing requires the police to work with the community.
It may include,
1. Patrolling by the police for non-emergency interactions with the public
2. Community based crime prevention
3. Coming up with mechanisms for grassroots feedback from the community
It may include,
1. Patrolling by the police for non-emergency interactions with the public
2. Community based crime prevention
3. Coming up with mechanisms for grassroots feedback from the community

Some of Community Policing Initiatives by State police are,
Kerala ‘Janamaithri Suraksha Project’
Rajasthan ‘Joint Patrolling Committees’
Assam ‘Meira Paibi’
West Bengal ‘Community Policing Project’
Andhra Pradesh ‘Maithri
Maharashtra ‘Mohalla Committees’
Kerala ‘Janamaithri Suraksha Project’
Rajasthan ‘Joint Patrolling Committees’
Assam ‘Meira Paibi’
West Bengal ‘Community Policing Project’
Andhra Pradesh ‘Maithri
Maharashtra ‘Mohalla Committees’
Directions of the Supreme Court in @singh_prakash vs Union of India case 1996 were, 

However We are yet to see complete and total implementation of these directives in India.
It is good to read about recent developments towards the much talked about #PoliceReforms in India.
Under @HMOIndia India is looking to achieve a fresh change in the system of Policing.
It is good to read about recent developments towards the much talked about #PoliceReforms in India.
Under @HMOIndia India is looking to achieve a fresh change in the system of Policing.

The Current govt seems to walking on a path promised by their leaders.
An umbrella scheme of Modernisation of Police forces was launched in 2017 for a period of 3 years
Its target areas for improvement were,
CCTNS
ISPW
E-Prison
Forensic Infra & Equipment
Special focus
LWE
NE

An umbrella scheme of Modernisation of Police forces was launched in 2017 for a period of 3 years
Its target areas for improvement were,
CCTNS
ISPW
E-Prison
Forensic Infra & Equipment
Special focus
LWE
NE


The @HMOIndia have repeatedly said on various platforms about the need to amend the Penal & Procedure Code in order to empower the police for a wide range of Modern day challenges.
It is indeed worth applauding that MHA has begun online consultation on the same.
#PoliceReforms


It is indeed worth applauding that MHA has begun online consultation on the same.
#PoliceReforms


Why this Long thread?
What happened in #Bengaluru yesterday hints at the failure of Human intelligence network of @BlrCityPolice
Why did it fail? The very obvious reason - Ineffective/No community Policing Policy!
Identification of rioters require tech & non tech Infra
1/2
What happened in #Bengaluru yesterday hints at the failure of Human intelligence network of @BlrCityPolice
Why did it fail? The very obvious reason - Ineffective/No community Policing Policy!
Identification of rioters require tech & non tech Infra
1/2
2/2
In the previous tweets i've mentioned how our States suffer from acute shortage of both Man power as well as Resources.
This leads to delay in identification of accused who either disappears/ slip because of delay/lack of conclusive evidence.
In the previous tweets i've mentioned how our States suffer from acute shortage of both Man power as well as Resources.
This leads to delay in identification of accused who either disappears/ slip because of delay/lack of conclusive evidence.
Bengaluru represents #NewIndia
It is the center of rising expectations and the might of Indian Minds. Such incidents not only puts the city in bad light globally, it highlights the fact that India is not yet prepared to tackle the challenge of Modern day Urban Policing!
It is the center of rising expectations and the might of Indian Minds. Such incidents not only puts the city in bad light globally, it highlights the fact that India is not yet prepared to tackle the challenge of Modern day Urban Policing!
Urban Policing is a wast concept, We will discuss it some other day
But with the final tweet on this thread, I'd expect @BlrCityPolice to live up to its motto of 'Satyamev Jayate'
With mamy able Officers & Policemen, it has a big task to keep the city Secure & Peaceful, Again!
But with the final tweet on this thread, I'd expect @BlrCityPolice to live up to its motto of 'Satyamev Jayate'
With mamy able Officers & Policemen, it has a big task to keep the city Secure & Peaceful, Again!
Thank you @DevendraPai @iidlpgp for inspiring me to write this thread.
A big thanks to My friends from Policy Research Studies for their extensive work on the same.
A big thanks to My friends from Policy Research Studies for their extensive work on the same.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh









