1/14
Why doesn't daptomycin treat pneumonia?
The answer also explains why dapto raises serum CK levels.
#medtwitter #tweetorial
Why doesn't daptomycin treat pneumonia?
The answer also explains why dapto raises serum CK levels.
#medtwitter #tweetorial
2/
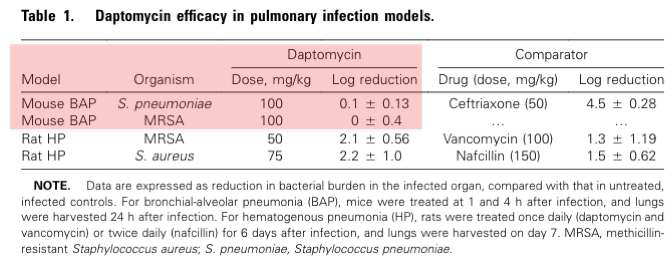
First let's establish that daptomycin (bactericidal against gram positives) lacks efficacy in treating lung infections.
⚡️ In this study with mouse lungs, daptomycin didn't reliably kill strep pneumo or MRSA, even at high doses of the drug.
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15898002/
First let's establish that daptomycin (bactericidal against gram positives) lacks efficacy in treating lung infections.
⚡️ In this study with mouse lungs, daptomycin didn't reliably kill strep pneumo or MRSA, even at high doses of the drug.
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15898002/
3/
What about lung infections in humans?
Compared to ceftriaxone, daptomycin had lower cure rates for treatment of community acquired pneumonia (CAP).
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18444848/
What about lung infections in humans?
Compared to ceftriaxone, daptomycin had lower cure rates for treatment of community acquired pneumonia (CAP).
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18444848/

4/
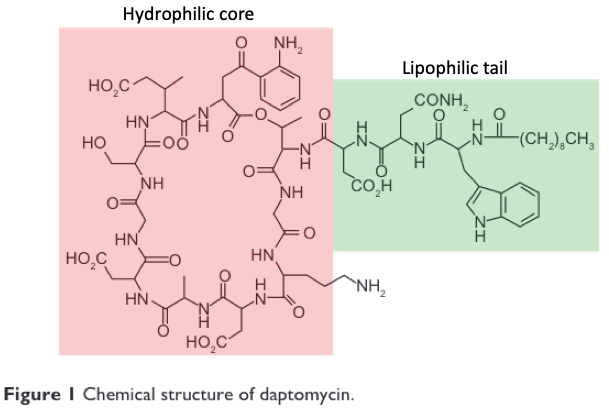
Next we need to review daptomycin's structure and mechanism of action.
💡 It's structure consists of a hydrophilic lipoprotein core with a lipophilic, fat-soluble “tail”.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
Next we need to review daptomycin's structure and mechanism of action.
💡 It's structure consists of a hydrophilic lipoprotein core with a lipophilic, fat-soluble “tail”.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
5/
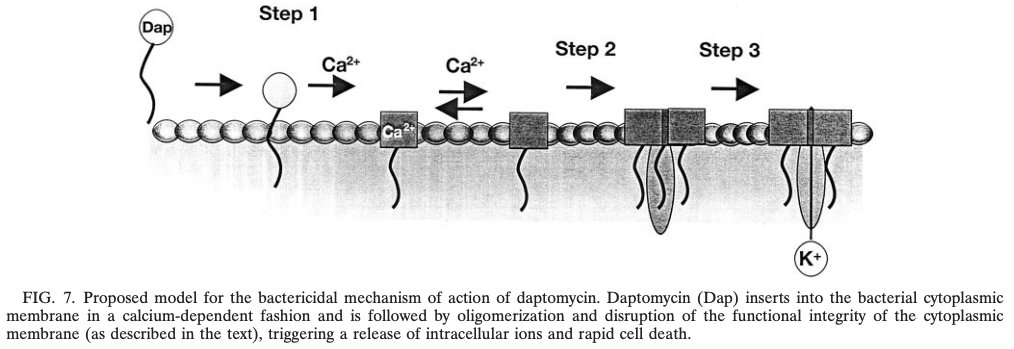
As a lipopeptide with a fat-soluble tail, daptomycin inserts into bacterial membranes (and cell walls) in the presence of calcium.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
As a lipopeptide with a fat-soluble tail, daptomycin inserts into bacterial membranes (and cell walls) in the presence of calcium.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…

6/
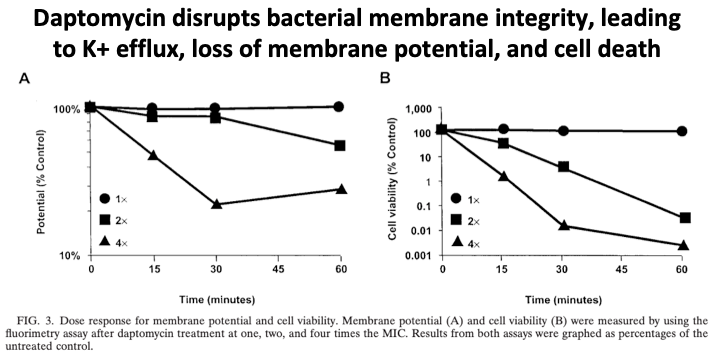
Once inserted into a bacterium's cellular membrane, daptomycin disrupts its integrity.
🔑 This disruption leads to K+ efflux out of the cell and loss of membrane potential, which causes failure of cellular machinery and eventually cell death.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…

Once inserted into a bacterium's cellular membrane, daptomycin disrupts its integrity.
🔑 This disruption leads to K+ efflux out of the cell and loss of membrane potential, which causes failure of cellular machinery and eventually cell death.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
7/
Now that we understand how daptomycin works, let's learn why it doesn't work in the lungs.
You may have heard that it has something to do with pulmonary surfactant...
Now that we understand how daptomycin works, let's learn why it doesn't work in the lungs.
You may have heard that it has something to do with pulmonary surfactant...
8/
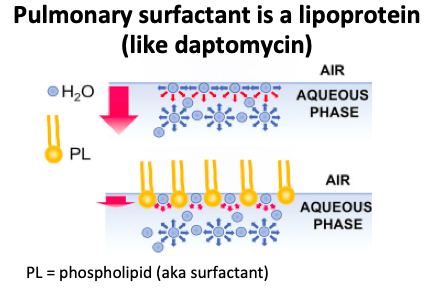
(Very) brief pulmonary surfactant review:
Surfactant, similar to daptomycin, is a lipoprotein with fat and water soluble components. It reduces surface tension at the air-liquid interface in the lung and prevents alveolar collapse.
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30552091/
(Very) brief pulmonary surfactant review:
Surfactant, similar to daptomycin, is a lipoprotein with fat and water soluble components. It reduces surface tension at the air-liquid interface in the lung and prevents alveolar collapse.
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30552091/
9/
It turns out that adding surfactant to daptomycin in vitro leads to almost immediate loss of antibacterial activity.
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15898002/
It turns out that adding surfactant to daptomycin in vitro leads to almost immediate loss of antibacterial activity.
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15898002/

10/
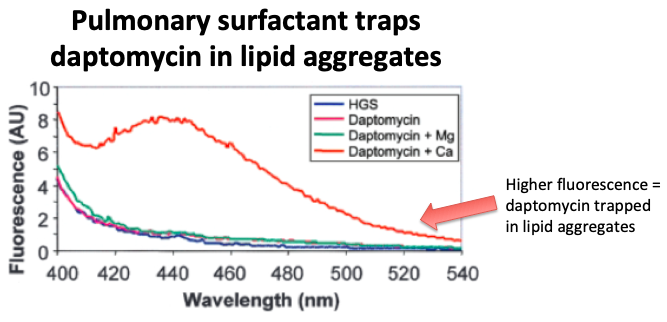
Why?
Recall that daptomycin has a hydrophobic tail that allows it to insert into/disrupt phospholipid bacterial membranes (tweets 4,5).
💥 Pulmonary surfactant instead acts as a decoy for dapto, trapping it in lipid aggregates (at least in vitro).
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15898002/
Why?
Recall that daptomycin has a hydrophobic tail that allows it to insert into/disrupt phospholipid bacterial membranes (tweets 4,5).
💥 Pulmonary surfactant instead acts as a decoy for dapto, trapping it in lipid aggregates (at least in vitro).
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15898002/
11/
We are left with the mechanism for why daptomycin is ineffective in the lungs:
Pulmonary surfactant sequesters dapto via its hydrophobic tail. This prevents access to bacterial membranes.
🔑 In effect, daptomycin's very mechanism of action precludes treatment of pneumonia.
We are left with the mechanism for why daptomycin is ineffective in the lungs:
Pulmonary surfactant sequesters dapto via its hydrophobic tail. This prevents access to bacterial membranes.
🔑 In effect, daptomycin's very mechanism of action precludes treatment of pneumonia.
12/
A final interesting correlate:
Creatine kinase (CK) elevation, and even skeletal muscle myopathy, are known complications of daptomycin therapy.
Can you think of how this might relate to its mechanism of action?
A final interesting correlate:
Creatine kinase (CK) elevation, and even skeletal muscle myopathy, are known complications of daptomycin therapy.
Can you think of how this might relate to its mechanism of action?
13/
While the cause isn't definitively known, serum CK elevation is thought to result from daptomycin-induced disruption of skeletal muscle membranes.
This is the exact same type of membrane damage that causes bacterial killing.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
While the cause isn't definitively known, serum CK elevation is thought to result from daptomycin-induced disruption of skeletal muscle membranes.
This is the exact same type of membrane damage that causes bacterial killing.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…

14/
💡Daptomycin disrupts bacterial membranes via a fat-soluble “tail”
💡It’s ineffective in lung infections b/c pulmonary surfactant traps it in lipid aggregates
💡Serum CK elevation likely results from the same mechanism (impacts on integrity of skeletal muscle membranes)
💡Daptomycin disrupts bacterial membranes via a fat-soluble “tail”
💡It’s ineffective in lung infections b/c pulmonary surfactant traps it in lipid aggregates
💡Serum CK elevation likely results from the same mechanism (impacts on integrity of skeletal muscle membranes)
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh