The @guardian has a new piece on the well known problems related to electric vehicles, solar and wind.
I think the focus on resource use and responsible mining is great. As long as we also remind ourselves that fossil fuels are worse.
theguardian.com/environment/20…
I think the focus on resource use and responsible mining is great. As long as we also remind ourselves that fossil fuels are worse.
theguardian.com/environment/20…
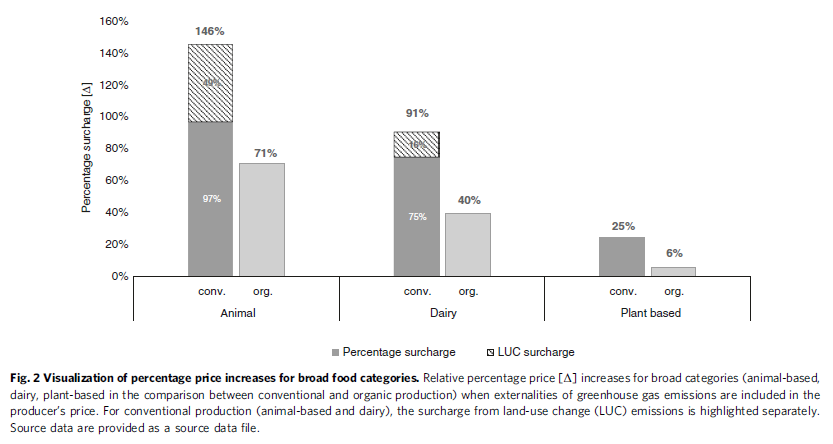
Remember that a car burns ~ 25 000 liters of fossil fuel over its lifetime. Do you really think that's better than 200 kg battery materials that's recyclable? And cobalt is also used for cleaning fossil fuel.
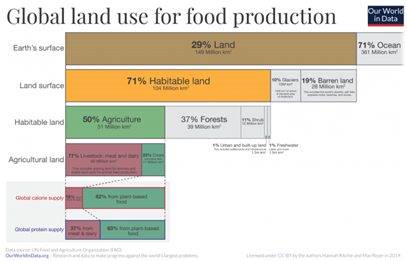
Apart from climate change the amount of ecosystem degradation, direct human suffering, conflict and corruption due to oil is much larger but that apparently generates less clicks.
doi.org/10.1111/rode.1…
doi.org/10.1111/rode.1…
Unfortunately, as it stands now, I agree with the article but for many readers this is just a reason for pearl clutching and renewables bashing before taking a ride back in a far worse fossil fueled car. Shame.
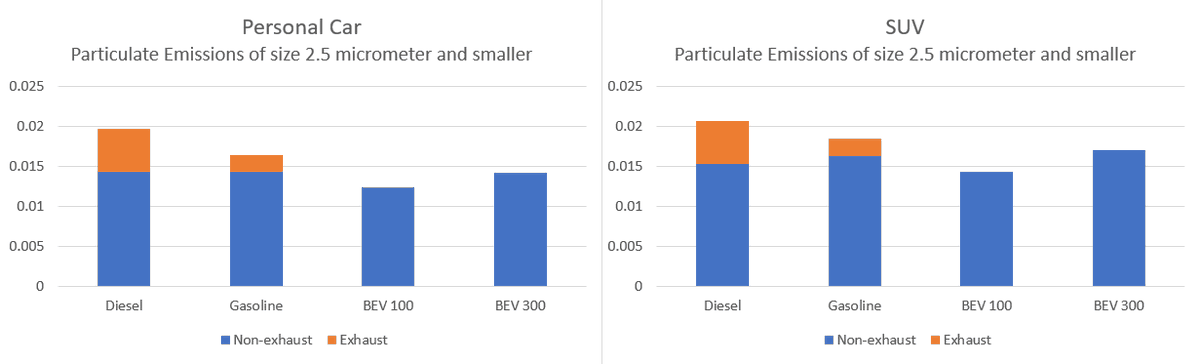
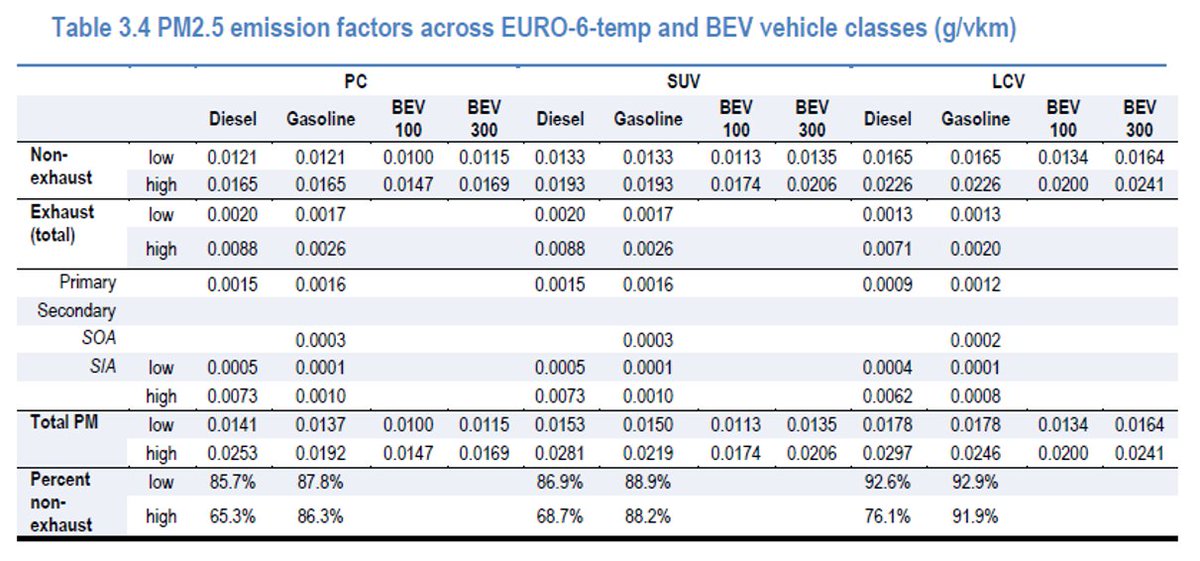
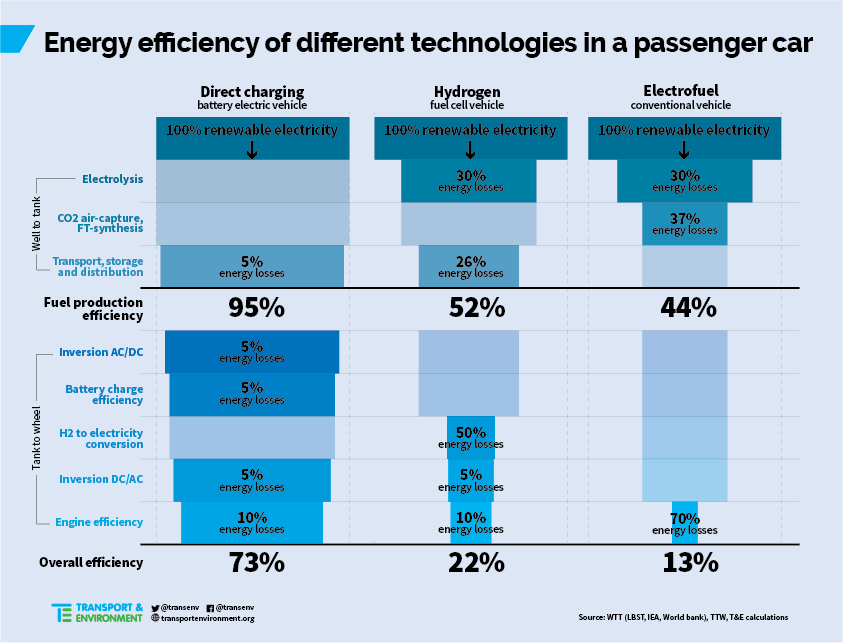
In the real world: electric vehicles cause much less greenhouse gas, energy demand, ozone, particulate matter, human toxicity and water use. But yes, a *bit* more minerals. So let's indeed mine more sustainably. But never forget fossil cars are worse.
ec.europa.eu/clima/sites/cl…
ec.europa.eu/clima/sites/cl…

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh