Globally, 2020 was the hottest year on record, effectively tying 2016, the previous record. Overall, Earth’s average temperature has risen more than 2 degrees F since the 1880s. The effects of rising temperatures are felt around the world.
go.nasa.gov/3iakW5c
go.nasa.gov/3iakW5c
2020 was a year of extremes, with record-breaking hurricane and fire seasons. Higher surface temperatures and more heat in the climate system can fuel different extreme events, directly and indirectly, like increasing tropical storm intensity.
This year, we saw record-setting fires in Australia and the western U.S., after years of high temperature and drought set the stage. Smoke from fires in both regions reached so high into the atmosphere that it formed clouds.
go.nasa.gov/396zPBt
go.nasa.gov/33oxoqO

go.nasa.gov/396zPBt
go.nasa.gov/33oxoqO


In Siberia, unusually high temperatures drove fires burning peat soil -- decomposed organic materials -- that stores a lot of carbon. Peat fires release vast amounts of carbon into the atmosphere, potentially leading to even more warming.
go.nasa.gov/3mf8fre
go.nasa.gov/3mf8fre
The Arctic region is warming three times faster than the rest of the planet. Arctic sea ice reached a near-record low extent this year.
go.nasa.gov/33LwmFH
go.nasa.gov/33LwmFH
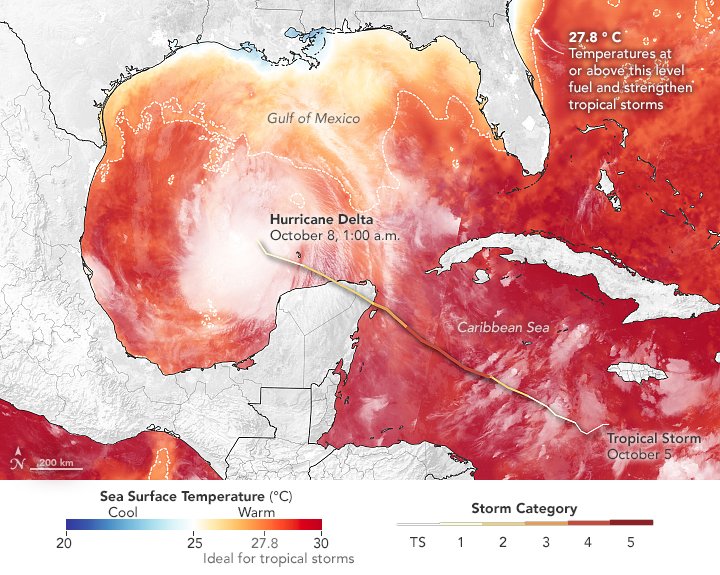
A warm Atlantic ocean helped fuel a record-breaking hurricane season, with 30 named storms. This year, a record 12 storms made landfall in the United States.
go.nasa.gov/3oxD6jq

go.nasa.gov/3oxD6jq


Heat & the energy it carries drive our planet: winds, weather, droughts, floods & more are expressions of heat. The right amount of heat even helps make life on Earth possible. But too much heat changes how our planet’s systems act.
go.nasa.gov/2XDI6rh
go.nasa.gov/2XDI6rh
We work with our partners at @NOAA to study our planet and the ways it’s changing. We also study the causes and effects of climate change from space, with a unique view of increasing carbon in the atmosphere.
https://twitter.com/NASAGISS/status/1349758978599886856?s=20
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh