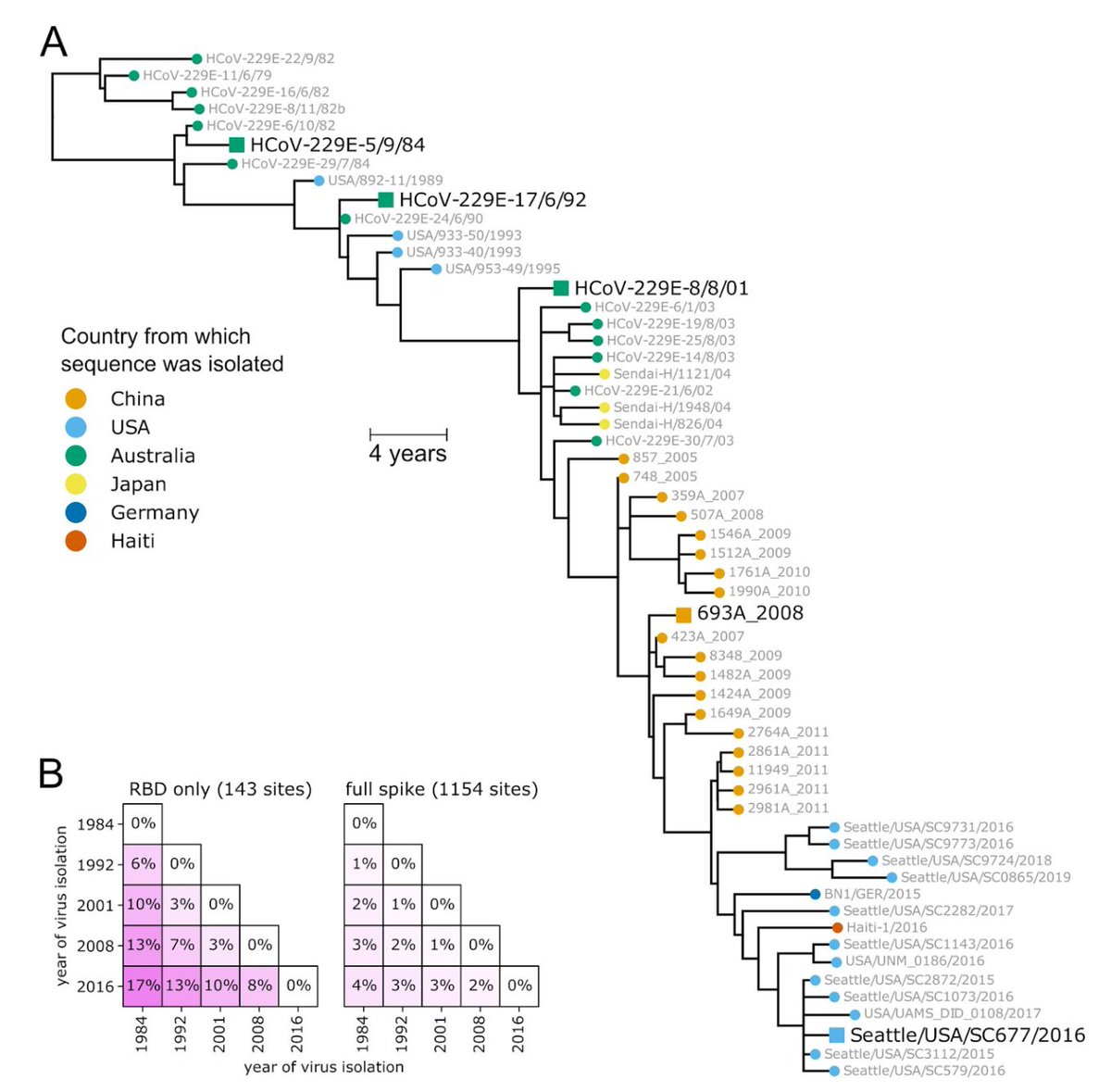
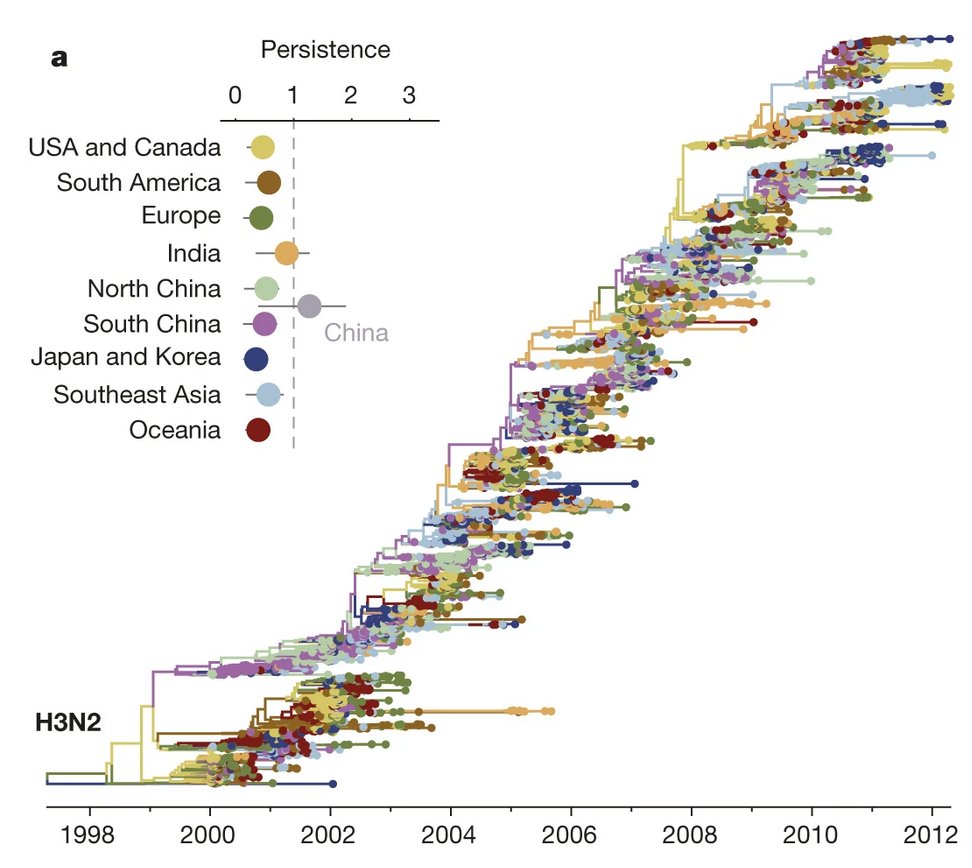
This is an interesting perspective on Taiwan (& glad it mentions data/privacy), although I'd like to see more references to what local officials were actually saying about approach in real-time, rather than what UK-based researchers later say it was: theguardian.com/world/2021/mar… 1/
E.g. from April 2020: "Covid-19 is becoming flu-like. It means that since it is highly contagious with many mild or asymptomatic cases, and can be transmitted through droplets and contaminated areas, we won’t get rid of this virus totally." telegraph.co.uk/global-health/… 2/
Taiwan has implemented several innovative, effective measures against COVID-19, but it will harm our ability to plan for the next pandemic if we don't look fully at how countries were interpreting - and acting on - available evidence in real-time. 3/
Another useful perspective on response in Taiwan (from March 2020): jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/… 4/4 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh