#Nature An exceptional view of phase transitions in non-equilibrium systems nature.com/articles/d4158…
A mathematical approach involving features called exceptional points now solves the far-reaching problem of phase transitions in certain non-equilibrium systems.
A mathematical approach involving features called exceptional points now solves the far-reaching problem of phase transitions in certain non-equilibrium systems.
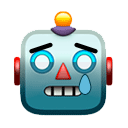
Exceptional points —locations in the parameter space of a system at which two or more modes of the system coalesce into a single mode— successfully captures the behaviour of non-reciprocal phase transitions. An example is the non-reciprocal interactions between flocking birds.
Another example: materials could be developed that exhibit one-way elasticity — that is, in which mechanical waves propagate undisturbed in one direction, but are totally reflected in the opposite direction. Devices could be engineered to produce coherent phonons.
And it might be possible to develop mechanical strain cloaking, in which a portion of a material is fully isolated from vibrations or shocks. #Nature Non-reciprocal phase transitions nature.com/articles/s4158… 

First identify a system with (i) non-reciprocal interactions and (ii) a continuous symmetry. Write down the dynamical system for the order parameter(s) V. Find a time-independent steady state Vss with spontaneously broken continuous symmetry (SSB, green regions). 

Linearize around the time-independent steady state. The linear operator (Jacobian matrix) L(V) has a vanishing eigenvalue (Goldstone mode). At the exceptional transition, the Goldstone mode collides with a damped mode. This leads to a spontaneous dynamical restoration of symmetry
All such systems are described by the evolution equation... like the Kuramoto model of synchronization or the Swift–Hohenberg model. 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh