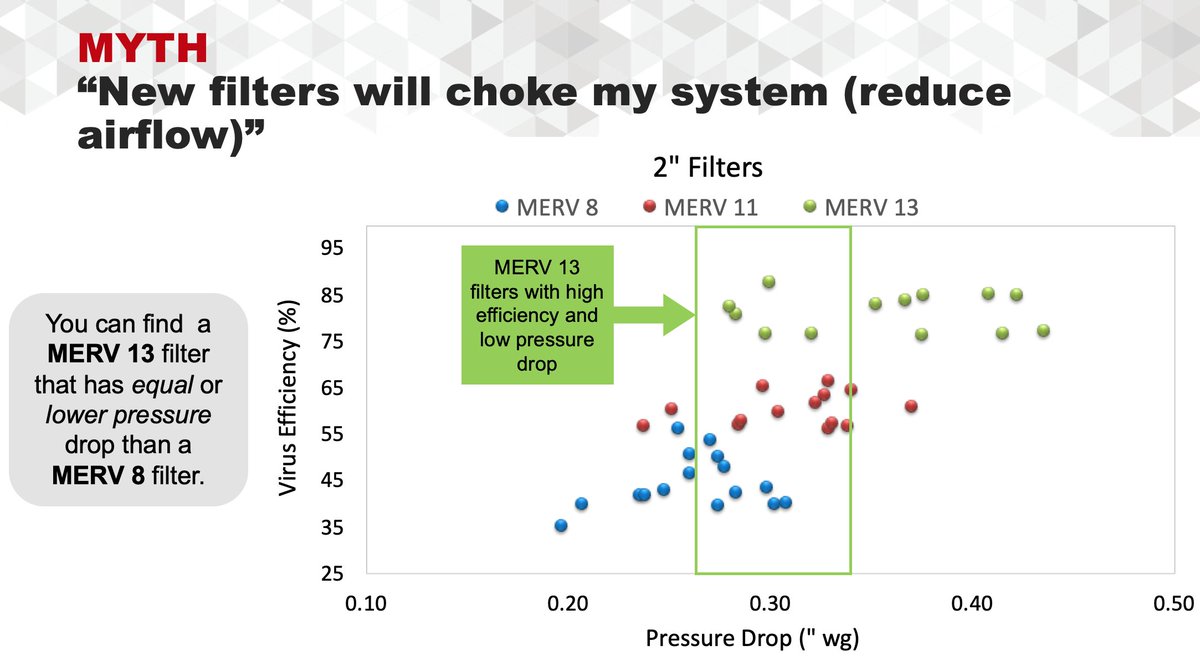
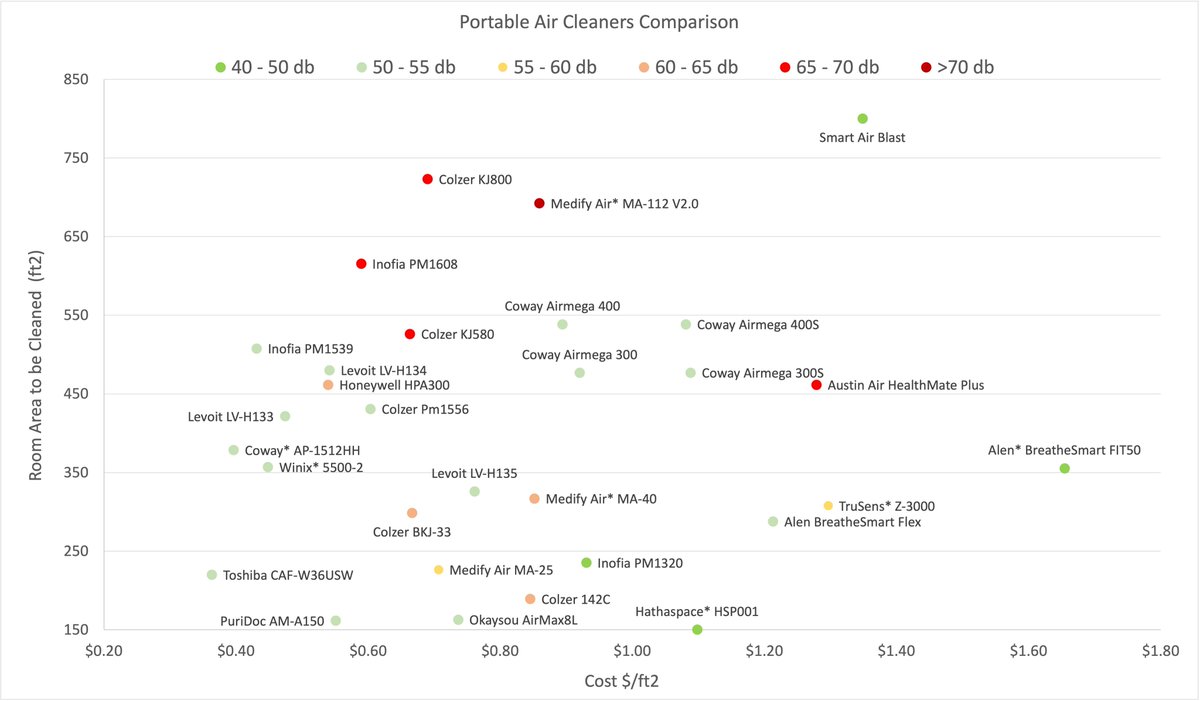
HVAC without V is a HAC(k) job
🧵 about ventilation
- Mechanical versus Natural ventilation
- ASHRAE Standard 62.1 historical rates
- Why schools are under-ventilated?
- What is the cost of outside air?
- What we should do about it?
🧵 about ventilation
- Mechanical versus Natural ventilation
- ASHRAE Standard 62.1 historical rates
- Why schools are under-ventilated?
- What is the cost of outside air?
- What we should do about it?
Note 1: According to ASHRAE Standard 62.1 (most prominent ventilation standard), ventilation is not only about outside air. Rather, it is the sum of outside air and return air that is cleaned.
In this thread, I will focus only on outside air.
In this thread, I will focus only on outside air.

Note 2: schools are either designed to have mechanical ventilation (intentional OA from HVAC unit) or natural ventilation (intentional OA through windows and doors).
Most schools in North America are mechanically ventilated (for many reasons mainly for comfort and safety).
Most schools in North America are mechanically ventilated (for many reasons mainly for comfort and safety).
Note 3: Ventilation rates from ASHRAE Standard 62.1 are minimum rates.
Every building need to comply with these rates at a minimum in order to be occupied. Buildings can not obtain certificate of occupancy without complying.
Every building need to comply with these rates at a minimum in order to be occupied. Buildings can not obtain certificate of occupancy without complying.
Mechanical Ventilat. case:
HVAC system lasts < 25 years, meaning that for old buildings HVAC was replaced > 1996.
To replace HVAC, you need a permit that shows that the new design complies with min OA rate 👇.
This means that schools have min OA (design) same or > 2019 rate.
HVAC system lasts < 25 years, meaning that for old buildings HVAC was replaced > 1996.
To replace HVAC, you need a permit that shows that the new design complies with min OA rate 👇.
This means that schools have min OA (design) same or > 2019 rate.

Natural ventilation case - 1: some schools uses natural ventilation. But this is not a slam dunk... It carefully requires designing windows, opening sizes, airflow/studying outside air conditions (three pages requirement in the standard).
Natural vent -2: It will NOT work all the time. Ventilation experts warn that “simply opening windows and doors without the use of exhaust fan, does not ensure adequate filtration – dependent on natural driving forces caused by the difference in temp wind speed."
Natural vent -3: this is why Standard 62.1 requires every natural ventilation design to have a backup mechanical ventilation design.
If the building is NOT designed for natural ventilation, opening windows will not work all the time.
If the building is NOT designed for natural ventilation, opening windows will not work all the time.
We know that schools are under-ventilated:
Lit. review By Dr. Fisk (2017) of studies with large # of classrooms: CO2 concentrations often far exceed 1000 ppm👇
OA rate was ~50% rate of Standard with some studies showing only 2 cfm/person.
Lit. review By Dr. Fisk (2017) of studies with large # of classrooms: CO2 concentrations often far exceed 1000 ppm👇
OA rate was ~50% rate of Standard with some studies showing only 2 cfm/person.

Dr. @CorsIAQ reported similar results from a 4-yr study involving 7 high schools of different ages & construction, & 46 classrooms" 

Why are schools are under-ventilated?
I wrote about this in 2018. Below are the dirty half dozens reasons to why buildings operate without ventilation and what should we do about it.
The problem applies to all buildings including schools.


I wrote about this in 2018. Below are the dirty half dozens reasons to why buildings operate without ventilation and what should we do about it.
The problem applies to all buildings including schools.



@CorsIAQ reported that each schools they tested had mechanical ventilation with capability to increase OA.
The reason why schools were under-ventilated was to save energy (energy required to condition the outside air)
The reason why schools were under-ventilated was to save energy (energy required to condition the outside air)

How much energy does outside air cost?
According to Fisk (2017), annual costs range from few dollars to max of $10 per person PER YEAR --> "small price to pay given evidence of benefits"
According to Fisk (2017), annual costs range from few dollars to max of $10 per person PER YEAR --> "small price to pay given evidence of benefits"

Minimum ventilation is key to decrease risk of transmission during COVID. Beyond COVID, there is a compelling evidence of association of increased student performance by few % to as much as 15%, reduced absence (and diseases) with ventilation (i.e., lowering indoor pollutants).
All of this to say is that schools should prioritize looking into their ventilation systems especially with the available relief money:
1) check what type of OA system (mech versus natural),
2) perform a test and balance,
3) determine maximum OA capability at worst conditions
1) check what type of OA system (mech versus natural),
2) perform a test and balance,
3) determine maximum OA capability at worst conditions
There is NO excuse!!
We have a moral obligation to protect our children.
Money is available to be used for basic and proven strategies: outside air, mech. filtration, UV.
and should NOT be spent on adding chemicals to the air (No To Ionizers, UV-PCO, O3, DHP, etc.)
We have a moral obligation to protect our children.
Money is available to be used for basic and proven strategies: outside air, mech. filtration, UV.
and should NOT be spent on adding chemicals to the air (No To Ionizers, UV-PCO, O3, DHP, etc.)
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh