Let’s talk about B.1.617. It is unlikely it will be able to evade vaccine-induced immunity. Why?
•Vaccines are polyclonal (Abs)
•Mutations compared to VOCs
•CD8+ T-cells covering 52 epitopes across the spike protein
•CD4+ T-cells covering 23 epitopes across the spike protein
•Vaccines are polyclonal (Abs)
•Mutations compared to VOCs
•CD8+ T-cells covering 52 epitopes across the spike protein
•CD4+ T-cells covering 23 epitopes across the spike protein
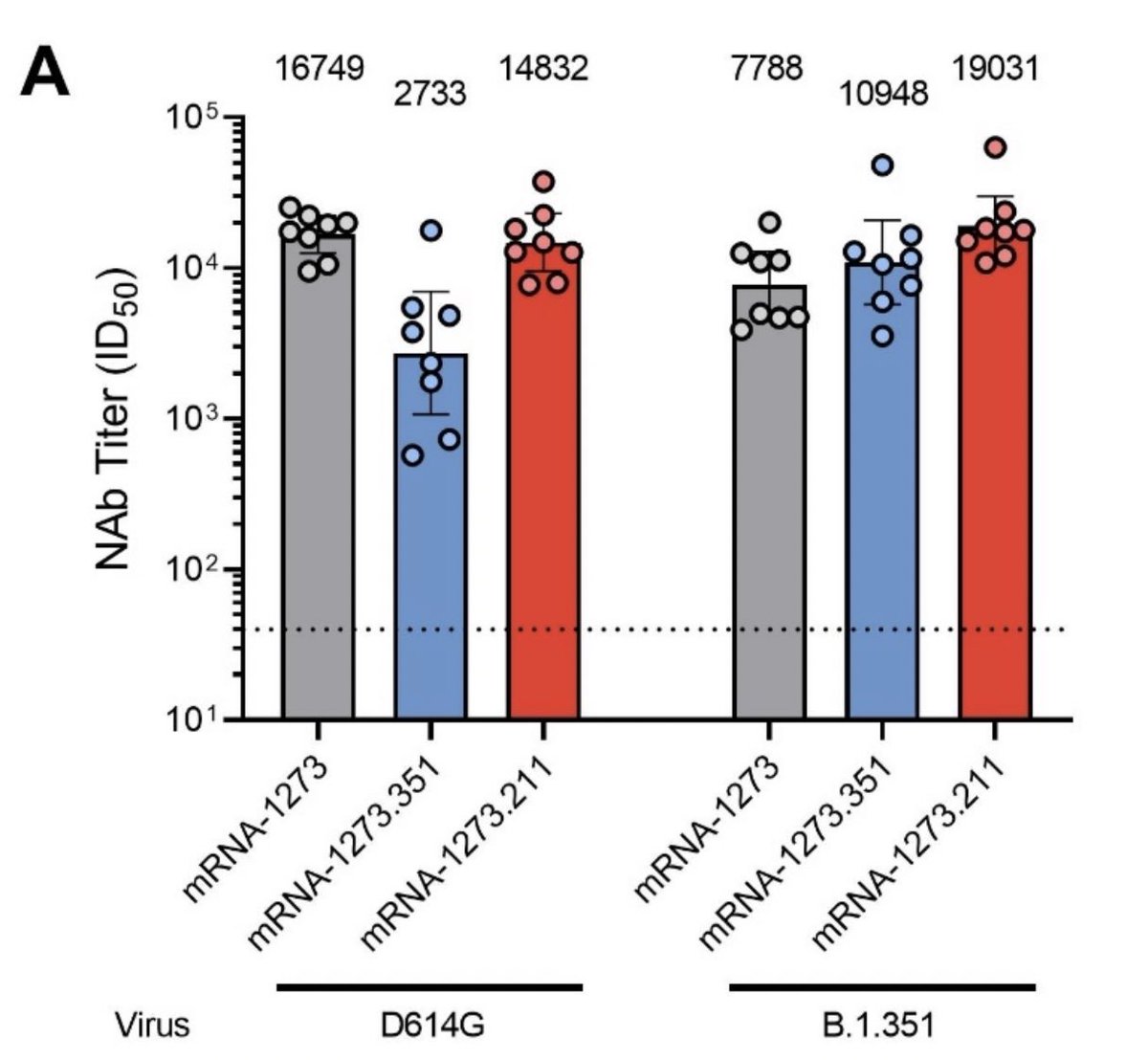
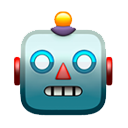
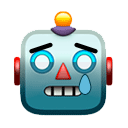
Concerning mutations, our attention is focused on E484Q and L452R. While both these mutations have shown evidence of reduced neutralization (in monoclonal antibodies mind you), we have to remember something vital: Vaccines are polyclonal! Unlike monoclonal antibody therapies,
vaccines make polyclonal antibody responses and involve T-cell responses. This means that the antibodies you make after vaccination will be able to bind the coronavirus spike in multiple places, not just one. With this in mind, it is unlikely variants will truly “escape” them.
Concerning, E484Q. Compared to E484K that we see in B.1.1.7, B.1.351 and P.1, it has not demonstrated to select for better ACE2 binding (and therefore no increased infectivity) when compared to E484K. B.1.617 is also missing N501Y, a mutation known to help increase binding
once again seen in B.1.1.7, B.1.351, and P.1. Now, concerning L452R, before you hit me with this: biorxiv.org/content/10.110… that I see several people using as “proof” for evading cellular immunity (this article relates to B.1.429 in CA and uses pseudoviruses which are known to
produce varying results, let me give you this: medrxiv.org/content/10.110… which demonstrates California variant B.1.429 (L452R) exhibited neutralization that was similar to that of wild-type and the parental D614G variant amongst those who received two doses of vaccine AND
biorxiv.org/content/10.110… where this study found CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell mediated responses were MINIMALLY affected by mutations found in SARS-CoV-2 VOCs B.1.1.7, B.1.351, P.1 AND B.1.429 (the one that shares the same mutation as B.1.617). I noticed people were failing to mention
other studies expressing the effectiveness of the vaccines against a variant regardless of the fact it has L452R. Lastly, studies on antigen-specific CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, and antibodies together show us the magnitude of protective adaptive immune responses we have to these
variants: cell.com/cell/pdf/S0092…. We have CD8+ T-cells covering 52 epitopes across the spike protein and CD4+ T-cells covering 23 epitopes across the spike protein that have been shown to be minimally affected by variants.
TLDR. Do I think B.1.617 will be able to evade vaccines? No. Do I think B.1.617 will be able to evade T-cell responses? No. Do I think it’s important to control the spread of B.1.617? Absolutely. But, it is also important to remain calm, get vaccinated, and value facts over fear.
Lastly, so everyone is aware, convergent evolution can indeed happen with or without travel and we can see the exact same mutations occurring in different places regardless. Controlling spread and transmission is vital. Please do consider reading: thestreet.com/latest-news/th…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh