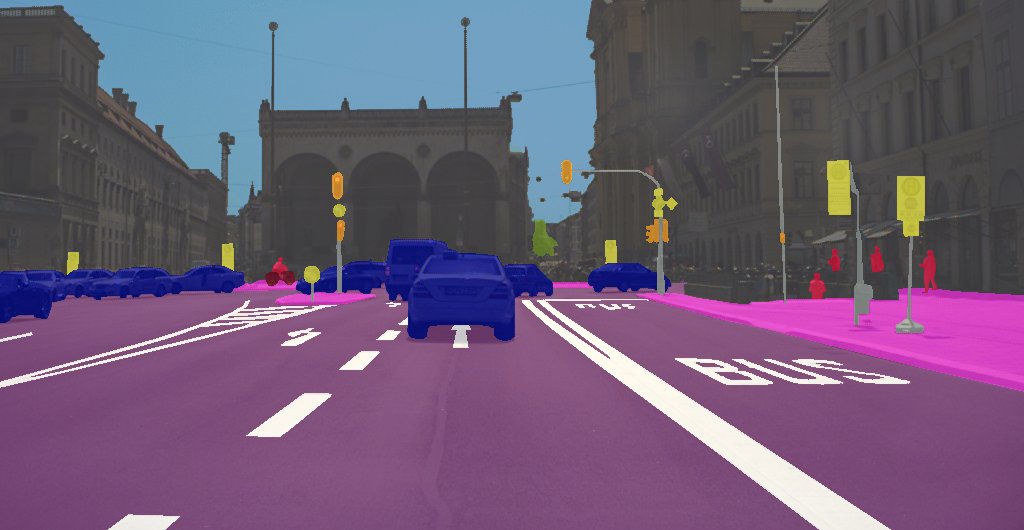
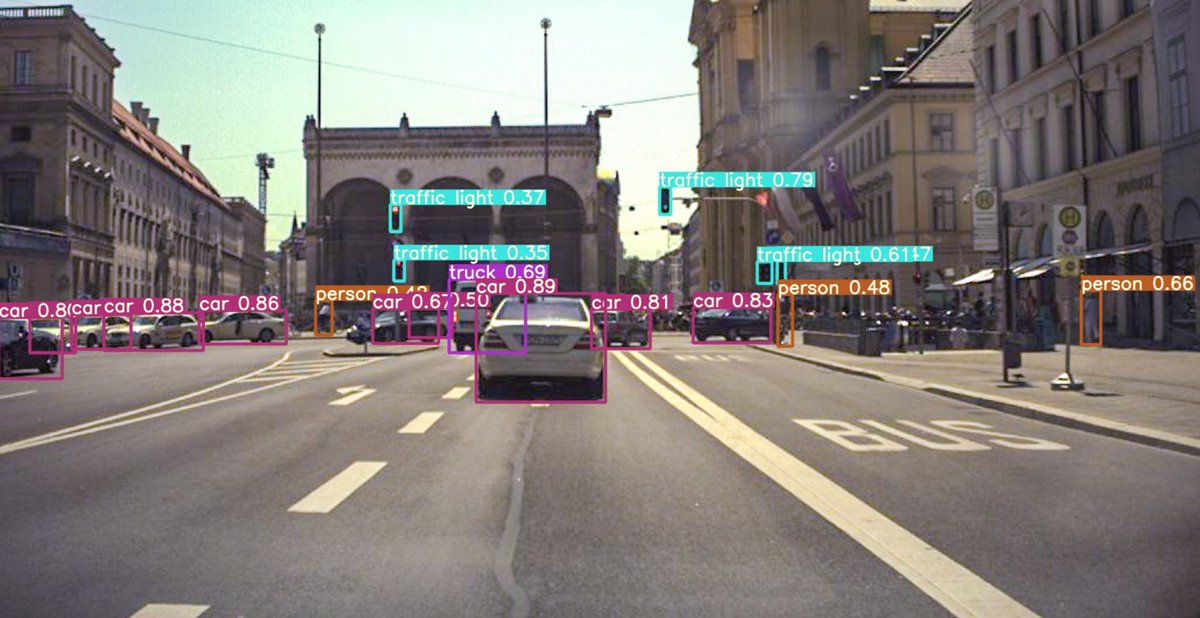
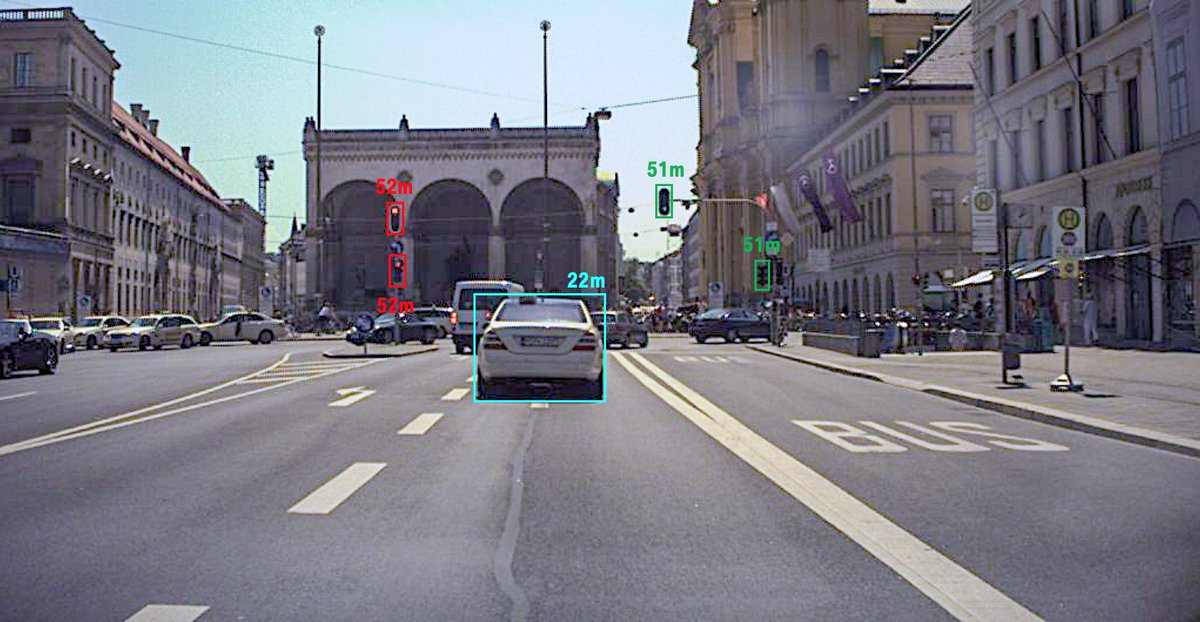
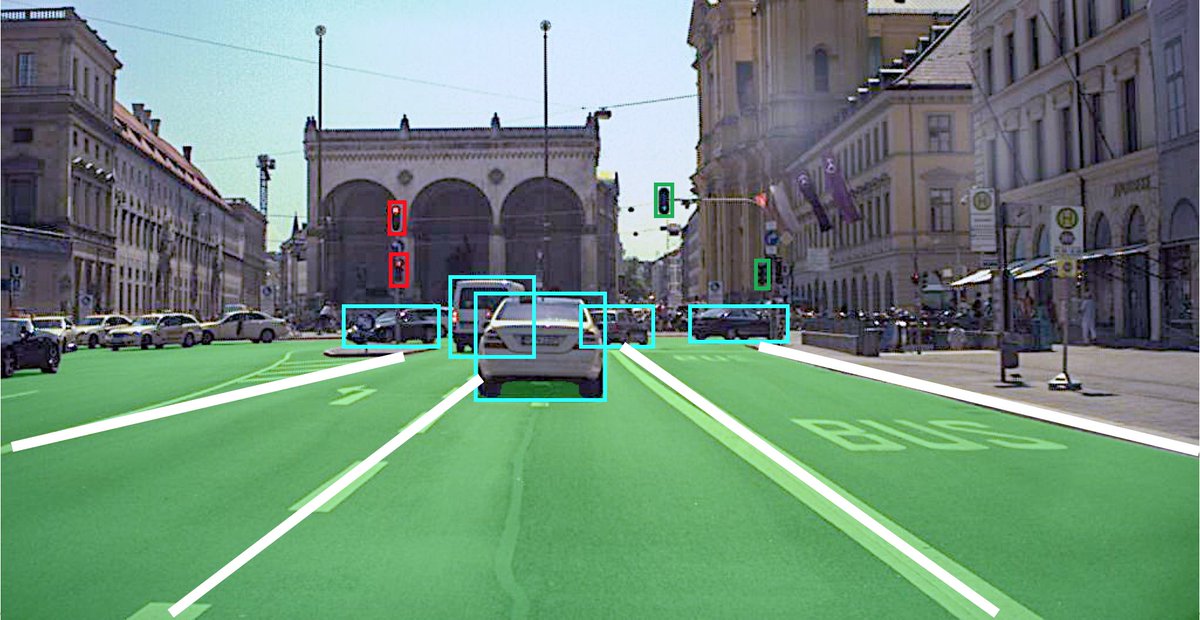
End-to-end approach to self-driving 🎥 🕸️ 🕹️
I recently wrote about the classical software architecture for a self-driving car. The end-to-end approach is an interesting alternative.
The idea is to go directly from images to the control commands.
Let me tell you more... 👇
I recently wrote about the classical software architecture for a self-driving car. The end-to-end approach is an interesting alternative.
The idea is to go directly from images to the control commands.
Let me tell you more... 👇

This approach is actually very old, dating back to 1989 and the ALVINN model by CMU. It is a 3-layer neural network using camera images and a laser range finder.
Again, this was back in 1989... 🤯
papers.nips.cc/paper/1988/fil…
Again, this was back in 1989... 🤯
papers.nips.cc/paper/1988/fil…

A modern example is Nvidia's PilotNet - a Convolutional Neural Network with 250M parameters, which takes as input the raw camera image and predicts directly the steering angle of the car.
No explicit lane boundary or freespace detection needed!
arxiv.org/abs/1604.07316
No explicit lane boundary or freespace detection needed!
arxiv.org/abs/1604.07316

How to train such network?
Easy! When a human drives the car, we can record the camera images and the actual steering angle as ground truth 🤷♂️
The network will then learn to predict a steering angle similar to what the human driver chose - this is called immitation learning.
Easy! When a human drives the car, we can record the camera images and the actual steering angle as ground truth 🤷♂️
The network will then learn to predict a steering angle similar to what the human driver chose - this is called immitation learning.
Take a look at this video to see the system in action. Around 8 minutes you can see what the network actually "sees".
Now, to be clear - this is not really a full self-driving car, but only a model that does the steering! There is much more you need to do to actually let the car drive by itself:
▪️ Longitudinal control (acceleration and breaking)
▪️ Lane changes
▪️ Emergency maneuvers
▪️ Longitudinal control (acceleration and breaking)
▪️ Lane changes
▪️ Emergency maneuvers
A similar approach is implemented by Comma AI in their newest version of Openpilot.
They train a version of EfficientNet combined with a network that predicts the trajectory the car needs to drive.
blog.comma.ai/end-to-end-lat…
They train a version of EfficientNet combined with a network that predicts the trajectory the car needs to drive.
blog.comma.ai/end-to-end-lat…

The good ✅
The advantage of end-to-end networks is that you can get small and efficient models. The net will only focus on solving the final task and no intermediate representations.
Collecting of training data is fairly easy as well - no manual labeling!
The advantage of end-to-end networks is that you can get small and efficient models. The net will only focus on solving the final task and no intermediate representations.
Collecting of training data is fairly easy as well - no manual labeling!
The bad ❌
The disadvantage is that it will be very difficult to understand why the net makes some mistakes - we don't have any explicit intermediate representations, like lane boundaries.
It will also need lots of data to cover all possible scenarios on the road.
The disadvantage is that it will be very difficult to understand why the net makes some mistakes - we don't have any explicit intermediate representations, like lane boundaries.
It will also need lots of data to cover all possible scenarios on the road.
There is an interesting paper by Prof. Shashua, CEO of Mobileye, arguing that in order to reach very high accuracy, end-to-end methods will require exponentially more training samples, than the more modular approaches.
arxiv.org/abs/1604.06915
arxiv.org/abs/1604.06915
The truth lies somewhere in the middle...
There are now approaches that try to combine the advantages of both the modular and the end-to-end approaches. I recommend watching this great talk by Prof. Raquel Urtasun from Uber ATG.
There are now approaches that try to combine the advantages of both the modular and the end-to-end approaches. I recommend watching this great talk by Prof. Raquel Urtasun from Uber ATG.
Read more about the classical software architecture for self-driving cars in my other thread:
https://twitter.com/haltakov/status/1382014488174530563
If you liked this thread and want to read more about self-driving cars and machine learning follow me @haltakov!
I have many more threads like this planned 😃
I have many more threads like this planned 😃
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh