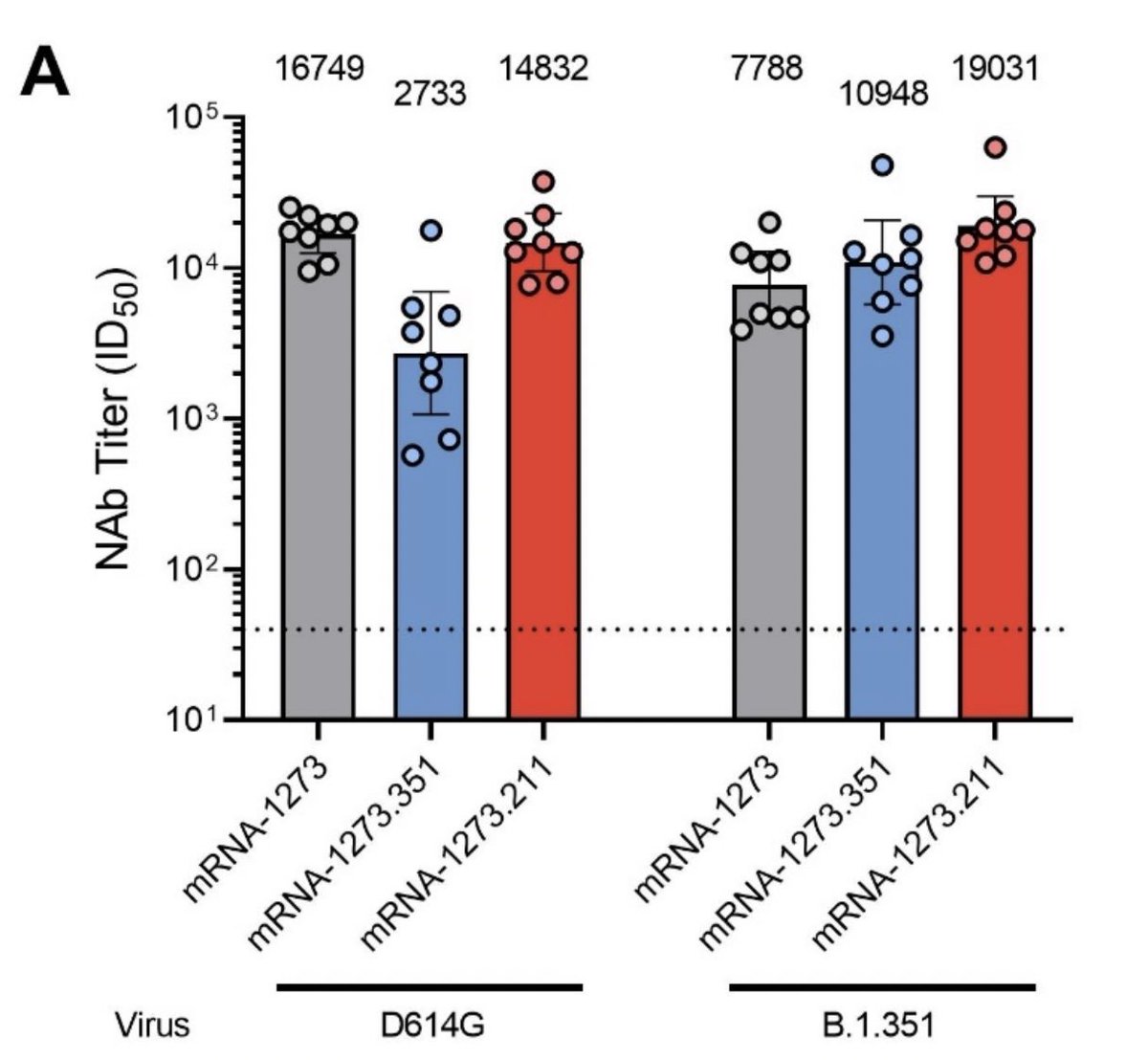
The Indian Council of Medical Research in New Delhi announced today that Covaxin, their inactivated virus-based COVID-19 vaccine being developed with Bharat Biotech effectively neutralizes several variants of concern as well as variant B.1.617!
hindustantimes.com/india-news/icm…
hindustantimes.com/india-news/icm…
Covaxin shows 78% overall interim efficacy, 100% efficacy against severe COVID. Latest update from today: timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/covaxin-…
While we wait for the data from the ICMR study on the variants you can find out more about the vaccine here: bmj.com/content/373/bm…
While we wait for the data from the ICMR study on the variants you can find out more about the vaccine here: bmj.com/content/373/bm…
Latest report on breakthrough infections. 2-4/10,000 breakthrough infections have been reported from Covaxin and Covishield. This is super encouraging when we look at these numbers. Thank you @getmefive & @munna_jajbati for the heads up! 



To clarify, Covaxin is the inactivated virus-based COVID-19 vaccine being developed with Bharat Biotech and Covishield is the Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccine being manufactured locally by the Serum Institute of India under that name.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh