A security guard at the Pan Pacific hotel in #Perth has tested positive, along with two housemates. Short thread with the details.
If you’ve visited any of these sites, you must get tested & quarantine until you receive a negative result.
Masks are mandatory when leaving home.
If you’ve visited any of these sites, you must get tested & quarantine until you receive a negative result.
Masks are mandatory when leaving home.
A hotel quarantine security guard who received their first dose of the Pfizer-BNT vaccine about 1 week ago, worked at the Pan Pacific hotel on the 24th, 25th, and 26th of April.
On the 24th, two international arrivals who would later test positive arrived at the hotel.
On the 24th, two international arrivals who would later test positive arrived at the hotel.
The arrivals were from Indonesia and the US. One was infected with a variant common in the US.
The security guard, who developed symptoms on the 29th, is believed to have become infectious on the 27th. He tested positive yesterday, on the 30th of April.
The security guard, who developed symptoms on the 29th, is believed to have become infectious on the 27th. He tested positive yesterday, on the 30th of April.
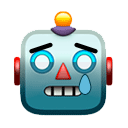
Here are the locations visited in Perth by people who may have been infected.
If you have been at any of the locations below at the times specified, you must get tested and quarantine at home until you receive a negative test result.
healthywa.wa.gov.au/Articles/A_E/C…
If you have been at any of the locations below at the times specified, you must get tested and quarantine at home until you receive a negative test result.
healthywa.wa.gov.au/Articles/A_E/C…

These outbreaks are preventable, and will continue until we take action to prevent airborne transmission.
Here’s what we need to do:
Here’s what we need to do:
https://twitter.com/drzoehyde/status/1384742921530855425
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh