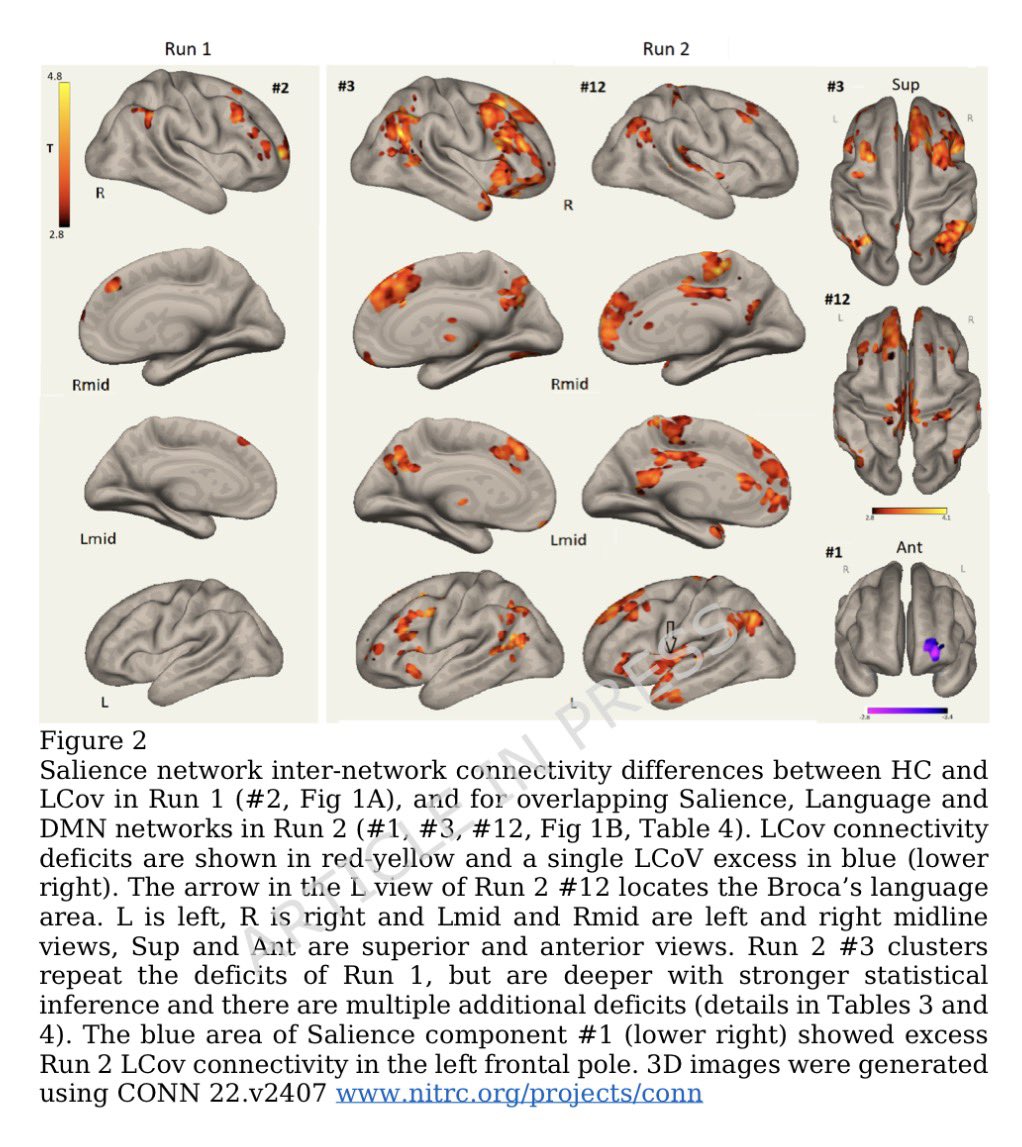
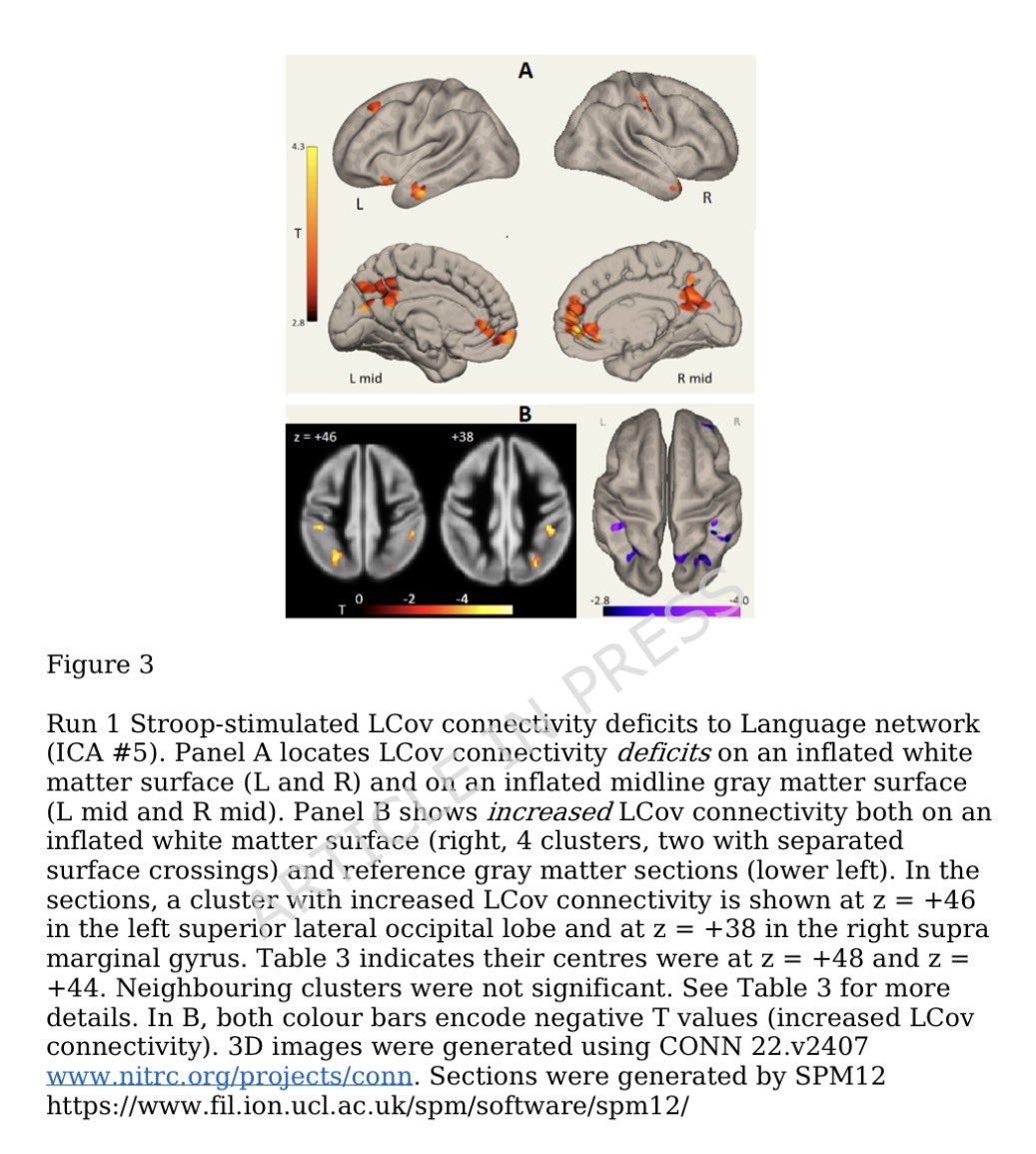
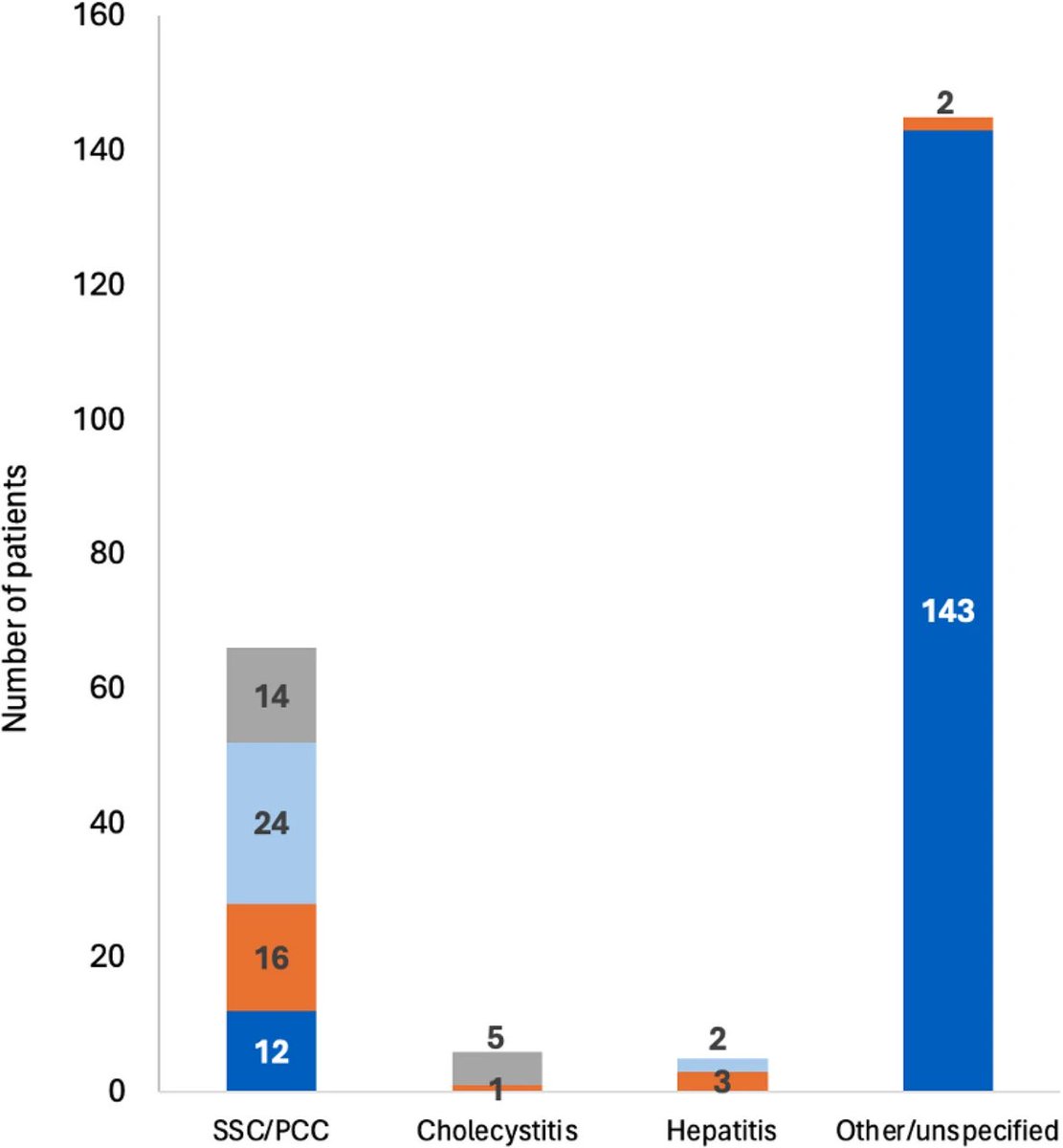
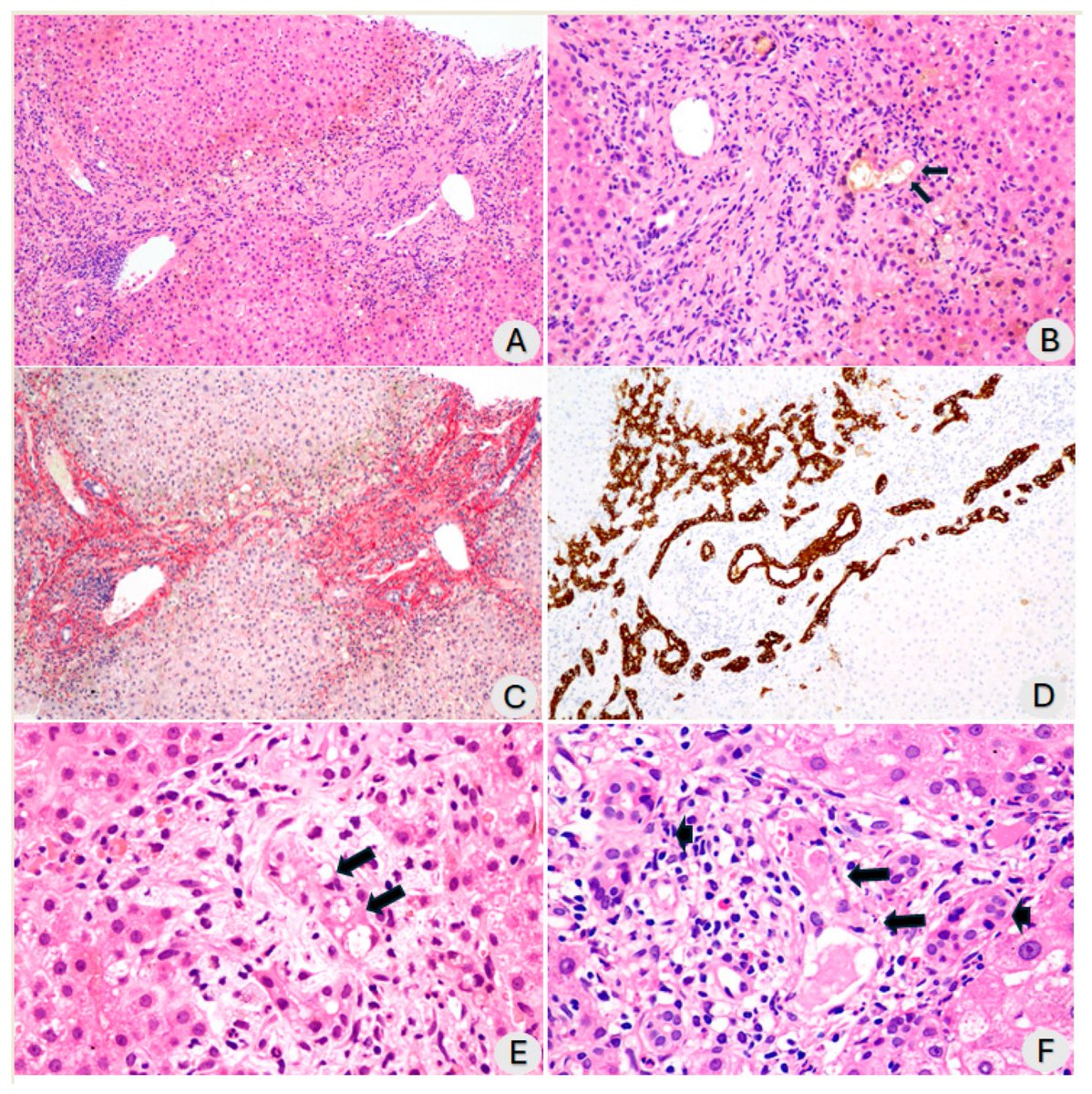
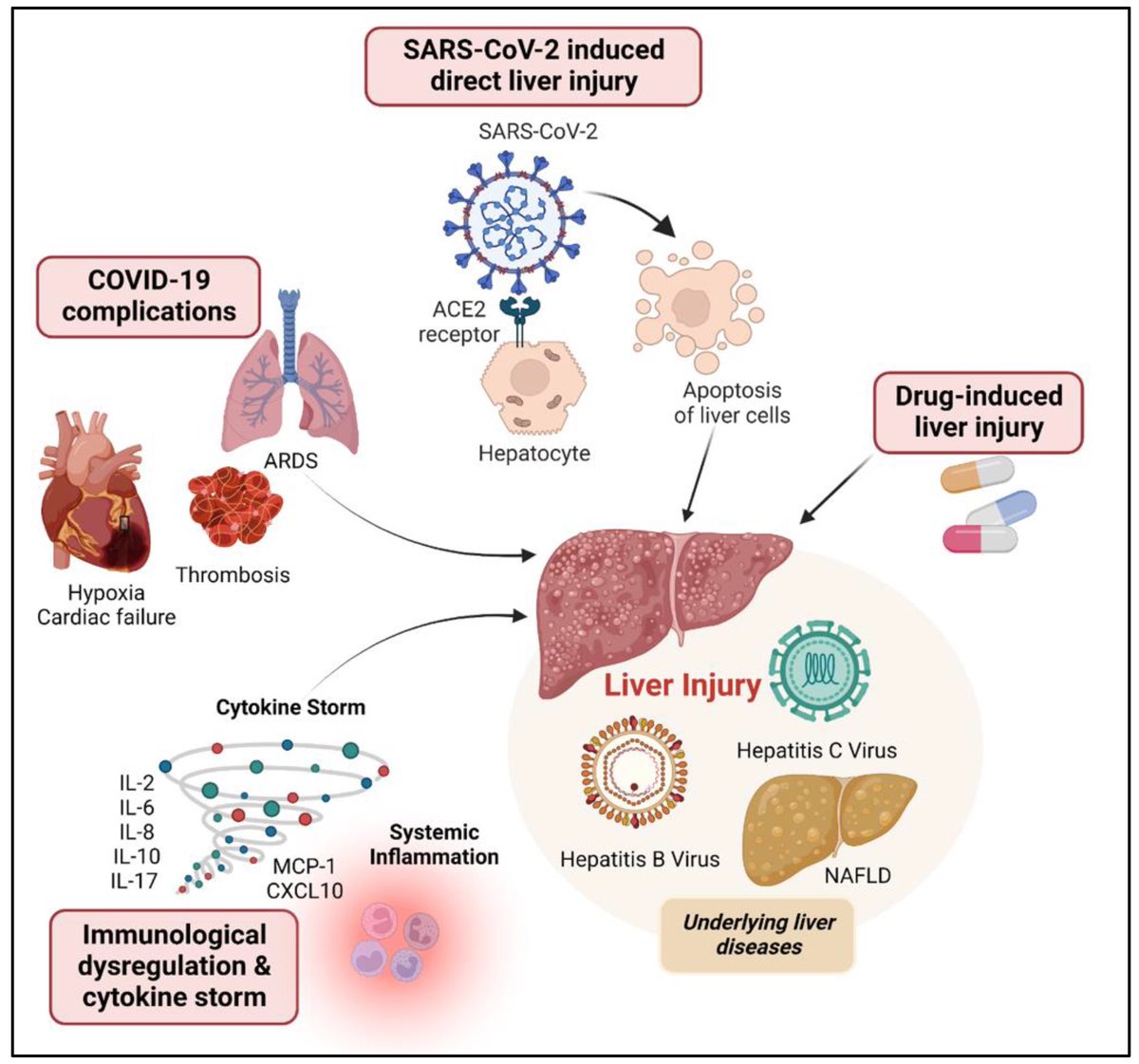
Antibodies or the T-cells?
Which arm is crucial for viral clearance & protection against #SARSCoV2? 1/
Which arm is crucial for viral clearance & protection against #SARSCoV2? 1/

Early on in the #pandemic questions arose regarding how #SARSCoV2 is cleared during acute/primary infection & what aspects of the #adaptive immune were necessary and sufficient for protection from repeat infection 2/
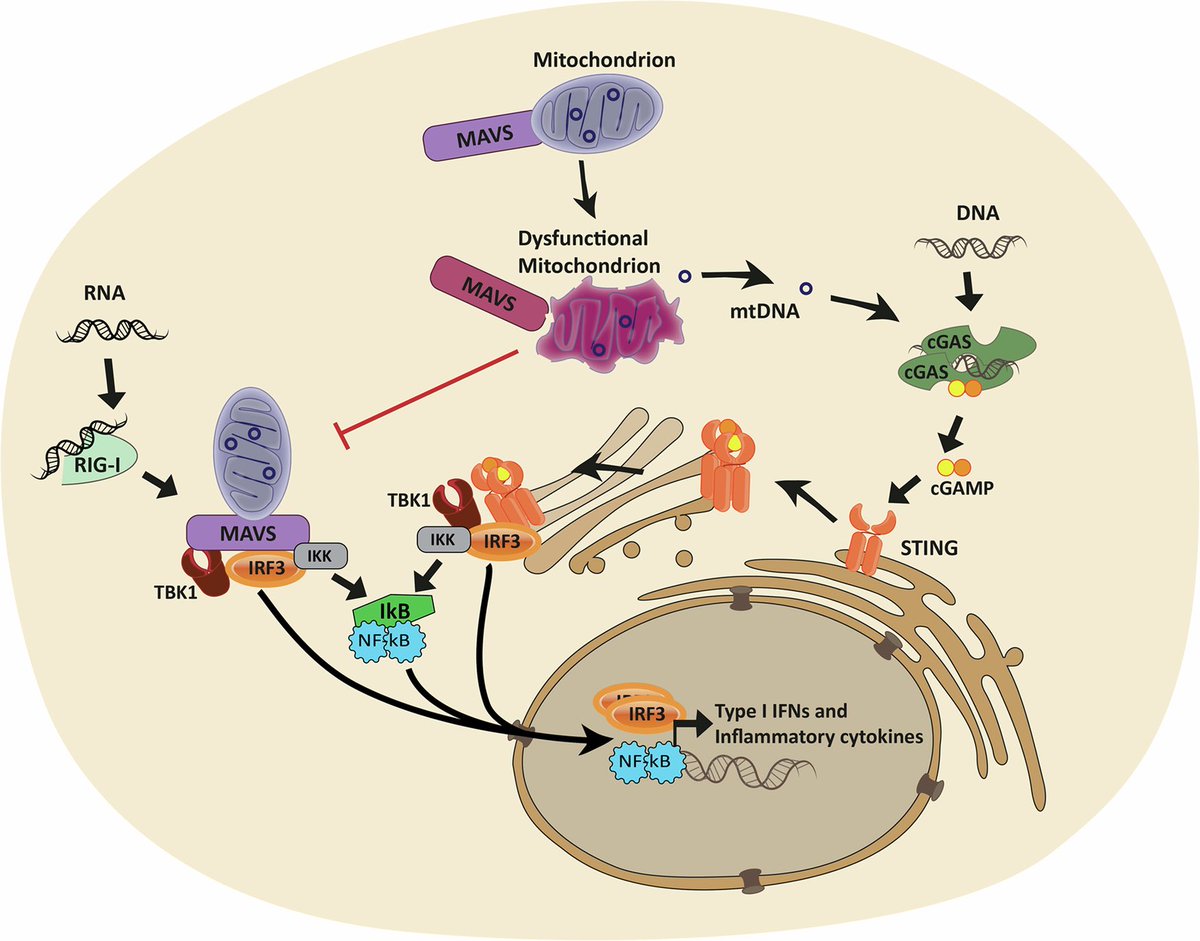
Using mouse models of SARSCoV2,@BenIsraelow Rt al demonstrate that both humoral and cellular adaptive immunity contributes to viral clearance in the setting of primary infection 3/ 



Either convalescent mice, or mice that receive #mRNA vaccination are protected from both homologous infection & infection with a VOC, B.1.351 4/ 

Additionally, they conclude that protection is largely mediated by antibody response and not cellular immunity, and highlight the in vivo protective capacity of antibodies generated to both vaccine & natural infection @VirusesImmunity @SaadOmer3 5/
biorxiv.org/content/10.110…
biorxiv.org/content/10.110…
Another study on Rhesus #Macaques finds that T cells play a role in the recovery from acute #SARSCoV2 infections, their depletion does not induce severe disease, & T cells do not account for the natural resistance of rhesus macaques to severe #COVID19 @fitterhappierAJ 6/ 

Neither primed CD4+ or CD8+ T cells appeared critical for immunoglobulin class switching, the development of immunological memory or protection from a second infection 7/ 

CD4, CD8, & CD4/8 depletion in Macaques prior and during infection did not affect disease course and only mildy attenuated viral clearance! 8/
biorxiv.org/content/10.110…
biorxiv.org/content/10.110…
The debate continues.....Difficult to write-off the importance of T-cells. This virus is weird. Need more studies before we dump cellular arm. What we know, a harmony between the two is needed for a successful immune response! 9/
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh