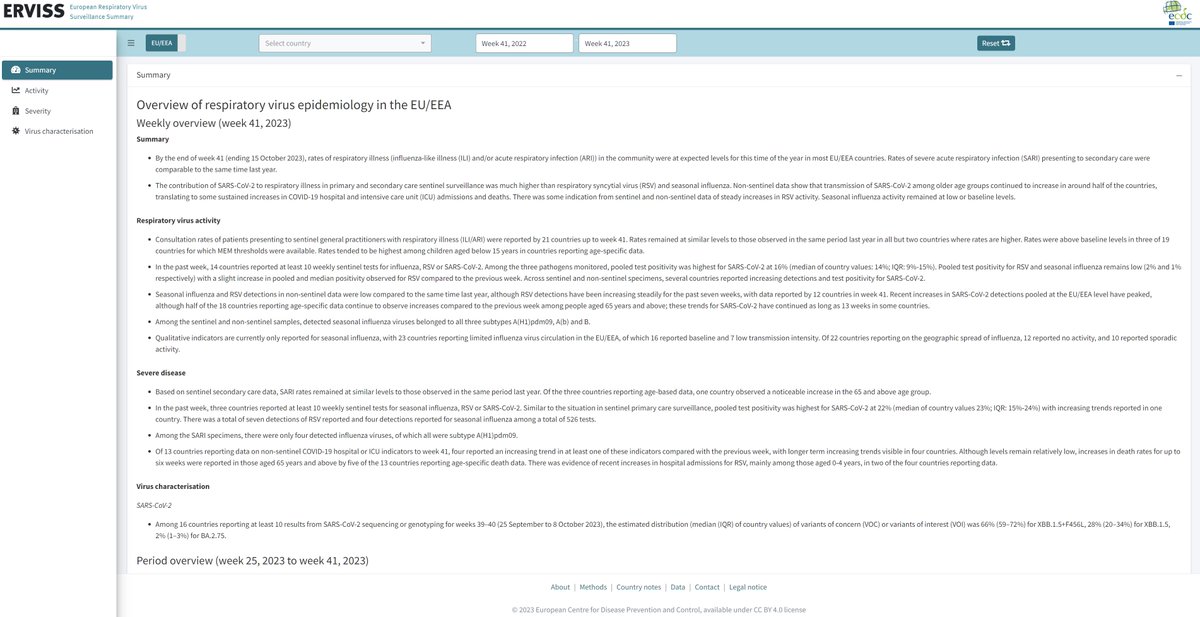
#JustPublished!
Interim public health considerations for the provision of additional #COVID19 vaccine doses.
Read full report here: bit.ly/ECDCBoosterDoc
Interim public health considerations for the provision of additional #COVID19 vaccine doses.
Read full report here: bit.ly/ECDCBoosterDoc

Providing all eligible individuals with the recommended dose regimen should remain the current
priority for #COVID19 vaccination programmes in the EU/EEA.
All vaccines authorised in the EU/EEA are highly protective against COVID19 related hospitalisation, severe disease & death.
priority for #COVID19 vaccination programmes in the EU/EEA.
All vaccines authorised in the EU/EEA are highly protective against COVID19 related hospitalisation, severe disease & death.

Administering an additional vaccine dose to people who may experience a limited response to the primary #COVID19 vaccination, such as some categories
of immunocompromised individuals, should already be considered now.
bit.ly/ECDCBoosterDoc
of immunocompromised individuals, should already be considered now.
bit.ly/ECDCBoosterDoc

In context of many countries outside EU struggling to receive & administer enough vaccines to their populations, special consideration should be given to current global shortage of vaccines which could be worsened by the administration of boosters for general population in EU/EEA 

#FaceMasks, #PhysicalDistancing, #HandHygiene, #RespiratoryHygiene & #Ventillation
These measures should always complement vaccination, in particular in high-risk settings such as care homes or hospitals with patients at risk of severe #COVID19.
These measures should always complement vaccination, in particular in high-risk settings such as care homes or hospitals with patients at risk of severe #COVID19.

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh