New @ippsr report on Michigan redistricting draft maps for hearings this week:
ippsr.msu.edu/sites/default/…
We analyzed the collaborative maps across their criteria
Some initial findings:
ippsr.msu.edu/sites/default/…
More resources:
ippsr.msu.edu/redistricting
ippsr.msu.edu/sites/default/…
We analyzed the collaborative maps across their criteria
Some initial findings:
ippsr.msu.edu/sites/default/…
More resources:
ippsr.msu.edu/redistricting

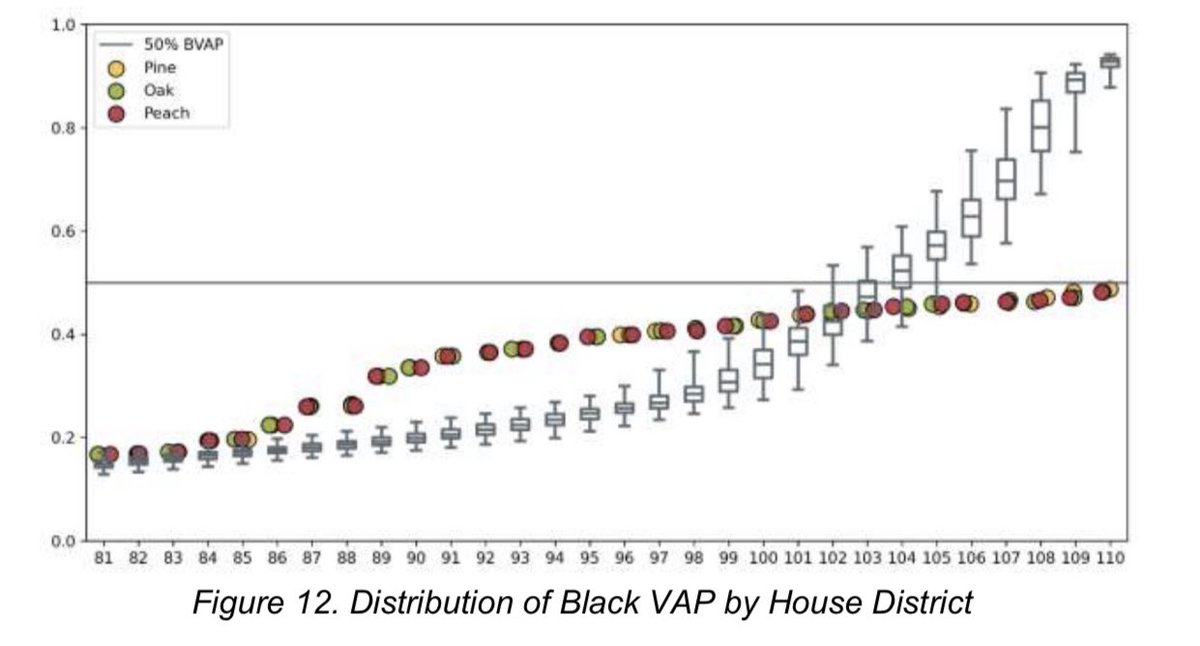
The Commission pursued a voting rights strategy that maximizes districts with Black population around 40%. Compared to the computer-generated random maps, this looks quite different. Here are draft maps for state House with the highest Black populations:
ippsr.msu.edu/sites/default/…
ippsr.msu.edu/sites/default/…
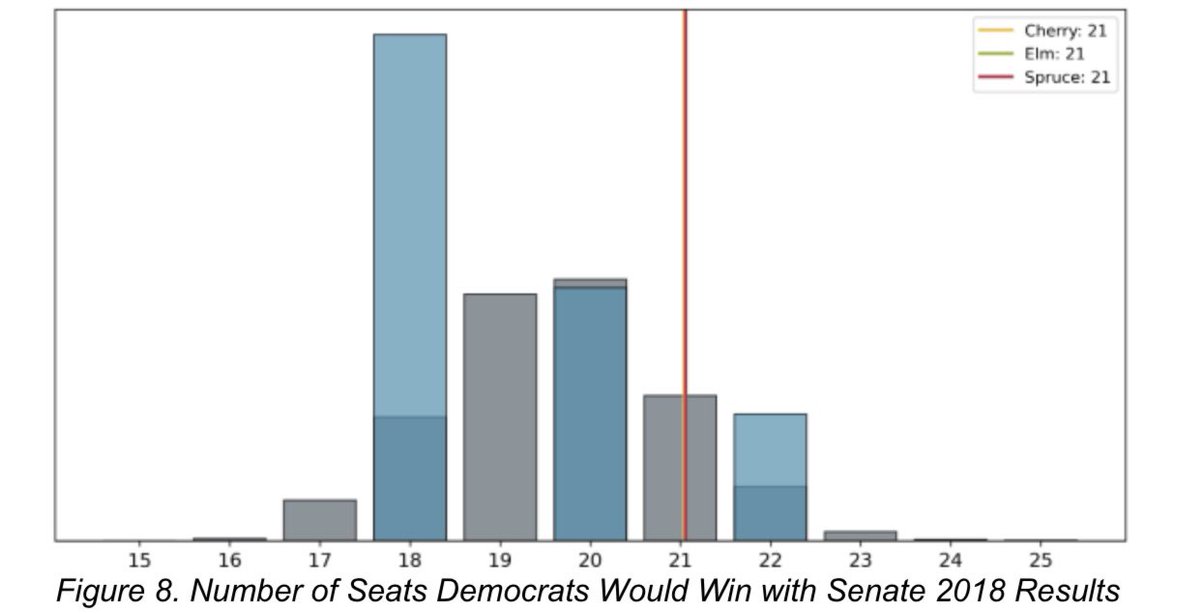
On partisan fairness, the maps are between perfect symmetry & what would be expected from randomly-drawn maps (which would favor Reps). For example, here is seat share for 38 member senate based on the 2018 Senate results compared to computer & public maps
ippsr.msu.edu/sites/default/…
ippsr.msu.edu/sites/default/…
I’ll speak more about our report on the draft maps & the Michigan redistricting tonight at 7pm at @LWVLansing
lwvlansing.org
lwvlansing.org
A report on the Michigan draft maps from @princetongerry finds similar results to our report:
metrotimes.com/news-hits/arch…
metrotimes.com/news-hits/arch…
We also have new public opinion data on Michigan's redistricting commission. Most Michiganders are not very familiar with the Commission, but most expect the process to result in fairer maps. In a separate survey, policy insiders are more familiar but still positive overall. 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh