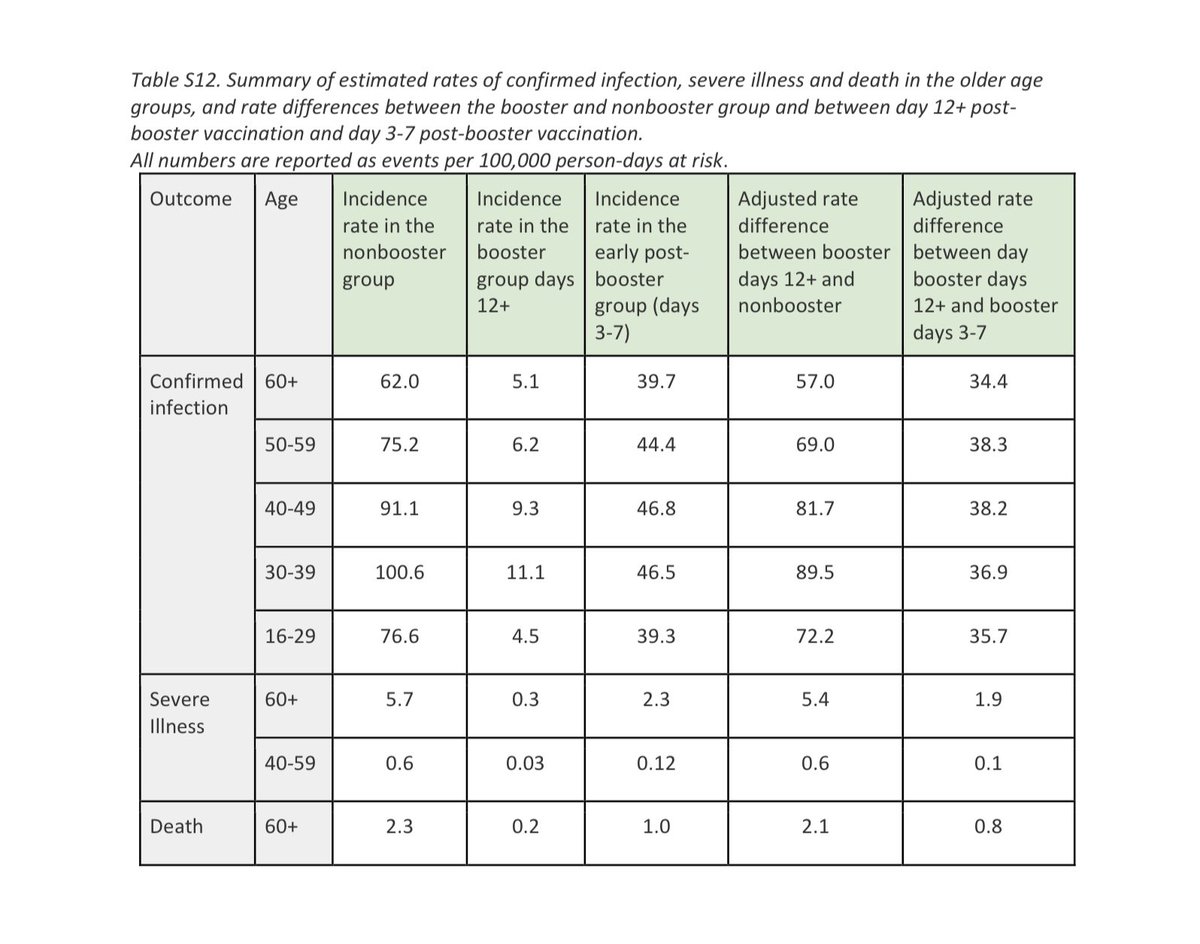
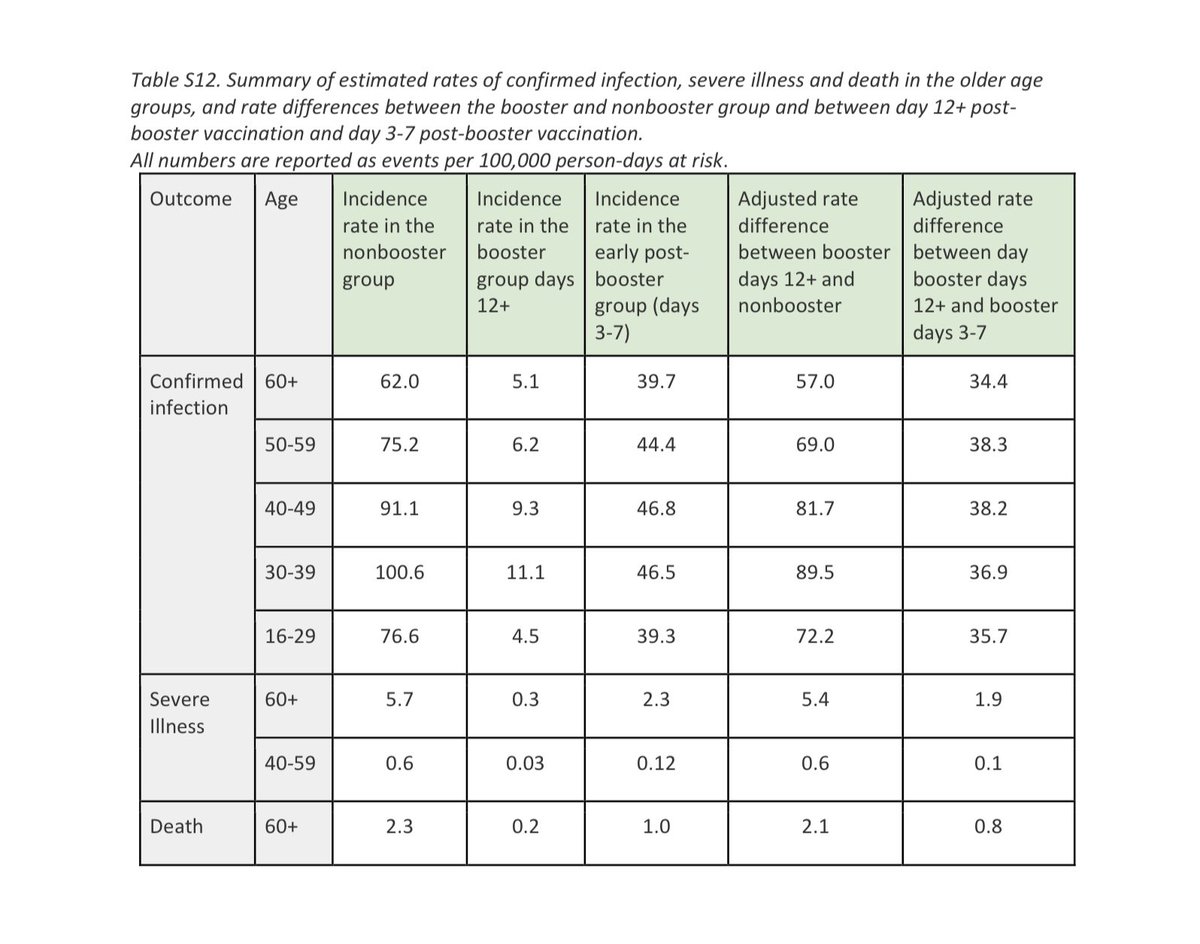
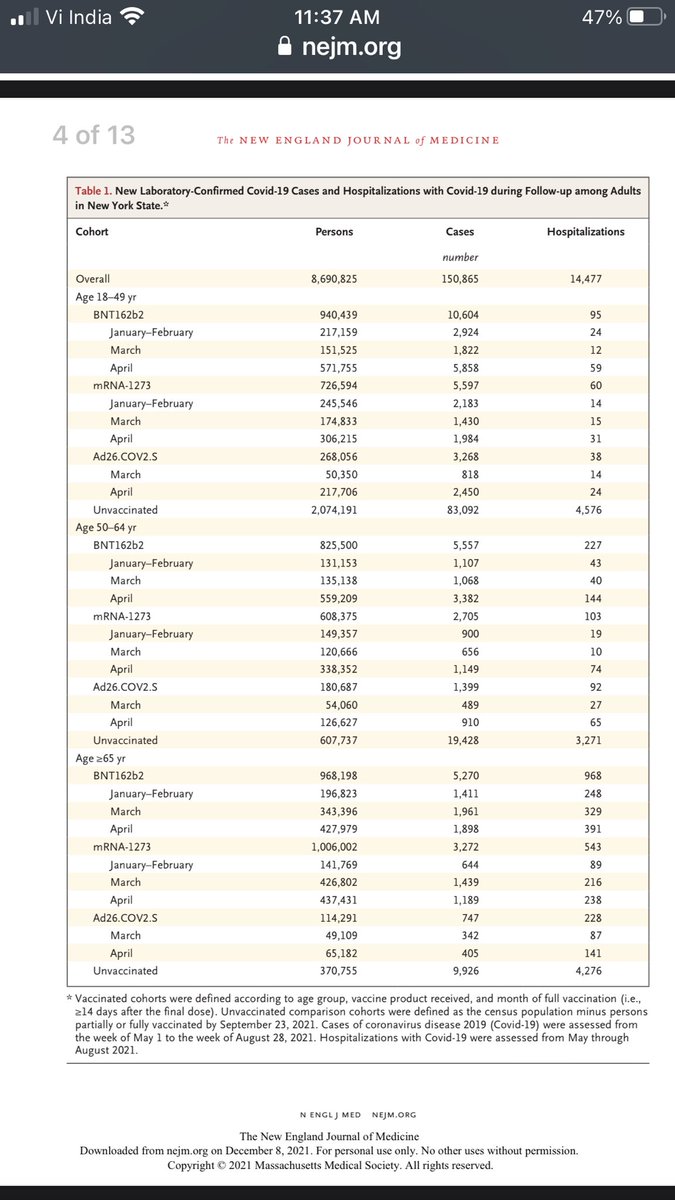
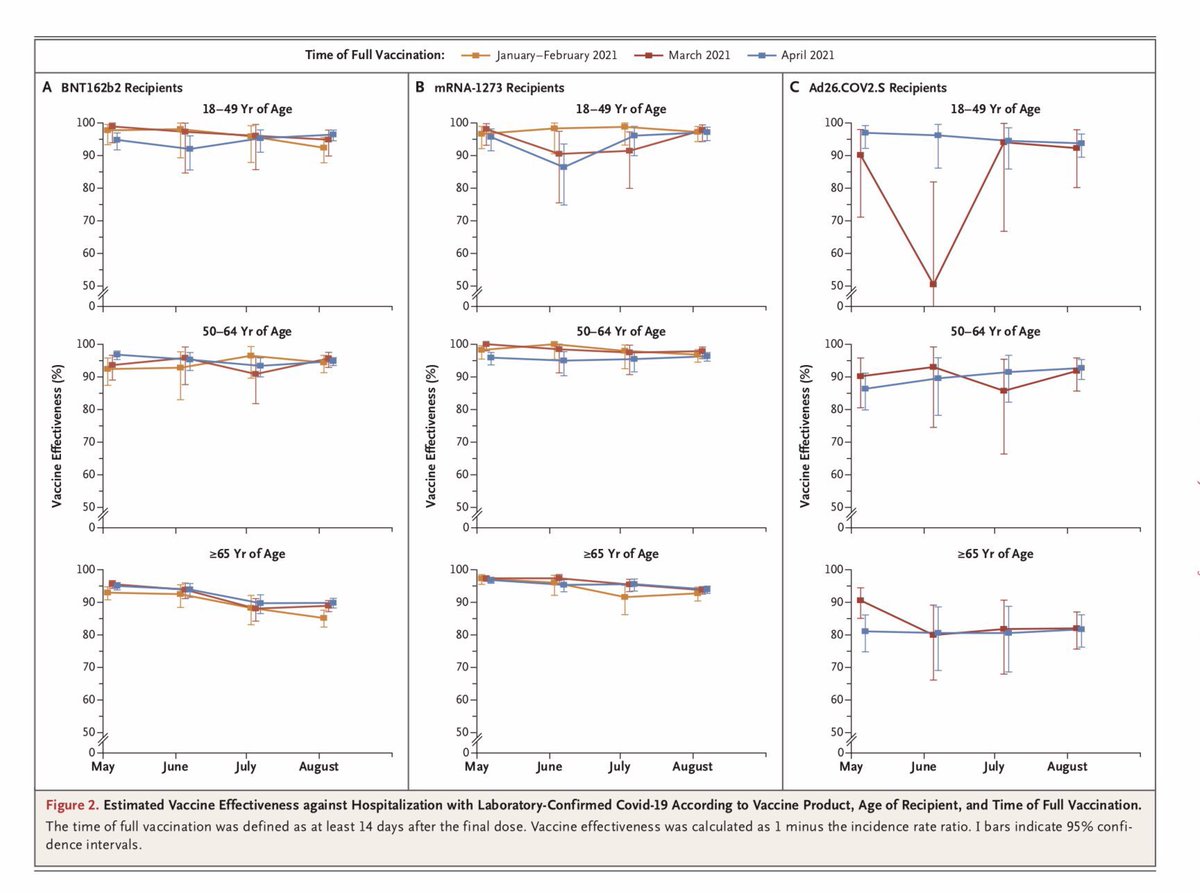
Immunology simplified
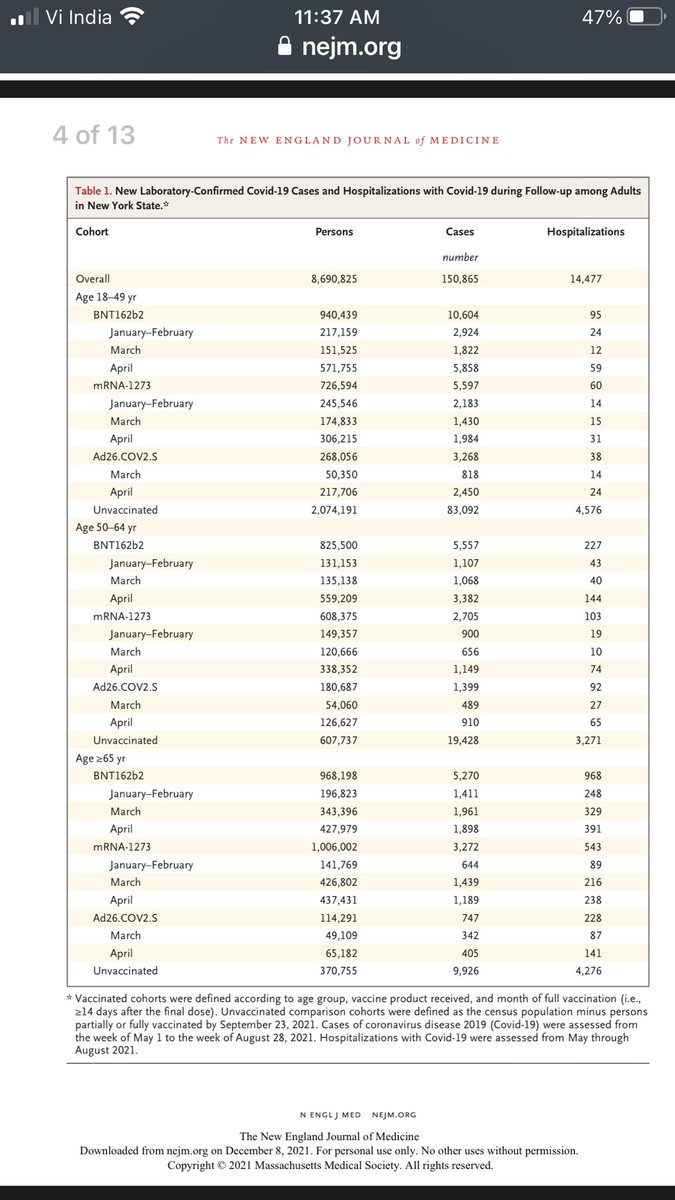
A map of our immune response to viral infection shared by @papaphone2002
I have added (in red) the role of the much-discussed neutralising antibody, thread👇
Our immunity team has so many more players, who cannot be fooled by the virus.
Here’s why
1/5
A map of our immune response to viral infection shared by @papaphone2002
I have added (in red) the role of the much-discussed neutralising antibody, thread👇
Our immunity team has so many more players, who cannot be fooled by the virus.
Here’s why
1/5
https://twitter.com/papaphone2002/status/1468659504644567047
Please note the diagram only presents an outline, not the whole thing.
Neutralising antibodies form only a tiny fraction of our TOTAL antibody response. Most antibodies are produced AFTER the attack occurs, helping eliminate virus.
(Labs measure Ab’s ALREADY in circulation)
2/
Neutralising antibodies form only a tiny fraction of our TOTAL antibody response. Most antibodies are produced AFTER the attack occurs, helping eliminate virus.
(Labs measure Ab’s ALREADY in circulation)
2/
In other words, neutralising antibodies aren’t everything.
And, importantly, a “loss of neutralisation” (‼️🔴alarmist language that lab researchers love to use while describing their work to a clueless public) doesn’t mean “we have lost against the virus”.
3/
And, importantly, a “loss of neutralisation” (‼️🔴alarmist language that lab researchers love to use while describing their work to a clueless public) doesn’t mean “we have lost against the virus”.
3/
The virus has so many other parts that our system recognises.
In fact even after delta arrived, upto 97% of the T cell epitopes haven’t been altered (the mutations affect only about 3%)
Epitopes are parts of the virus that the body picks up as specific “identifying marks”
4/
In fact even after delta arrived, upto 97% of the T cell epitopes haven’t been altered (the mutations affect only about 3%)
Epitopes are parts of the virus that the body picks up as specific “identifying marks”
4/
Specifically, epitopes are ultra short sequences of 4-17 amino acids (basic building blocks of protein).
❗️If antigen is a mango tree, epitopes are the mangoes.
T cells and other parts of our immune system learn to recognise specific epitopes of specific viruses.
5/
❗️If antigen is a mango tree, epitopes are the mangoes.
T cells and other parts of our immune system learn to recognise specific epitopes of specific viruses.
5/
Our immune system learns about these epitopes after vaccination (when we introduce harmless components of the virus) or through natural infection or both.
Note: There are 100’s of epitopes that get recognised for each infective agent. (A few are on the RBD of spike protein)
6/
Note: There are 100’s of epitopes that get recognised for each infective agent. (A few are on the RBD of spike protein)
6/
❗️The virus will NEVER be able to change ALL of these epitopes (or even 20% of ‘em) because it will “lose fitness”. In other words, some parts are ESSENTIAL for the virus to work.
(For example, a plane cannot take off if its propeller blades are cut in half by some mutation)
5/
(For example, a plane cannot take off if its propeller blades are cut in half by some mutation)
5/
The spike protein itself has 1273 amino acids, and many immovable or unchangable epitopes on it.
Antibodies target these areas too, and help eliminate infection in many ways (not just by neutralisation).
Eg. they flag our infected cells to be killed by immune cells (ADCC)
6/
Antibodies target these areas too, and help eliminate infection in many ways (not just by neutralisation).
Eg. they flag our infected cells to be killed by immune cells (ADCC)
6/
Ab’s can also tag infected cells to be eliminated by a series of destroyer proteins called “C”or “Compliment system” (C is gun powder)
Ab’s can directly flag the virus by attaching to parts of it, hanging on tight and then inviting our immune cells to come and swallow them.
7/
Ab’s can directly flag the virus by attaching to parts of it, hanging on tight and then inviting our immune cells to come and swallow them.
7/
There are other ways by which antibodies work.
And then there are our CD8 T-cells which come & destroy infected cells, preventing the virus from getting any further.
It is like bombing the building where some real bad thugs are huddled together, so that they don’t get out.
8/
And then there are our CD8 T-cells which come & destroy infected cells, preventing the virus from getting any further.
It is like bombing the building where some real bad thugs are huddled together, so that they don’t get out.
8/
Our CD4 T cells work like choirmasters, coordinating the immune response in a seamless manner, they also boost other players into action.
After the action settles, some of these B and T cells retire and live peacefully forever as memory cells in remote parts of our body.
9/
After the action settles, some of these B and T cells retire and live peacefully forever as memory cells in remote parts of our body.
9/
These normally peace-loving memory cells get activated at the slightest hint of a future infection, losing absolutely no time in recreating the original task force (only 10 times bigger and meaner), thus taking out the offender without breaking a sweat.
10/
10/
And the best part is that our immune system is continuously learning and upgrading its skills, even after the infection or vaccination period is over, so that the next time around, the antibodies stick better and work faster.
This process is called affinity maturation.
11/
This process is called affinity maturation.
11/
Immunology is fascinating and complicated. I have given the highlights above.
Just to show that our systems are well-equipped to handle the virus regardless of alarmist messaging based on lab studies.
12/12
Just to show that our systems are well-equipped to handle the virus regardless of alarmist messaging based on lab studies.
12/12
@threadreaderapp please unroll
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh