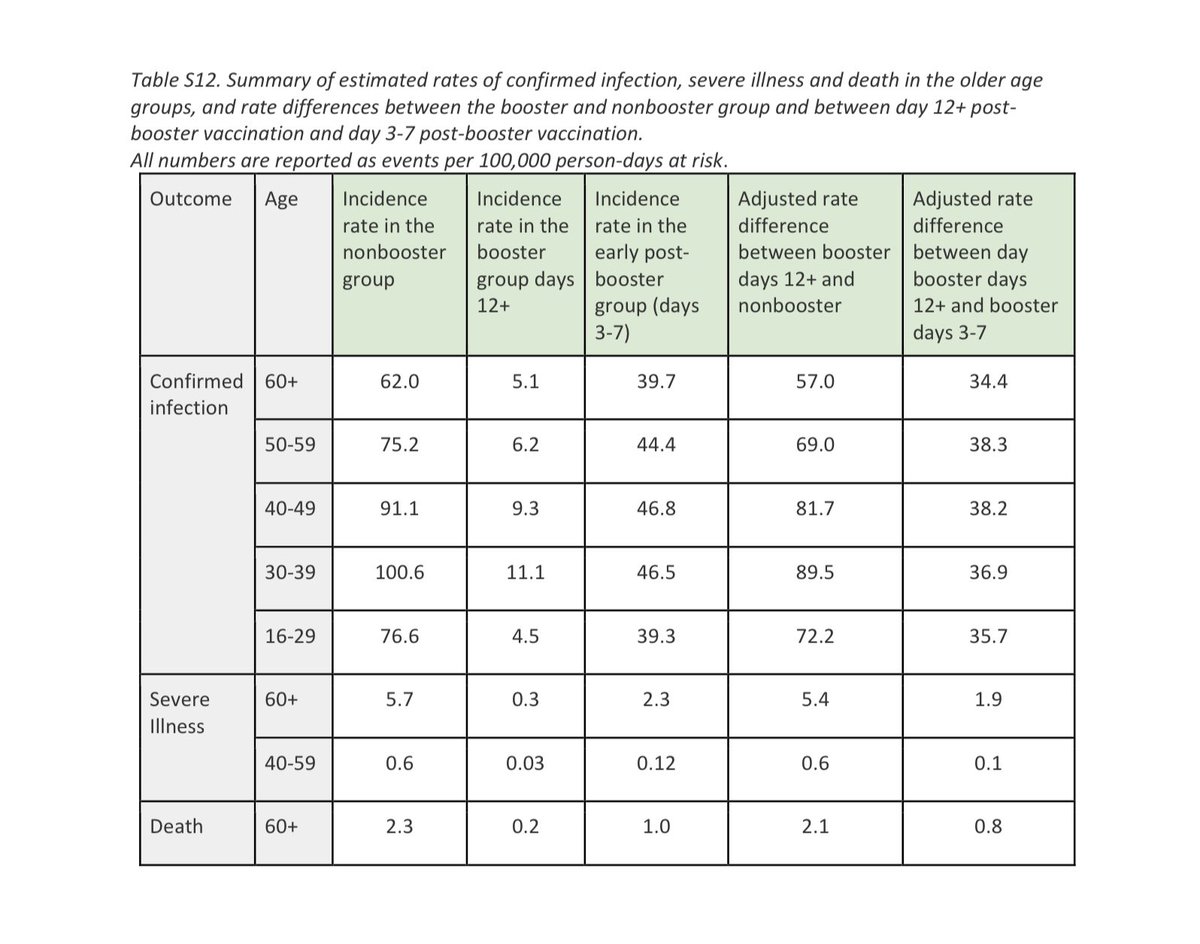
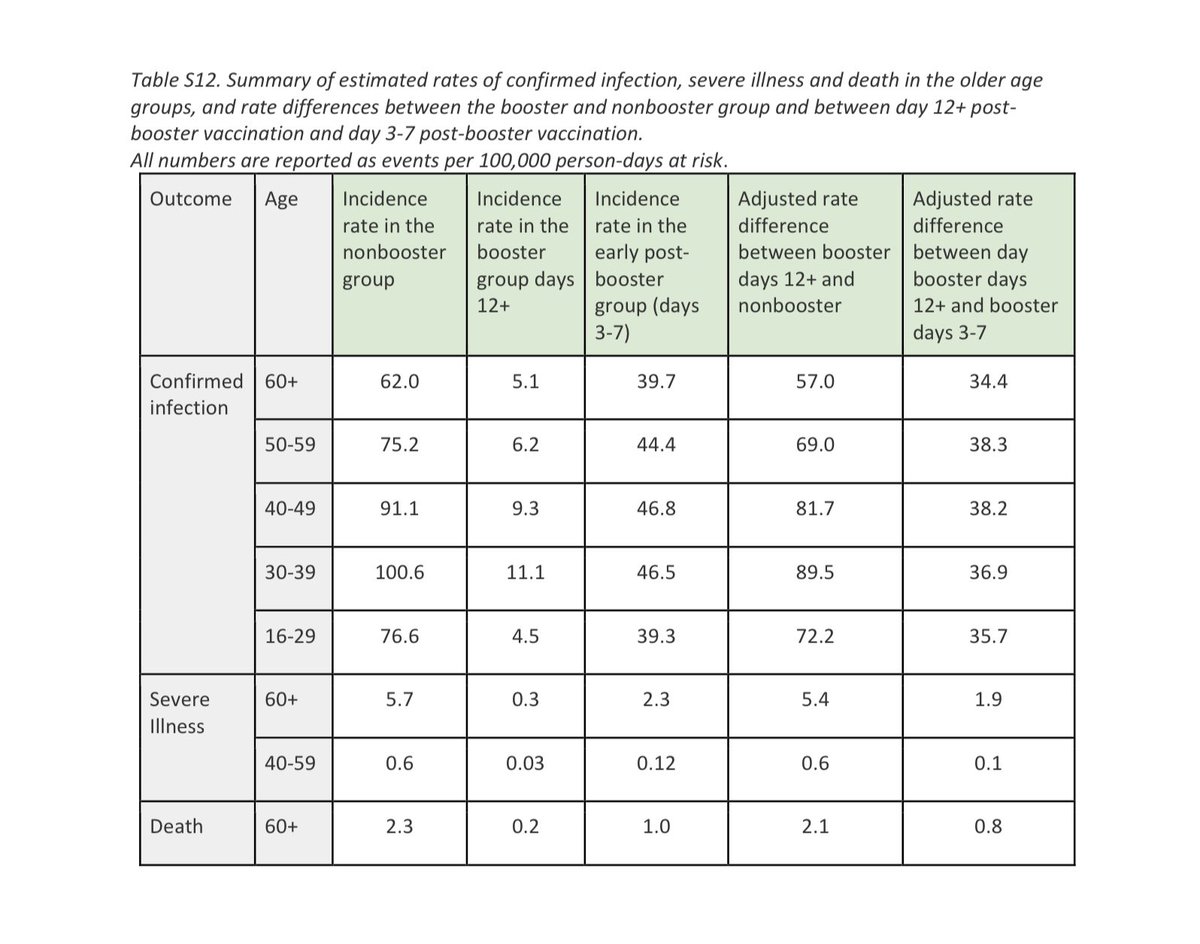
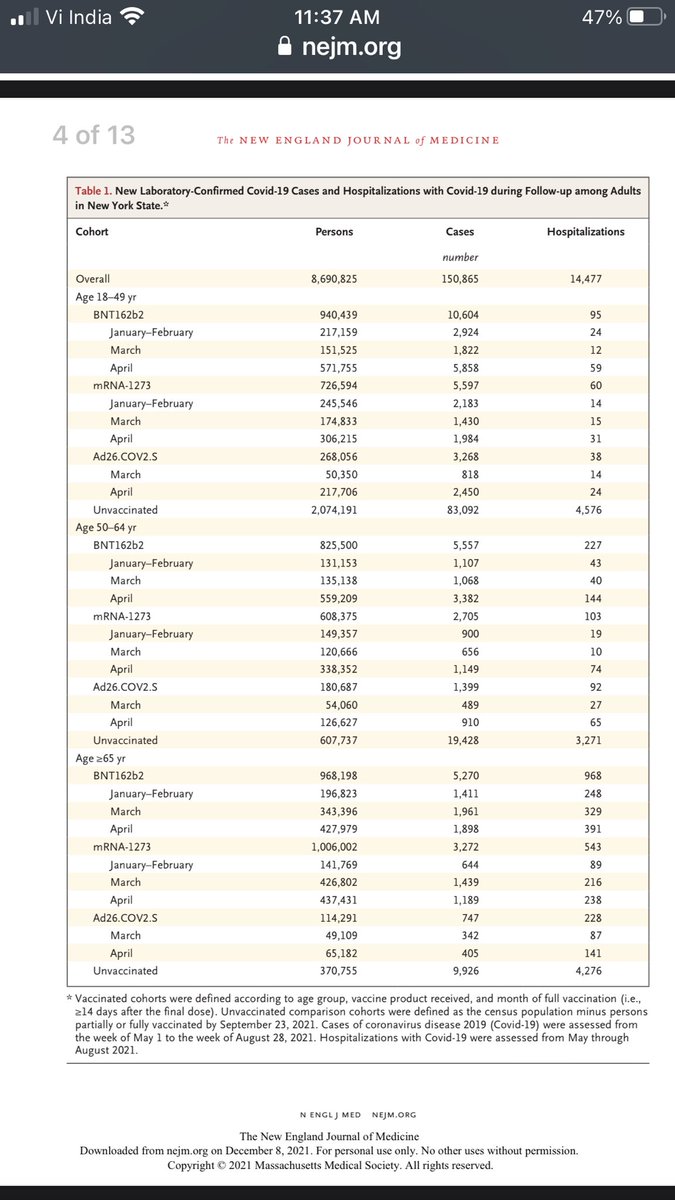
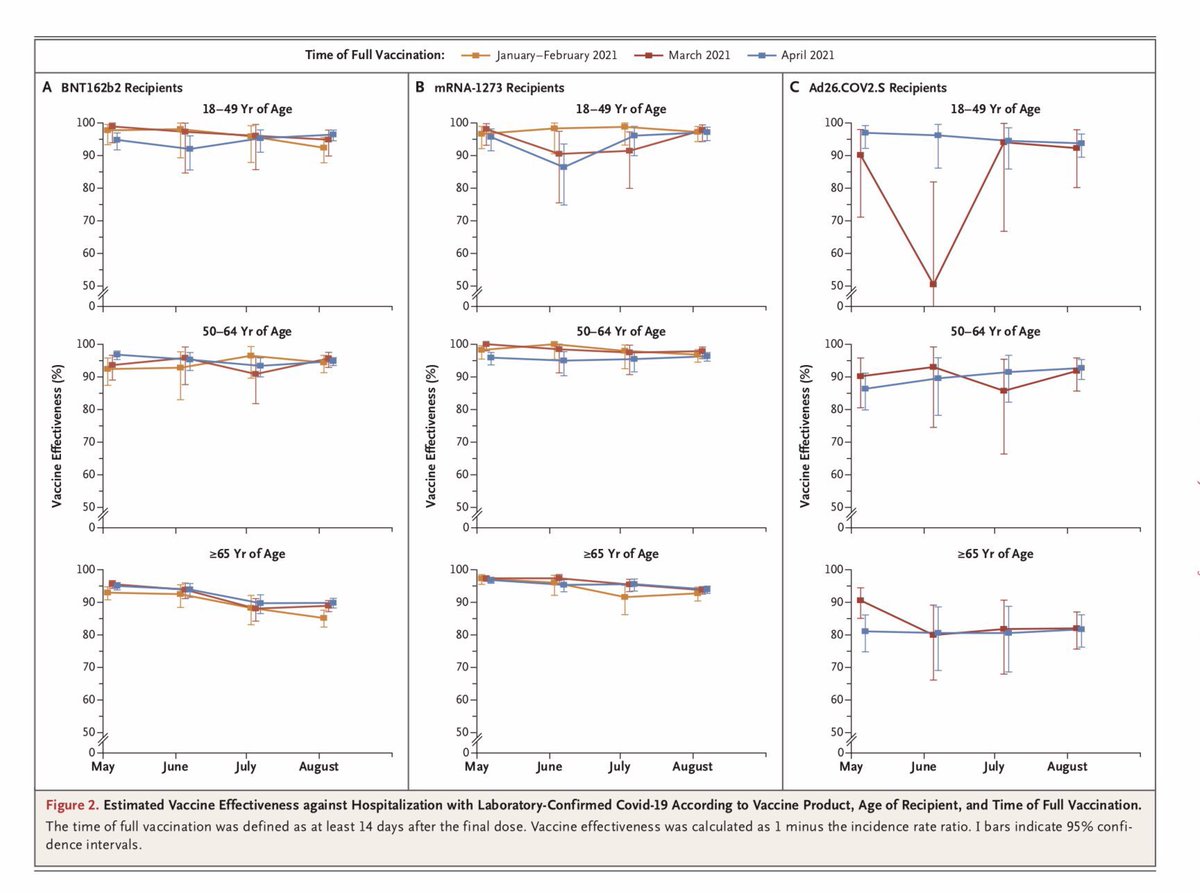
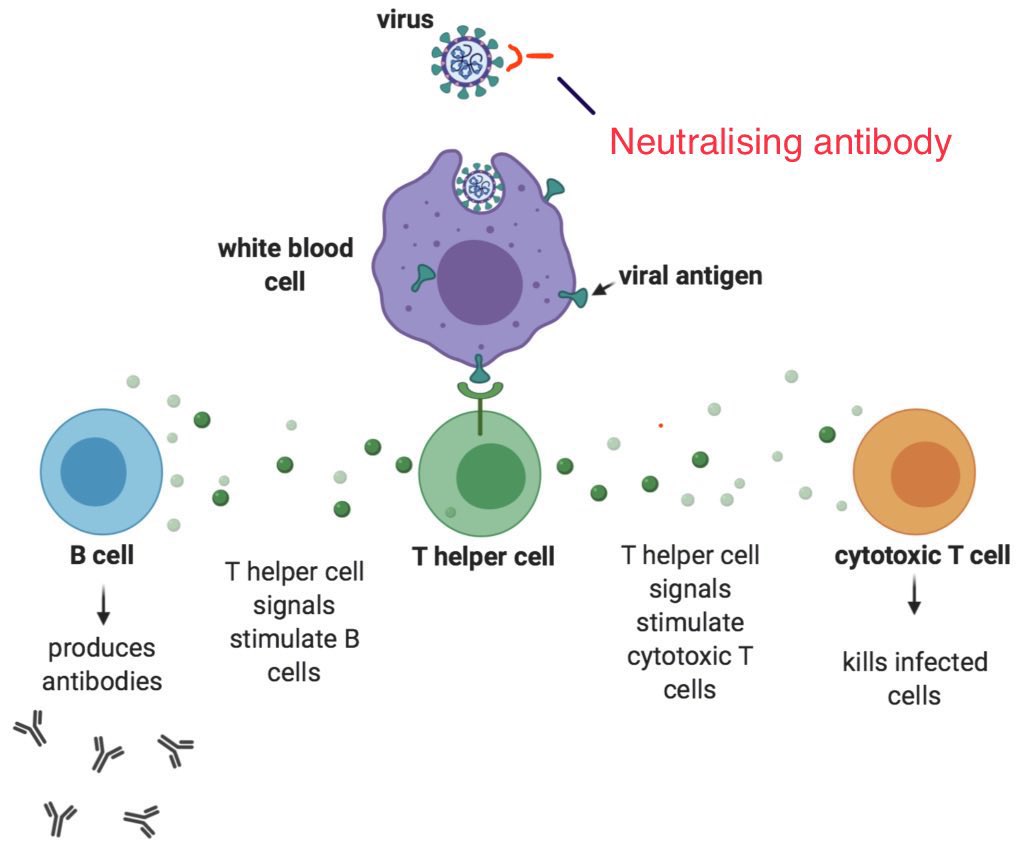
Long lived T memory cells one year after COVID-19.
Authors studied CD8 memory cells that persisted after the initial effector response, followed by contraction.
They noted phenotypical differences between memory cells in mild & severe COVID-19.
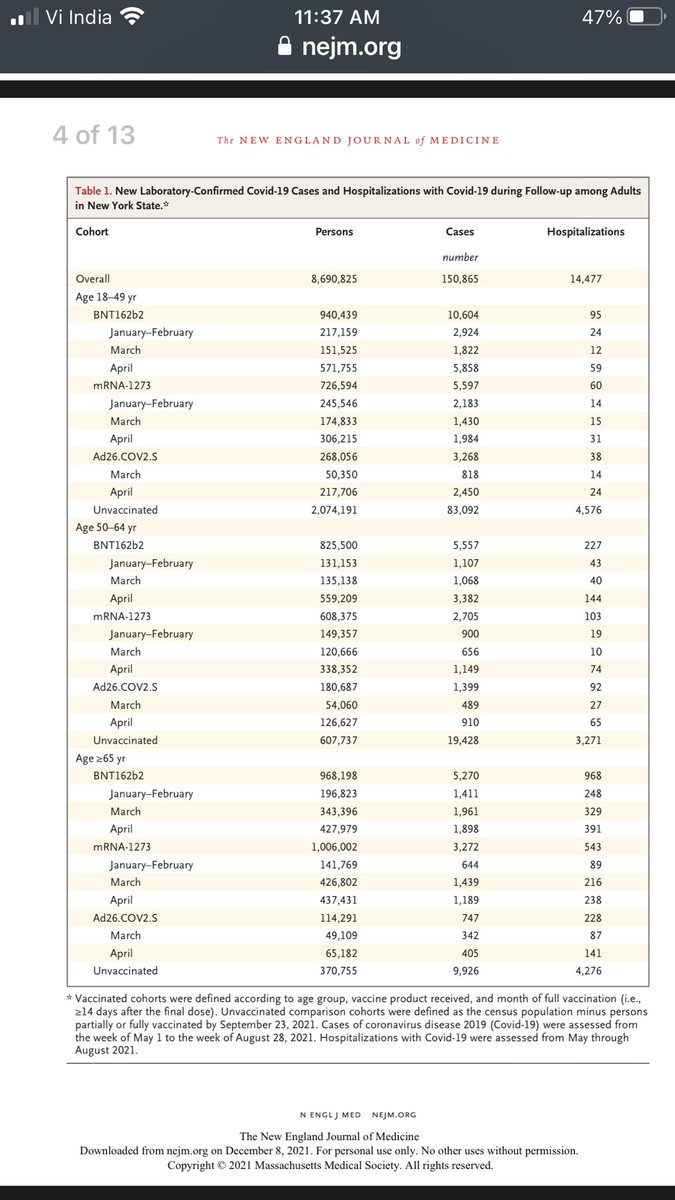
1/12
nature.com/articles/s4158…
Authors studied CD8 memory cells that persisted after the initial effector response, followed by contraction.
They noted phenotypical differences between memory cells in mild & severe COVID-19.
1/12
nature.com/articles/s4158…
Authors believe that factors such as antigen availability, type of antigen-presenting cells, and cytokine milieu – might influence the type of memory formed.
Note: T cell memory cells are of multiple categories, not all of which are detected in peripheral blood.
2/
Note: T cell memory cells are of multiple categories, not all of which are detected in peripheral blood.
2/
Some memory cells live in tissue and others in lymph nodes.
This study looked only at peripheral blood, and hence is not a description of T rm or T cm memory cells.
T rm’s live in tissues and do not move out. They defend tissues (e.g. lungs & mucosa) when an attack occurs.
3/
This study looked only at peripheral blood, and hence is not a description of T rm or T cm memory cells.
T rm’s live in tissues and do not move out. They defend tissues (e.g. lungs & mucosa) when an attack occurs.
3/
These T rm cells, who live in tissues, are able to quickly respond to a dendritic cell that presents an antigen, without having to involve the headquarters (lymph node).
This saves time, compared to the initial infection.
4/
This saves time, compared to the initial infection.
4/
Remember that during the initial infection (in someone who has not been previously infected or vaccinated), dendritic cells have to travel all the way to lymph nodes to find naive T cells to match, activate & expand.
This process takes some time, and the delay can be costly.
5/
This process takes some time, and the delay can be costly.
5/
This research however mainly dealt with T emra cells and NOT with other types of memory cells, for the reasons explained above.
I just mentioned the diversity of T memory cells to introduce the various subtypes.
6/
I just mentioned the diversity of T memory cells to introduce the various subtypes.
6/
Past research with Yellow fever that dealt with human memory CD8+ T cells, examined several years after vaccination, found T scm to persist.
The authors believe T emra & T Scm could be part of the same phenotypical trajectory, with progressive enrichment in T scm over time.
4/
The authors believe T emra & T Scm could be part of the same phenotypical trajectory, with progressive enrichment in T scm over time.
4/
After studying effector T cell response over time, authors hypothesise that increased T emra (Terminally differentiated effector memory cells) form after severe disease, versus T scm (stem cell memory) in mild disease & upon inoculation with live attenuated virus vaccines.
5/
5/
T emra cells circulate in blood and represent the subset of effector memory cells, called “terminally differentiated”.
As they lack CCR7 receptors, they don’t home into lymphoid tissues unlike T cm (central memory) cells.
6/
As they lack CCR7 receptors, they don’t home into lymphoid tissues unlike T cm (central memory) cells.
6/
T scm have the capacity to live long and convert to other different memory cell types, upon subsequent exposure to cognate antigen.
These cells (which have sub populations) possess properties of self-renewal & clonal longevity necessary to maintain long-lived immune memory.
7/
These cells (which have sub populations) possess properties of self-renewal & clonal longevity necessary to maintain long-lived immune memory.
7/
While it is tempting to draw overtly optimistic conclusions based on these descriptions, it is critical to realise that the body works as a whole, rather than as a sum of its individual components.
Correlation with actual outcomes in real patients - over time - is important.
8/
Correlation with actual outcomes in real patients - over time - is important.
8/
Let me point out an example of such an exaggerated optimism that happened early in the pandemic.
When mRNA vaccine phase 3 trials were announced, they said “efficacy in the 94-95% range” which led many to believe that vaccines could do more than they were really capable of.
9/
When mRNA vaccine phase 3 trials were announced, they said “efficacy in the 94-95% range” which led many to believe that vaccines could do more than they were really capable of.
9/

What the vaccine makers meant was that when they looked at “symptomatic COVID-19” as the endpoint, there was a “95% difference” between the vaccinated and unvaccinated groups.
Importantly, this was measured during a period IMMEDIATELY following vaccination.
10/
Importantly, this was measured during a period IMMEDIATELY following vaccination.
10/
There was no mention of asymptomatic cases, or of efficacy decline when the antibody levels would naturally drop in a few months (IgG half life < 25 days; plasmablasts do not live long)
Moral of the story is to not mix our own optimism to technical terms in immunology.
11/
Moral of the story is to not mix our own optimism to technical terms in immunology.
11/
In summary, there is proof of long-term T cell memory after natural infection.
This can be expected to protect against future infection.
The observation that reinfections are asymptomatic or mild, lends strong supporting evidence to the findings in this research paper.
12/12
This can be expected to protect against future infection.
The observation that reinfections are asymptomatic or mild, lends strong supporting evidence to the findings in this research paper.
12/12
@threadreaderapp please unroll
A related thread
https://twitter.com/rajeevjayadevan/status/1463807837335814146
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh