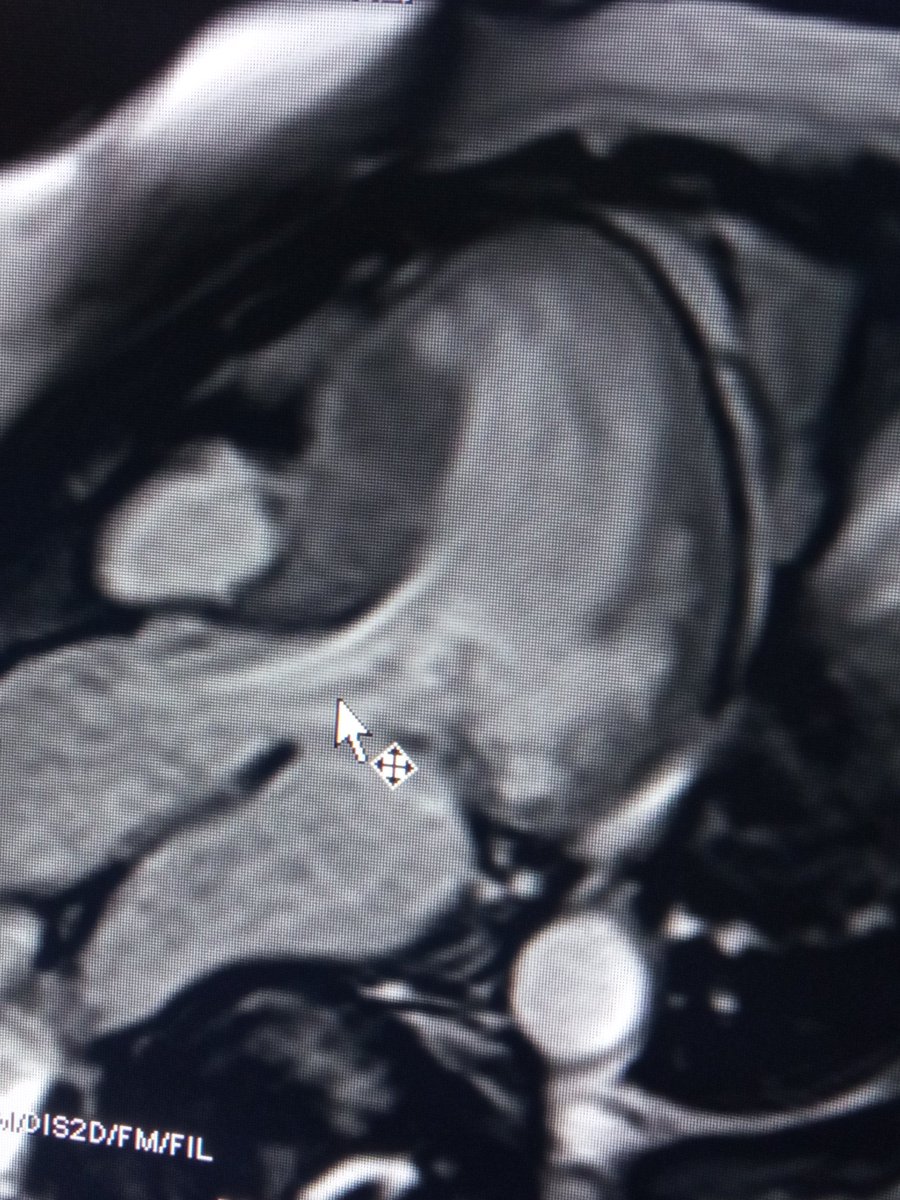
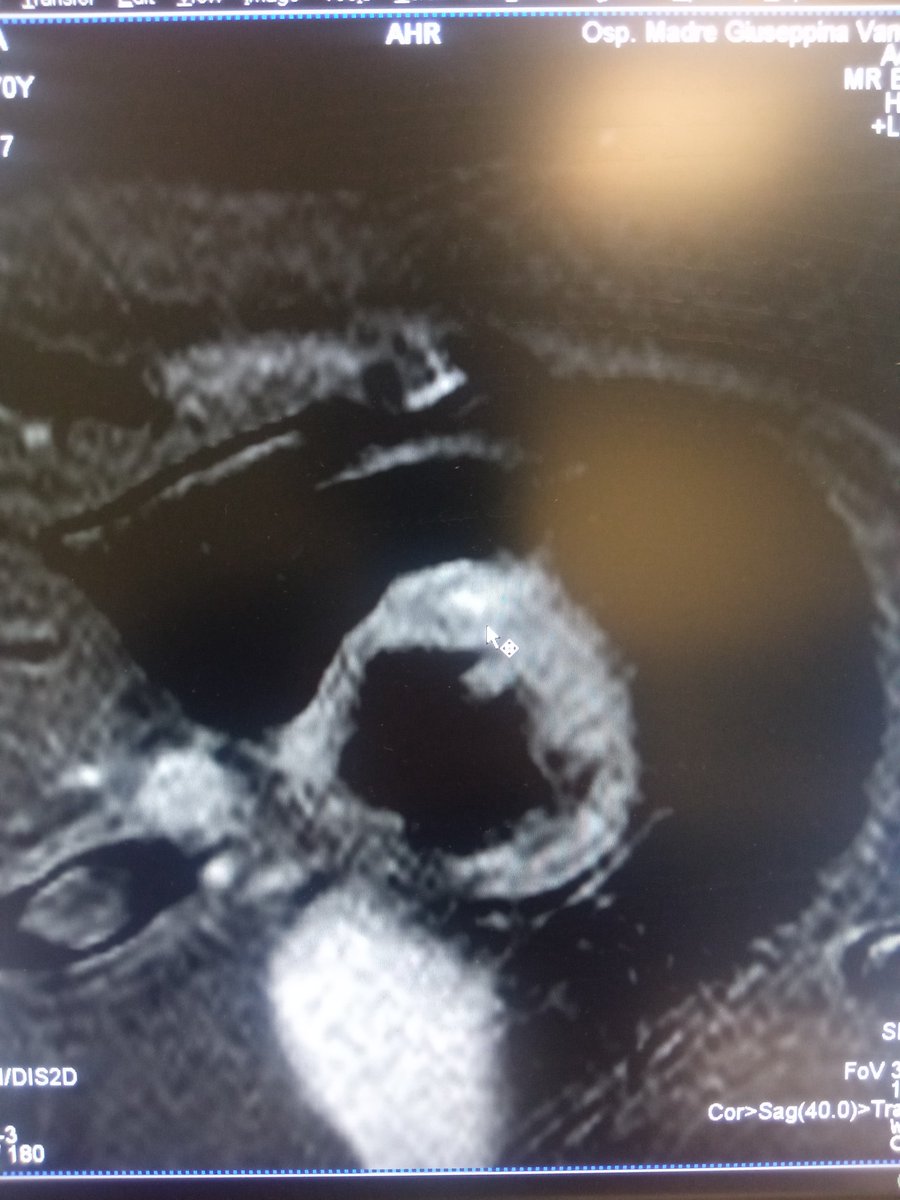
4/ Classic LGE at insertion points, not so large, not a bad prognostic sign. Edema partly matches scarred area 

6/ normal T2 in the area of increase T1 (fibrosis more than edema) - increased T2 (>50 msec) within the bright Stir region. Kill the colours by windowing, parametric assesment of T2 maps is more reliable than visual evaluation
@threadreaderapp please unroll
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh