1/ If only there was a way to make hippocampal anatomy memorable!
Here is a #tweetorial of the basics of hippocampal #anatomy that will hopefully stay in your #hippocampus! #medtwitter #FOAMed #FOAMrad #medstudent #neurorad #radres @medtweetorials #Neurology @StefanTigges
Here is a #tweetorial of the basics of hippocampal #anatomy that will hopefully stay in your #hippocampus! #medtwitter #FOAMed #FOAMrad #medstudent #neurorad #radres @medtweetorials #Neurology @StefanTigges

2/Its name “hippocampus” comes from its shape on gross anatomy. Early anatomists thought it looked like an upside down seahorse—w/its curved tail resembling the tail of a seahorse. Hippocampus literally means seahorse. 

3/In cross section, it has a spiral appearance, leading to its other name, Cornu Ammonis, translated Ammon’s Horn. Ammon was an Egyptian god w/spiraling rams horns. The hippocampal subfields are abbreviated CA-1, CA-2, etc, w/CA standing for “Cornu Ammonis” 

4/First is the hippocampal head. It has a wavy appearance, called the pes hippocampus, meaning “hippocampal foot” bc the waves look like toes. I don’t like that bc a head shouldn’t have toes. I think they look like teeth—so if you see teeth, it makes sense you are in the head. 

5/The amygdala sits above the hippocampus (A is for Above), also in the region of the hippocampal head. Amygdala means almond, bc it is shaped like an almond. This makes sense bc when I hear almond, I think almond eyes, and eyes are in the region of the head. 

6/As we go posterior, we come to the body. The body is where you can see the spiraling line that is the Cornu Ammonis. The Cornu Ammonis spirals into the dentate nucleus, which is cupped around the end of the Cornus Ammonis so that they look like a ying-yang. 

7/You can see this ying-yang on imaging. You can follow the T2 dark line of the Cornu Ammonis until it spirals into the bright dentate. This is the internal architecture of the hippocampus that you must burn into you memory—bc this is lost in mesial temporal sclerosis 

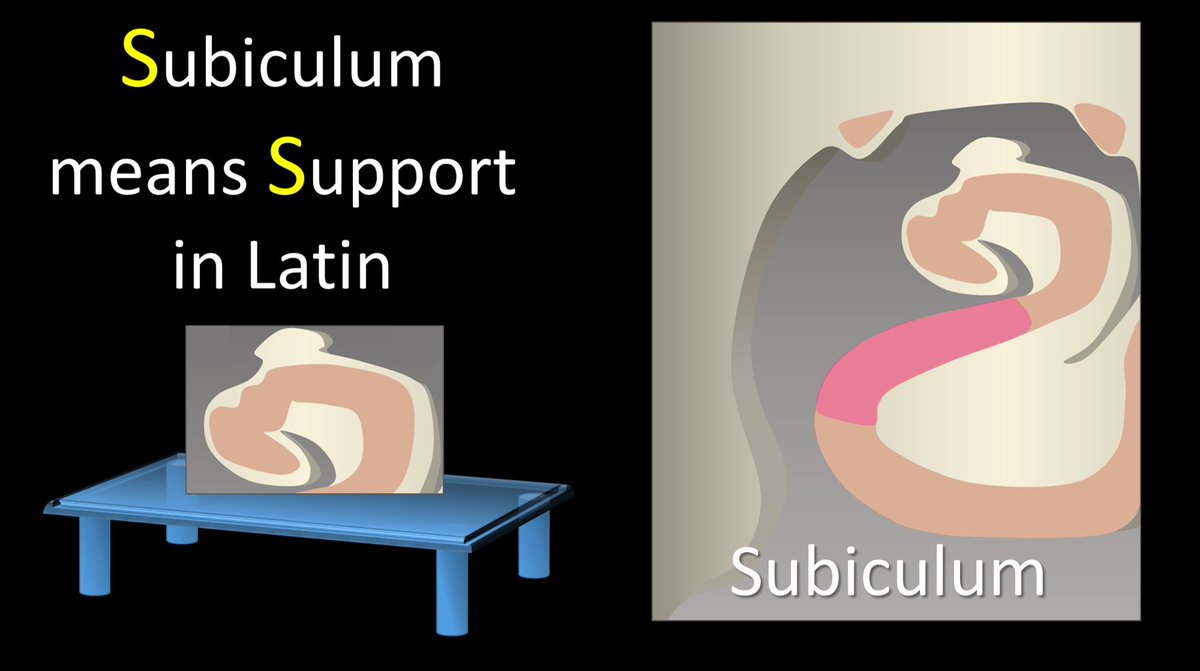
8/Below the Cornu Ammonis, is the subiculum. This name literally means support. It also helps that both Subiculum and Support start with S—so you can remember that the Subiculum is right below the Cornu Ammonis, Supporting it like a table. 
9/Below the subiculum is the entorhinal cortex. It is the last part of the hippocampal formation—so you can remember this bc it is at the edge of the hippocampal formation & both Entorhinal & Edge start w/ the letter E. 

10/Also here is the fimbria. Fimbria means cilia projections. This looks like a small cilia projection off of the Cornu Ammonis. I remember Fimbria & Flapping & Free all start w/F & this structure looks like it is flapping free. It connects to the Fornix which also starts w/F 

11/The term “hippocampus” proper only refers to the Cornu Ammonis—the T2 dark, spiraling line. All the other important structures, like the dentate, subiculum, & entorhinal cortex are part of the “hippocampal formation” when combined w/the Cornu Ammonis 

12/As we go more posterior, we come to the tail, which is very thin and tapers rapidly as it spirals upward behind the brainstem, just like the tail of a real hippocampus/seahorse 

13/The theme of hippocampal anatomy is the spiral—on every single hippocampal MRI, you should look for that T2 dark line of the Cornu Ammonis, spiraling into the dentate to make a ying yang. If this is lost & the dark line stops before it spirals, that is an early sign of MTS. 

14/So now you know the basics of hippocampal anatomy. May the hippocampal spiral stay always in your hippocampus--both literally and figuratively 😂 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh






















