1/Feeling lucky? Or feeling evidence based?
A #tweetorial about how to read a #pituitary #MRI using data and know if there’s cavernous sinus invasion w/the Knosp score.
#medtwitter #FOAMed #radres #neurorad #FOAMrad #neurosurgery #medicalstudent #meded #USMLE #endocrinology
A #tweetorial about how to read a #pituitary #MRI using data and know if there’s cavernous sinus invasion w/the Knosp score.
#medtwitter #FOAMed #radres #neurorad #FOAMrad #neurosurgery #medicalstudent #meded #USMLE #endocrinology

2/The hardest part of a pituitary MRI is deciding if there is cavernous sinus invasion. It makes sense that the more lateral a tumor goes on MRI, the more likely it has invaded the sinus—bc it is going the direction of the sinus. But how far is far enough? 

3/This is important bc each time a radiologist makes a call on imaging, they make a bet & they are betting their credibility. And unlike other bets, there is only 1 wager—all in! So it is important to not call it when you might be wrong, bc overcalls destroy credibility. 

4/We know for medial tumors we shouldn’t call it bc the chance of being wrong outweighs being right. And if it is very lateral, chance of being right outweighs being wrong & we should call it. But where does the chance of being right outweigh being wrong? Knosp score will tell us 

5/Knosp score is based on the position of the tumor w/respect to the ICA. Cavernous/supraclinoid ICA is shaped like a macaroni elbow, so when you cut it in cross section, you see circles that are the two ends of the macaroni—top one is supraclinoid ICA, bottom is cavernous ICA. 

6/Knosp grade draws 3 lines along the circles—(1)medial carotid line, medial to the circles, (2)intercarotid line through the center of the circles & (3)lateral carotid line, lateral to the circles. They are like 3 traffic lights—w/the color=the chance of cav sinus invasion 
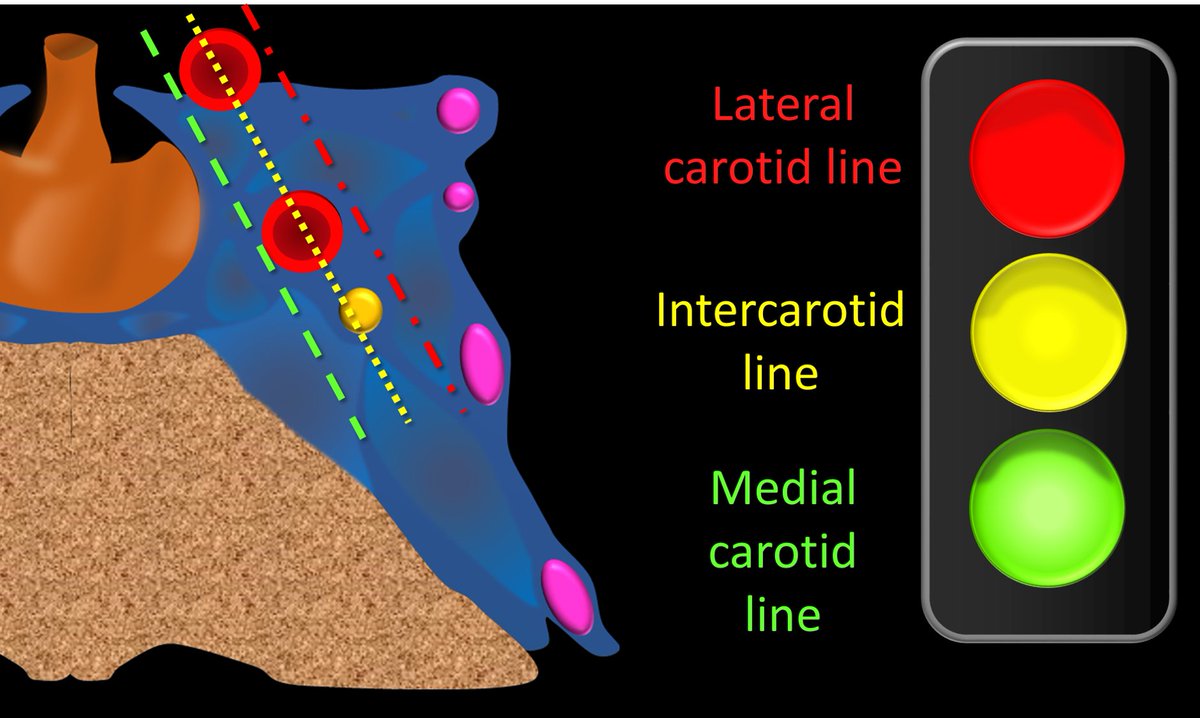
7/At the most medial the tumor does even reach the medial line. There is essentially no chance of cav sinus invasion (7%). But you don’t need a Knosp score for this—a tumor that doesn’t really approach the cav sinus probably doesn’t invade it (thank you Captain Obvious!) 

8/As the tumor goes more lateral, it crosses the medial carotid line. But it only crosses the green line, so green is still good to keep moving & pass up calling invasion. Only 1 in 5 of these will have invasion, so if you call it, you will be wrong 80%--not good 

9/Going more laterally, now you cross the intercarotid line—the yellow line. Yellow means caution or slow down. These will invade the cav sinus in about half of cases. So it is enough to make you slow down, and take a good look, but not enough to stop and call it. 

10/This is because 50% is still essentially a coin flip. You wouldn’t put all your money on black, so you shouldn’t put all your credibility on something that could be wrong half the time. So you want to hold back your chips here and say that it does not definitively invade. 

11/Finally you cross the lateral carotid line—this is the red line—which means stop and call it. This is bc you will be right almost 90% of the time. Red = bad = stop = in the cav sinus 

12/This is a bet that you want to make—you would put serious money on a bet that has a 90% chance of winning (you probably put it on bets that are less in the stock market nowadays!). So take advantage of knowing you will be right and call it. 

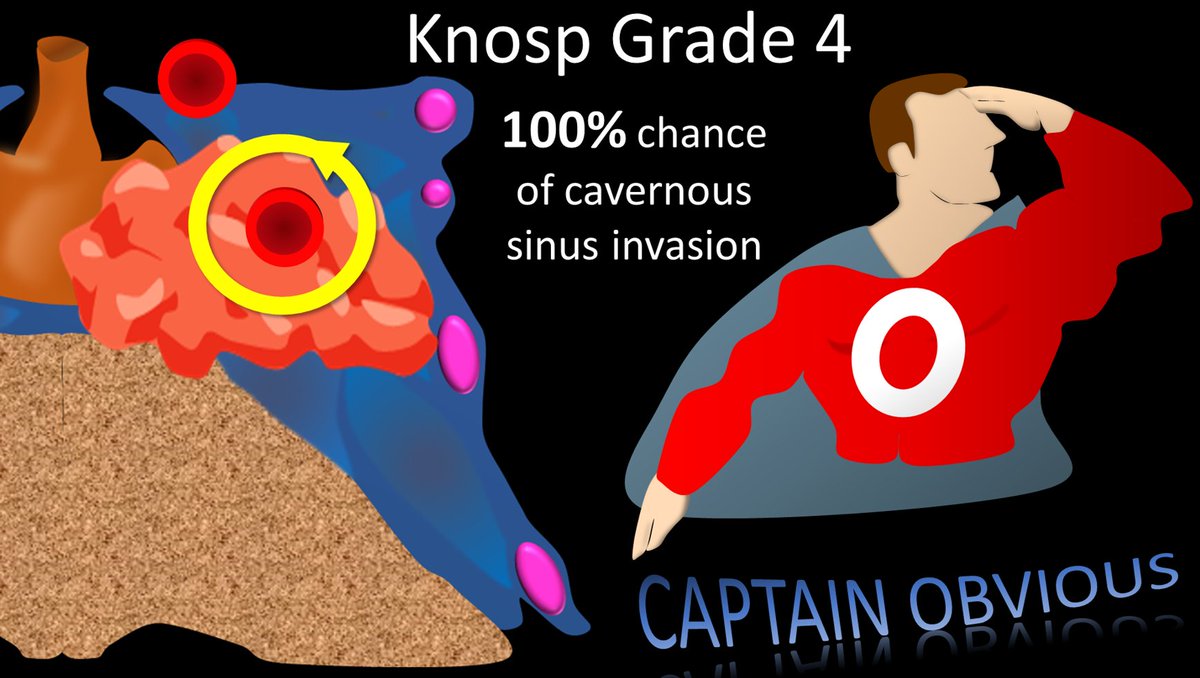
13/The last Knosp grade is when tumor surrounds the cavernous ICA. This has a 100% chance of cav sinus invasion. No surprise that if the tumor completely surrounds something in the cav sinus that the tumor is also, wait for it…in the cav sinus. Thanks Captain Obvious. 
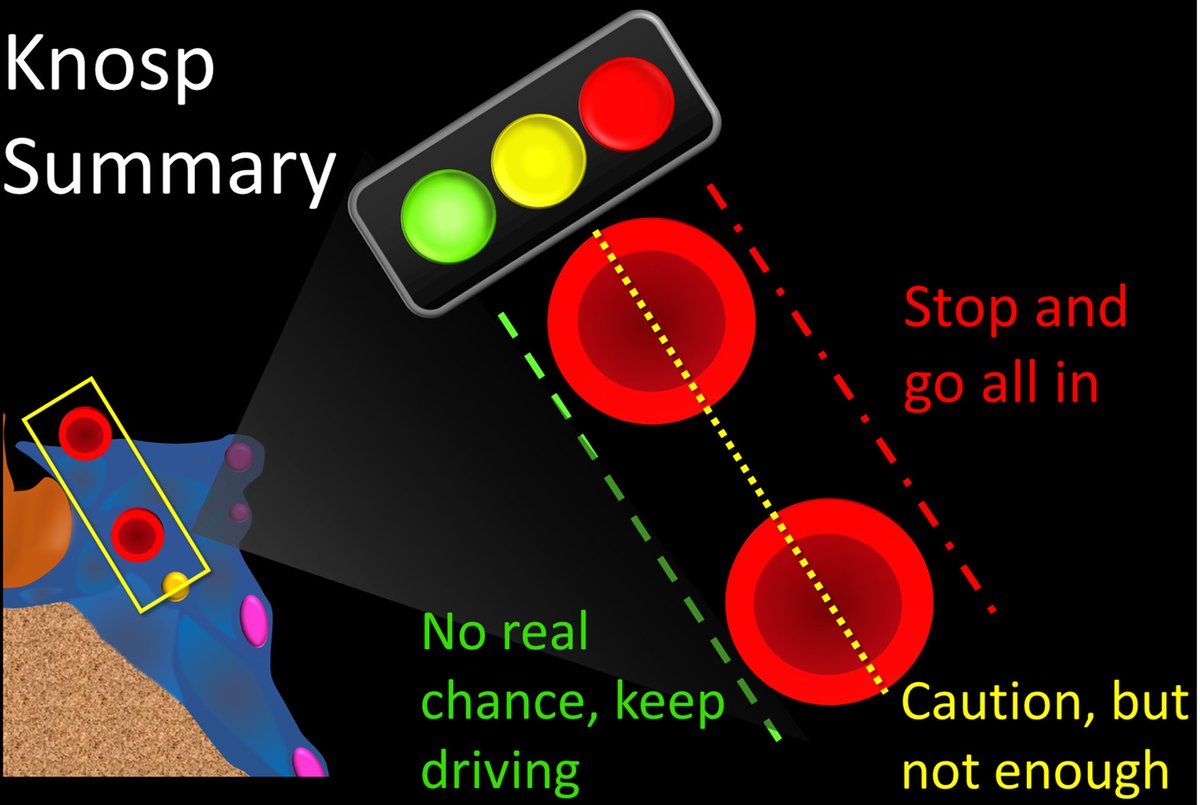
14/To summarize, think of the Knosp lines as 3 traffic lights—the color of the line crossed tells you what you should do. Cross medial green, keep going—there is nothing to call. Cross middle yellow—slow down, it is close but not definitive. Cross lateral red, stop & go all in. 
15/So now you know the Knosp score & how it can help you to be right. So use it and don’t settle for a cheap Knosp off 😂. Let the data be your superpower! 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh






















