1/
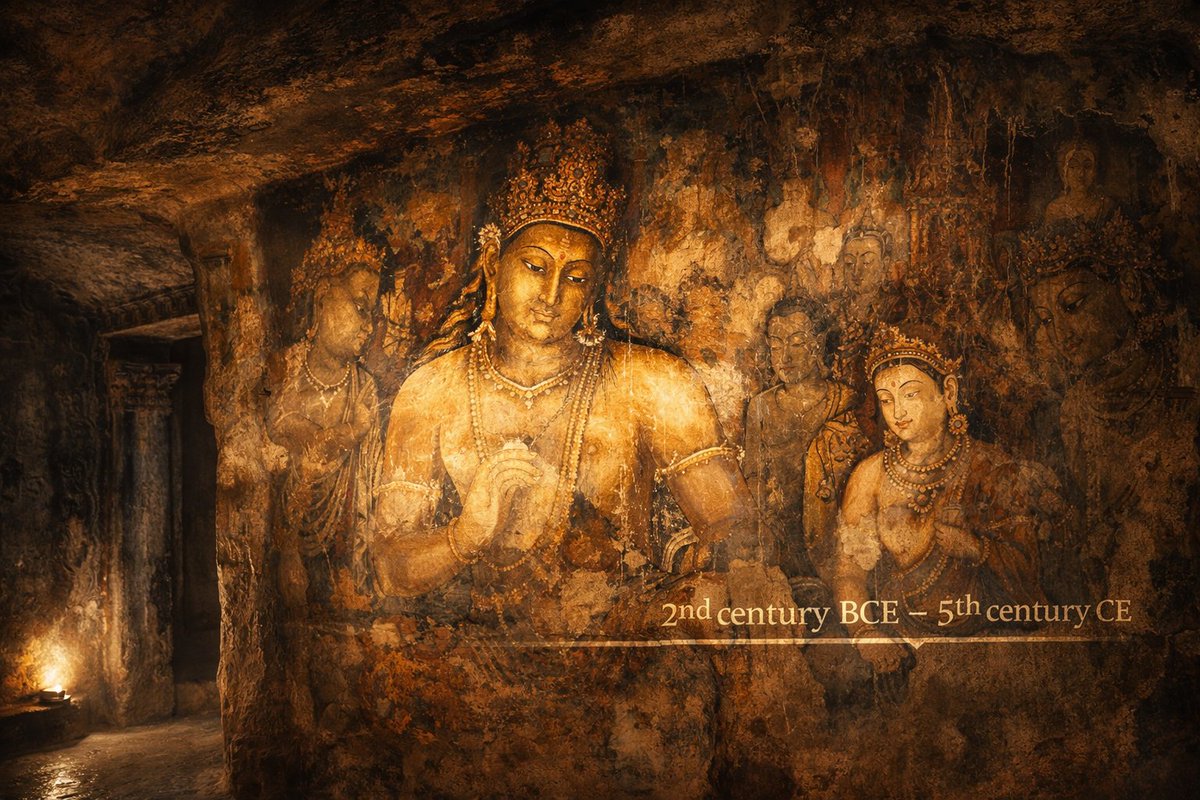
“The Athens of South India” - 'Madurai' c.500 bce
Megasthenese, Strabo 25BC, Pliny 75 AD Ptolemy 130AD mention of Madurai.
#Keeladi an excavation site in this small #Thread
#Archaeology
“The Athens of South India” - 'Madurai' c.500 bce
Megasthenese, Strabo 25BC, Pliny 75 AD Ptolemy 130AD mention of Madurai.
#Keeladi an excavation site in this small #Thread
#Archaeology

2/n
#Keeladi was an industrial area of #madurai dated back around 580 BCE determined from the excavated Artefacts
thehindu.com/news/national/…
#Archaeology

#Keeladi was an industrial area of #madurai dated back around 580 BCE determined from the excavated Artefacts
thehindu.com/news/national/…
https://twitter.com/gemsofindology/status/1284164651090157570?s=20
#Archaeology


3/n
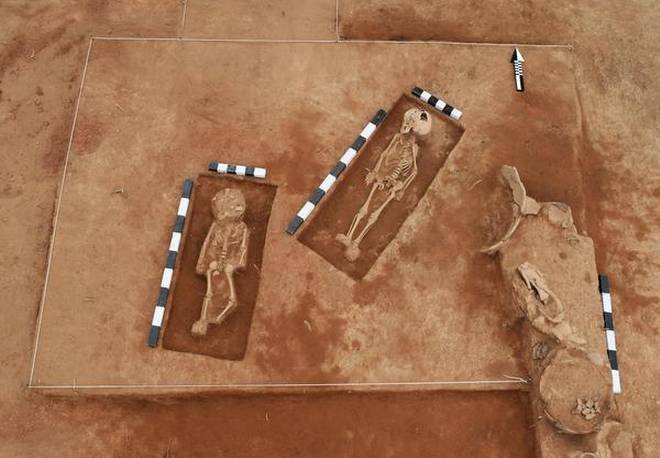
The Keeladi residents used to burry their deads in North South direction
thehindu.com/news/cities/Ma…
#Keeladi were experts in Structural #Engineering. They had Plumbing System, Draining system, Water storage system
#Archaeology
thehindu.com/news/cities/Ma…



The Keeladi residents used to burry their deads in North South direction
thehindu.com/news/cities/Ma…
#Keeladi were experts in Structural #Engineering. They had Plumbing System, Draining system, Water storage system
#Archaeology
thehindu.com/news/cities/Ma…




4/n
A researcher of #IVC, R. Balakrishnan, points to the similarities in urban planning between the Indus Valley and Keeladi. Some of the symbols found in pot sherds of Keeladi bear a close resemblance to Indus Valley signs. thehindu.com/news/national/…
#Archaeology

A researcher of #IVC, R. Balakrishnan, points to the similarities in urban planning between the Indus Valley and Keeladi. Some of the symbols found in pot sherds of Keeladi bear a close resemblance to Indus Valley signs. thehindu.com/news/national/…
#Archaeology


5/
The Literacy rate was very high among #keeladi. Their prime occupation was weaving, looming, yarning,, iron industry, carpentry, pottery. They were cultural rich & prosperous. Game objects posturizes the games and pastime activities for kids & elders
#Archaeology

The Literacy rate was very high among #keeladi. Their prime occupation was weaving, looming, yarning,, iron industry, carpentry, pottery. They were cultural rich & prosperous. Game objects posturizes the games and pastime activities for kids & elders
#Archaeology


6/
Some artifacts found overseas indicates South Indian traders exported as well.
#Archaeology
There were Port towns, and Minor Ports. The confluence of Palar, Cauvery, Vaigai and Tamiraparani played major role in logistics of goods.

Some artifacts found overseas indicates South Indian traders exported as well.
#Archaeology
There were Port towns, and Minor Ports. The confluence of Palar, Cauvery, Vaigai and Tamiraparani played major role in logistics of goods.
https://twitter.com/GemsOfIndology/status/1292788384587546624?s=20&t=T4n5aqy0JVLxwKvo08SIXQ

7/
Similarities in #IVC and #Southindian #Tamil #dravidian #ancient scripts are detailed in this thread
#Archaeology
Similarities in #IVC and #Southindian #Tamil #dravidian #ancient scripts are detailed in this thread
https://twitter.com/gemsofindology/status/1293043885288108034?s=20
#Archaeology
7/
Similarities in #IVC and #Southindian #Tamil #dravidian #ancient scripts are detailed in this thread
#Archaeology
Similarities in #IVC and #Southindian #Tamil #dravidian #ancient scripts are detailed in this thread
https://twitter.com/gemsofindology/status/1293043885288108034?s=20
#Archaeology
8/
Src: vinavu.com/wp-content/upl…
Src: vinavu.com/wp-content/upl…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh