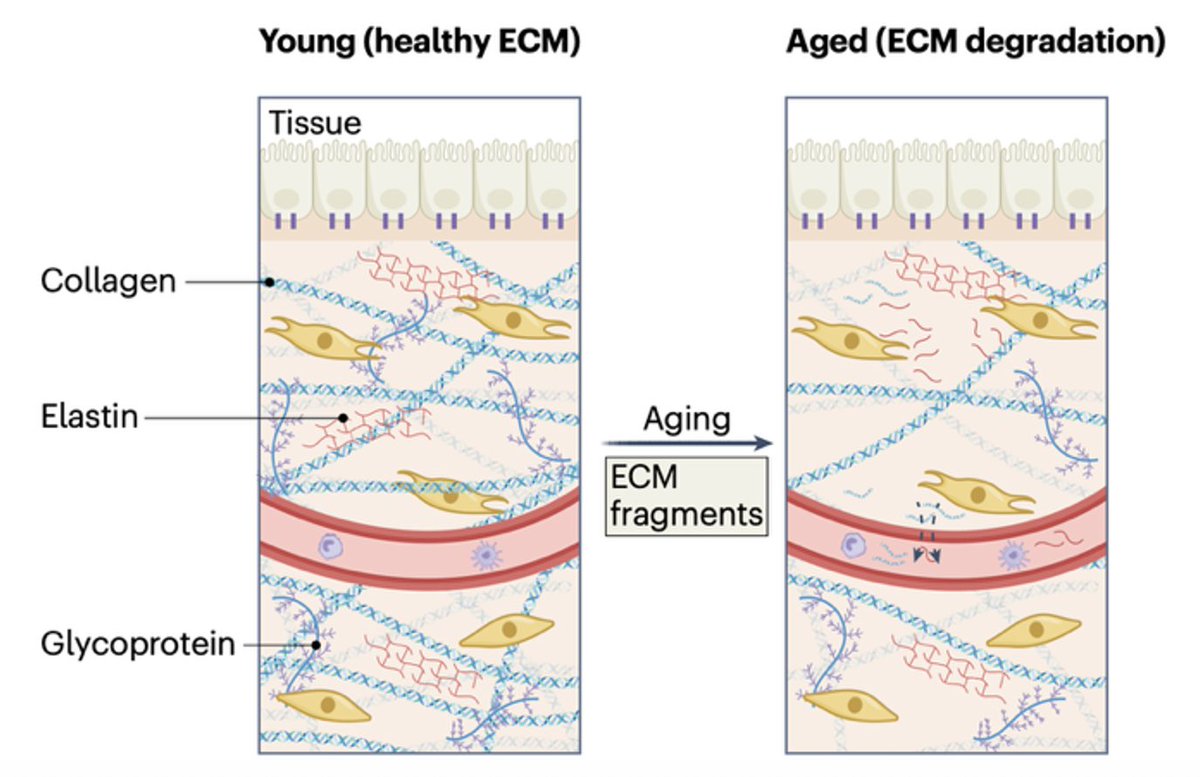
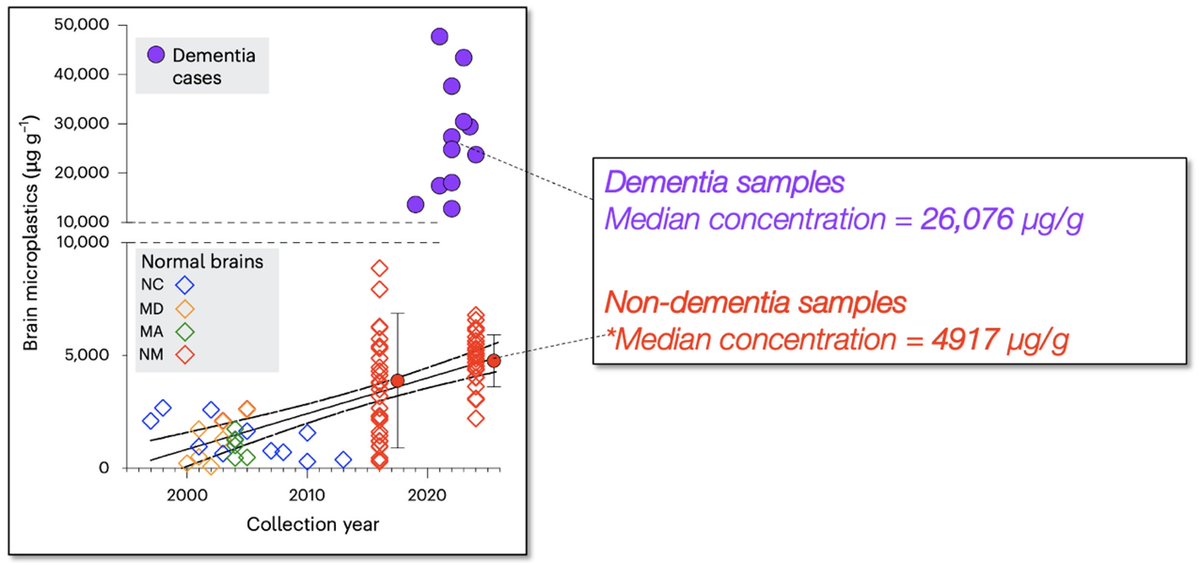
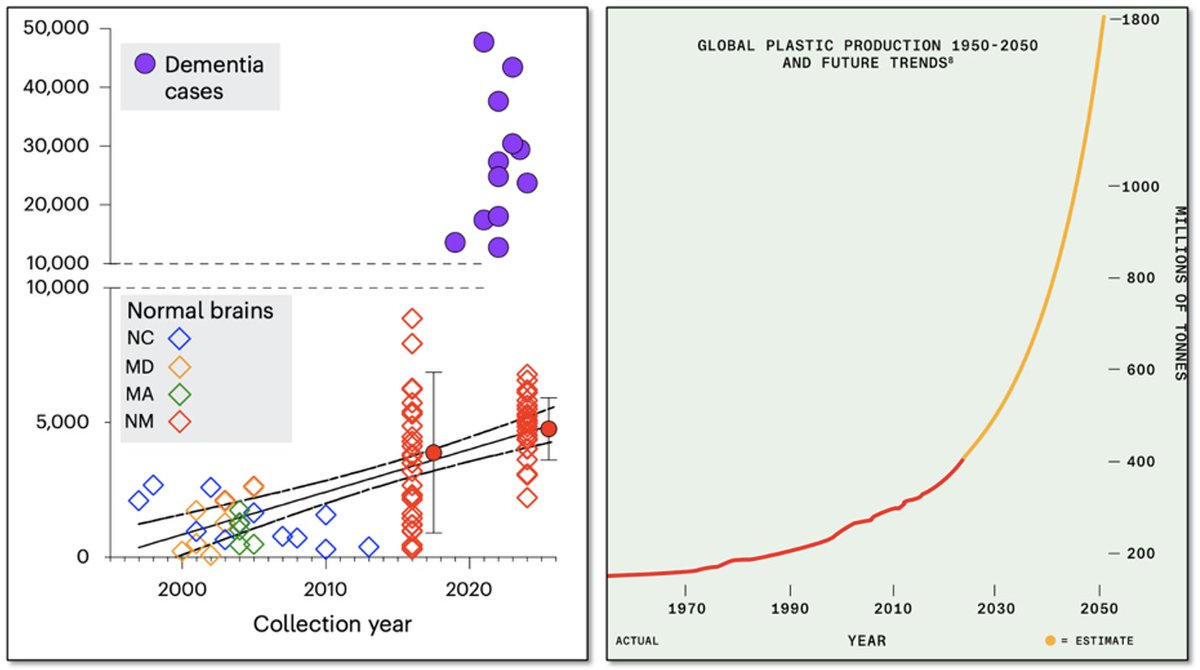
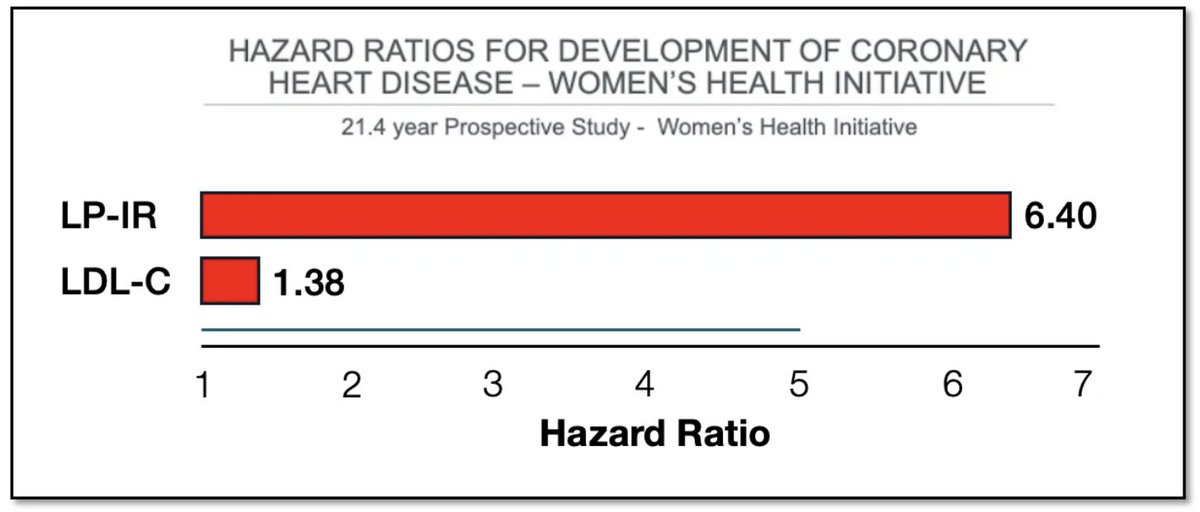
#Vegan🌱#keto (low sat fat, 0 cholesterol)
vs.
Meat and Egg heavy diet + 120g net carbs
N=1 Crossover experiment
Surprisingly, LDL >300 mg/dL on vegan keto and ~100 mg/dL on meat and egg plus carb diet 🤯
👉 If this doesn't make you curious, I don't get you
vs.
Meat and Egg heavy diet + 120g net carbs
N=1 Crossover experiment
Surprisingly, LDL >300 mg/dL on vegan keto and ~100 mg/dL on meat and egg plus carb diet 🤯
👉 If this doesn't make you curious, I don't get you

2/ This contradicts the explanation that sat fat is the primary driver of ⬆️ LDL on low-carb
While it may represent an outlier case (& sat fat may primarily drive⬆️LDL in others), that these lipid results can present in anyone requires an explanation beyond conventional wisdom
While it may represent an outlier case (& sat fat may primarily drive⬆️LDL in others), that these lipid results can present in anyone requires an explanation beyond conventional wisdom
3/ 2022 has been a good year for study of the Lean Mass Hyper-Responder phenotype with 5 manuscripts published:
-Demonstrating presence of the phenotype
-Providing explanation in the form of the Lipid energy model #LEM
-Calling for further research

-Demonstrating presence of the phenotype
-Providing explanation in the form of the Lipid energy model #LEM
-Calling for further research
https://twitter.com/nicknorwitz/status/1589271162995224578?s=20&t=VAEUS68gWtUfoN45auvc-Q

4/ Looking forward to 2023 and beyond, I am BEYOND excited to pursue further work to help better understand the "what" and "how" of LMHR!
We need to better classify the phenotype and untangle the mystery within the mechanism!
We need to better classify the phenotype and untangle the mystery within the mechanism!
5/ Importantly this isn't an "us vs. them"
This is NOT about diet tribes, disproving the lipid heart hypothesis, etc. Not at all
This is about pursuing an open ? with implications for our understanding of lipidology & help direct patient care... wherever the data fall
This is NOT about diet tribes, disproving the lipid heart hypothesis, etc. Not at all
This is about pursuing an open ? with implications for our understanding of lipidology & help direct patient care... wherever the data fall
6/ So, for now, all I have to ask is, "do you have a good explanation for these results in this patient?"
If not...
WATCH
THIS
SPACE!
If not...
WATCH
THIS
SPACE!

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh