1/Nothing strikes fear into the heart of a radiologist like the question,“Is it safe to do an MRI on this pt w/an implanted device?”
Never fear again! Here’s a #tweetorial on how to navigate implanted devices & #MRI
#medtwitter #meded #radtwitter #radres #neurotwitter #neurorad
Never fear again! Here’s a #tweetorial on how to navigate implanted devices & #MRI
#medtwitter #meded #radtwitter #radres #neurotwitter #neurorad

2/MRI & CT are like nuclear & coal power, respectively. Everyone knows CT is worse for you & usually MRI is very safe & better for your body
But like nuclear power, when things go bad in MRI, they can go horribly wrong. Flying chairs into the magnet wrong. So, people are afraid
But like nuclear power, when things go bad in MRI, they can go horribly wrong. Flying chairs into the magnet wrong. So, people are afraid

3/The trouble is from the magnetic attractive forces. There are 3 ways these attractions can wreak havoc. First is translation. Magnet literally pulls an object, like a chair, towards itself. This is the strongest attraction—like two lovers who literally can’t stay apart. 

4/Second is torque or rotation. This is when the force isn’t strong enough to pull the object away, but enough to make it wiggle or turn a bit.
It’s like an attraction that isn’t enough to make you run, but enough to make you turn your head & look.
It’s like an attraction that isn’t enough to make you run, but enough to make you turn your head & look.

5/Last is the sneakiest way the magnet damages—heat. Radiofrequency (RF) waves deposit heat, like other waves, such as microwaves. This causes internal heating w/o any movement.
It’s like the hot passion you feel deep inside for your lover, regardless of any physical contact
It’s like the hot passion you feel deep inside for your lover, regardless of any physical contact

6/All of these effects stem from the fact that the MR is just a giant magnet & its exerts forces on objects in the magnetic field.
Since these effects are from a magnet, it makes sense that metal objects would be the most affected—as metals can be magnetized.
Since these effects are from a magnet, it makes sense that metal objects would be the most affected—as metals can be magnetized.

7/But not all metals are affected the same by the magnetic field. We all know that metals like nickel & iron are very attracted to magnets, while other metals like calcium are not.
More affected objects will feel more force in the MRI & are more likely to move/cause damage.
More affected objects will feel more force in the MRI & are more likely to move/cause damage.

8/We classify implants by how likely they’ll move in the MR field. MR unsafe devices are highly magnetic & could fly into the MRI & thus are banned. MR safe means no metal or magnetic properties, completely unaffected. MR conditional is in between, some attraction, but not strong 

9/How do we know which metals are unsafe & which are possibly safe?
There are two main types of magnetic metals.
Ferromagnetic metals are very magnetic. I remember this b/c ferro sound like ferocious, & so they are ferociously magnetic.
These are MR unsafe.
There are two main types of magnetic metals.
Ferromagnetic metals are very magnetic. I remember this b/c ferro sound like ferocious, & so they are ferociously magnetic.
These are MR unsafe.

10/Four main ferromagnetic metals exist: iron, nickel, cobalt, & steel. Remember this by remembering a dashing, some might say magnetic, Knight. He wears wrought IRON armor, holds a strong STEEL sword, & rides a bolting colt (COBALT). He’s a poor mercenary, so he’s paid w/NICKELs 

11/While ferromagnetic metals are MR unsafe, their alloys are not. Adding other metals can counteract the magnetism or transform it into a completely new metal that isn’t magnetic.
Most medical devices are these alloys. You really only see true ferromagnetic metals in shrapnel
Most medical devices are these alloys. You really only see true ferromagnetic metals in shrapnel

12/While ferromagnetic objects are strongly magnetic, paramagnetic objects are only weakly magnetic.
I remember this b/c they are PARamagnetic & PAR in golf means just average, nothing really special.
So there is no special or strong magnetism in these metals.
I remember this b/c they are PARamagnetic & PAR in golf means just average, nothing really special.
So there is no special or strong magnetism in these metals.

13/Paramagnetic objects are MR conditional. They have the potential to cause tissue damage by torque objects or heating objects. This risk must be weighed against the benefit of getting an MRI 

14/Torque can be a problem.
However, if the device is in anything w/motion (vessel w/flowing blood, beating heart, moving bones), torque from physiologic motion is stronger than any from the magnet.
So if it stays in place w/natural forces, it won’t be moved by the magnet.
However, if the device is in anything w/motion (vessel w/flowing blood, beating heart, moving bones), torque from physiologic motion is stronger than any from the magnet.
So if it stays in place w/natural forces, it won’t be moved by the magnet.

15/They say you should wait 6 weeks after any implanted device before scanning, to let scar tissue form to further anchor the device.
While this is ideal, it isn’t really necessary—b/c if the physiologic forces haven’t dislodged it yet, neither will the magnet.
While this is ideal, it isn’t really necessary—b/c if the physiologic forces haven’t dislodged it yet, neither will the magnet.

16/But what if the paramagnetic device isn’t in a location where there is motion to test it? What if it’s in the kidney? Is it still safe? It probably is, b/c the magnetic forces are weak. Check the manufacturer recommendations to see how much magnetic force you can use & be safe 

17/Paramagnetic objects can heat up. Even w/low magnetism, you get heating—& it’s hard to predict b/c the heat amount depends on the patient, scan parameters, etc
So every pt w/a device should get a squeezy ball to squeeze if they feel heating—to stop the scan before any damage
So every pt w/a device should get a squeezy ball to squeeze if they feel heating—to stop the scan before any damage

18/A special problem for heating is 1 dimensional (1D) wires.
These collect RF energy like an old TV antenna & concentrate the energy at their tip—leading to high risk of burns at the tip.
So any device with a 1D wire needs a special protocol to prevent overheating
These collect RF energy like an old TV antenna & concentrate the energy at their tip—leading to high risk of burns at the tip.
So any device with a 1D wire needs a special protocol to prevent overheating
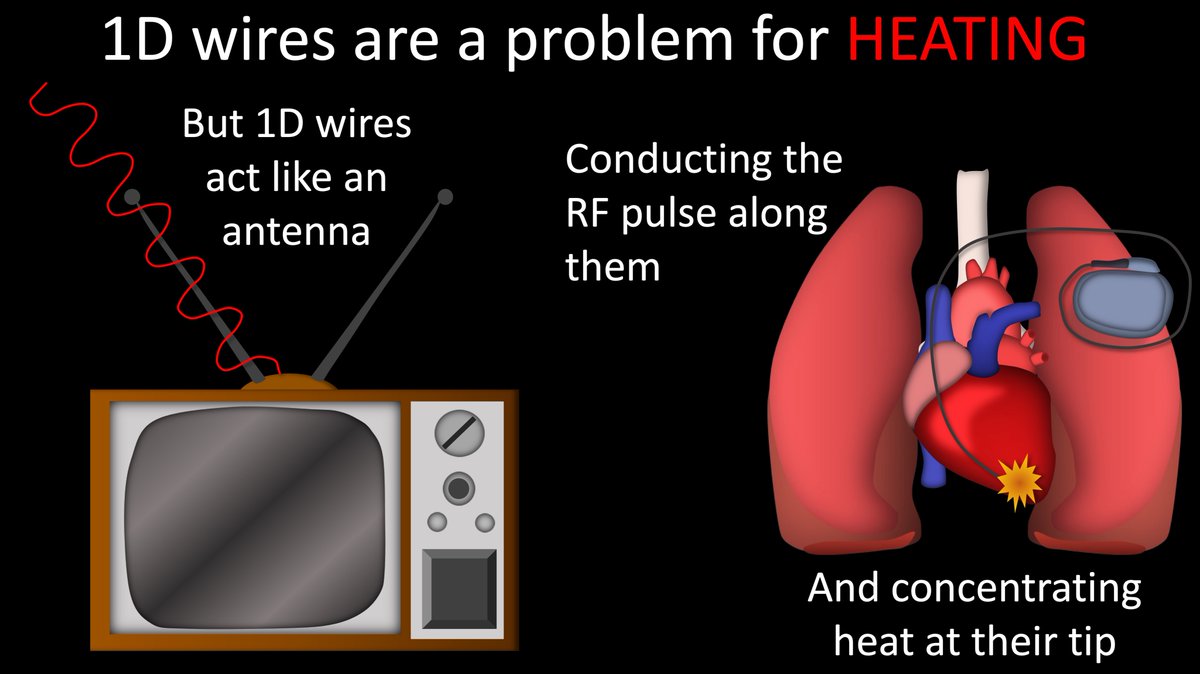
19/RF pulses not only heat, they also can interfere w/electronics of devices—like jamming radio signals.
This can lead to device malfunction or even delivery of incorrect signals that can cause arrhythmias.
Special care must be taken & devices should be checked after scanning
This can lead to device malfunction or even delivery of incorrect signals that can cause arrhythmias.
Special care must be taken & devices should be checked after scanning

20/As a result, scanning protocols for devices w/1D leads (pacers, DBS) are very strict & require oversight. Even then, there is hesitancy to scan 1D leads w/high risk of heating (abandoned leads, temporary leads) 

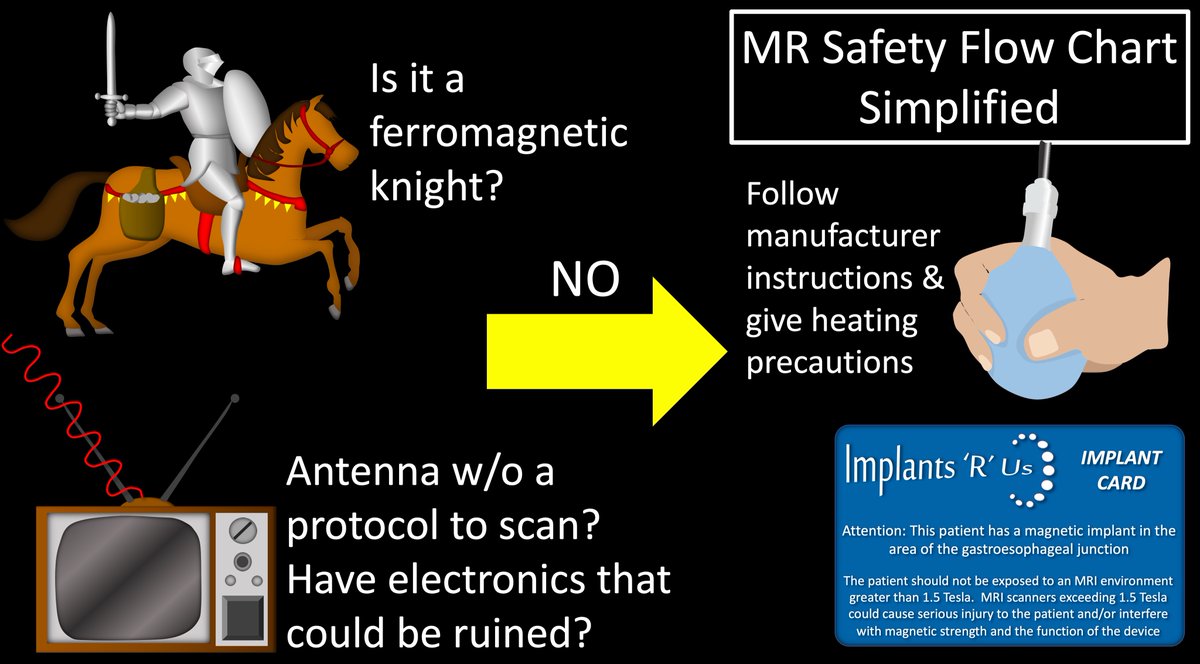
21/So there are 4 questions to ask yourself to determine if an device is safe:
Is it:
(1) ferromagnetic?
(2) a 1D lead?
(3) a device w/vulnerable electronics?
If not, it usually safe to scan using the protocol recommended by the manufacturer.
Is it:
(1) ferromagnetic?
(2) a 1D lead?
(3) a device w/vulnerable electronics?
If not, it usually safe to scan using the protocol recommended by the manufacturer.

22/The quick & dirty method: Is it a ferromagnetic knight? Is it an old TV w/electronics or antenna? If not, then scan carefully w/manufacturer’s recs.
Now you know the secret of safe MRI scanning w/implants. Hopefully this tweetorial has been a white knight to your rescue!
Now you know the secret of safe MRI scanning w/implants. Hopefully this tweetorial has been a white knight to your rescue!
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh






















