1/To call it or not to call it? That is the question!
Do you feel a bit wacky & wobbly when it comes to calling normal pressure hydrocephalus on imaging?
Here’s a #tweetorial about imaging NPH!
#medtwitter #meded #neurotwitter #neurorad #radres #dementia #neurosurgery #FOAMed
Do you feel a bit wacky & wobbly when it comes to calling normal pressure hydrocephalus on imaging?
Here’s a #tweetorial about imaging NPH!
#medtwitter #meded #neurotwitter #neurorad #radres #dementia #neurosurgery #FOAMed

2/First, you must understand the pathophysiology of “idiopathic” or iNPH. It was first described in 1965—but, of the original six in the 1965 cohort, 4 were found to have underlying causes for hydrocephalus.
This begs the question—when do you stop looking & call it idiopathic?
This begs the question—when do you stop looking & call it idiopathic?

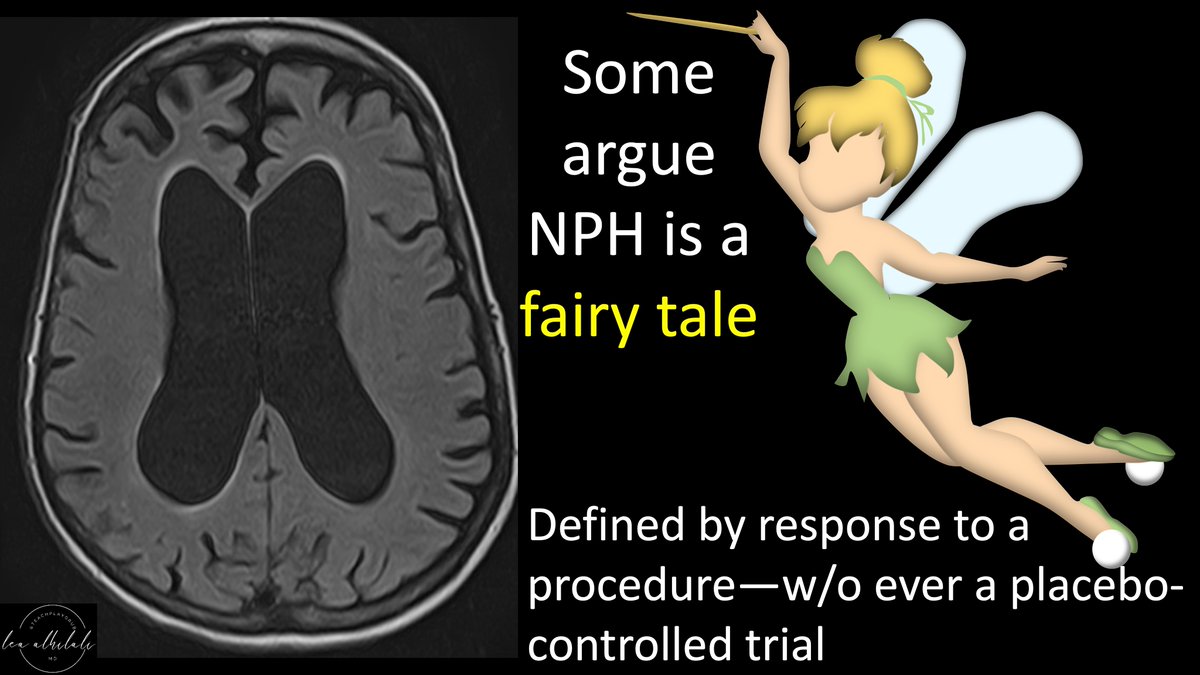
3/Thus, some don’t believe true idiopathic NPH exists. After all, it’s a syndrome defined essentially only by response to a treatment w/o ever a placebo-controlled trial.
However, most believe iNPH does exist--but its underlying etiology is controversial. Several theories exist
However, most believe iNPH does exist--but its underlying etiology is controversial. Several theories exist
4/Think of the aging brain like an aging body. What happens when you get old?
First, you get stiffer. So do vessels in the brain, so they’re less pulsatile. Their pulsatility helps move CSF in the brain. So you get less CSF movement & CSF build up. Some believe this causes iNPH
First, you get stiffer. So do vessels in the brain, so they’re less pulsatile. Their pulsatility helps move CSF in the brain. So you get less CSF movement & CSF build up. Some believe this causes iNPH

5/Next, you get constipated—you have trouble getting rid of your waste. Same in the brain
Glymphatic system removes brain waste. Diminished arterial pulsations also cause inefficient glymphatic flow & waste build up. Some believe underlying glymphatic insufficiency causes iNPH
Glymphatic system removes brain waste. Diminished arterial pulsations also cause inefficient glymphatic flow & waste build up. Some believe underlying glymphatic insufficiency causes iNPH

6/Finally, your prostate gets big & blocks your ability to get rid of fluid. Same for the brain.
NPH is associated w/sleep apnea—which blocks venous return/outflow & thus increases cerebral venous pressure—making it difficult to move CSF out of the brain into the venous system
NPH is associated w/sleep apnea—which blocks venous return/outflow & thus increases cerebral venous pressure—making it difficult to move CSF out of the brain into the venous system

7/How does iNPH cause symptoms?
Increased CSF expands ventricles. Expanding ventricles is like blowing up a balloon. Larger the balloon, the more surface pressure.
Larger ventricles lead to increased surface pressure & results in mechanical periventricular/ependymal damage
Increased CSF expands ventricles. Expanding ventricles is like blowing up a balloon. Larger the balloon, the more surface pressure.
Larger ventricles lead to increased surface pressure & results in mechanical periventricular/ependymal damage

8/It also causes ischemia. Blood flow in the brain is from the surface vessels inward. But ventricular pressure is pushing outward.
This opposing pressure increases how much pressure blood needs to reach the deep parts of the brain, resulting in chronic deep ischemia
This opposing pressure increases how much pressure blood needs to reach the deep parts of the brain, resulting in chronic deep ischemia

9/Similarly, solutes in your brain flow from the interstitial space to the CSF as a clearance mechanism
Increased pressure at the ventricular surface makes it harder for solutes to transit, thus resulting in build up of solutes like amyloid—causing damage just like Alzheimer’s
Increased pressure at the ventricular surface makes it harder for solutes to transit, thus resulting in build up of solutes like amyloid—causing damage just like Alzheimer’s

10/In fact, up to 2/3rd of NPH have underlying Alzheimer’s disease (AD) pathology. So it’s common for AD & NPH to coexist. NPH is a risk factor for AD!
This is why gait problems in some NPH patients are helped by shunting, but the dementia is not—bc there’s also underlying AD
This is why gait problems in some NPH patients are helped by shunting, but the dementia is not—bc there’s also underlying AD

11/So the classic question of “are the imaging findings related to volume loss/AD or hydrocephalus/NPH” isn’t really a fair question—bc it’s often both.
But shunting in NPH even w/AD can still help by improving gait & decreasing falls. So when do you suggest NPH on imaging?
But shunting in NPH even w/AD can still help by improving gait & decreasing falls. So when do you suggest NPH on imaging?

12/There’s an iNPH Radscale, which scores 7 different imaging features. Score above 8 is very sensitive for iNPH.
But who’s going to take out calipers & evaluate SEVEN different imaging findings on every dementia MR? Also this scale doesn’t predict who will respond to shunting
But who’s going to take out calipers & evaluate SEVEN different imaging findings on every dementia MR? Also this scale doesn’t predict who will respond to shunting

13/Measurements aren’t just burdensome, they also introduce inter-reader variability.
In fact, many of the Radscale measurements can vary depending on scan angle. Many are based on scans through the AC-PC line or perpendicular to it—& can change if the tech changes the angle
In fact, many of the Radscale measurements can vary depending on scan angle. Many are based on scans through the AC-PC line or perpendicular to it—& can change if the tech changes the angle

14/Luckily, the prospective SIHPHONI trial in NPH narrowed it down to 2 imaging criteria.
First is Evans index >0.3. This is the ratio of the max frontal horn diameter to the max cranial vault diameter—a ratio greater than 0.3 indicates hydrocephalus (of any kind) is present
First is Evans index >0.3. This is the ratio of the max frontal horn diameter to the max cranial vault diameter—a ratio greater than 0.3 indicates hydrocephalus (of any kind) is present

15/An Evans index >0.3 means the ventricles look like the eyes of the mask that the killer wears in the “Scream” movies.
If the ventricles are so big that they look like horror movie mask eyes, it’s hydrocephalus. So if I see the eyes of a ghost mask looking at me, I call it.
If the ventricles are so big that they look like horror movie mask eyes, it’s hydrocephalus. So if I see the eyes of a ghost mask looking at me, I call it.

16/So Evans >0.3 means hydro. How do we know the hydro is iNPH?
For this, SIMPHONI used the finding of tight medial CSF spaces but wide Sylvian fissures. Some call this disproportiately enlarged subarachnoid spaces (DESH). This specific type of DESH is best seen on coronals
For this, SIMPHONI used the finding of tight medial CSF spaces but wide Sylvian fissures. Some call this disproportiately enlarged subarachnoid spaces (DESH). This specific type of DESH is best seen on coronals

17/I think that this finding makes the brain on coronal images look like a chipmunk.
Widened Sylvian fissures separate the temporal lobes from the rest of the brain, making them look like chipmunk cheeks & the tight vertex looks like the little chipmunk tuft of hair at the top
Widened Sylvian fissures separate the temporal lobes from the rest of the brain, making them look like chipmunk cheeks & the tight vertex looks like the little chipmunk tuft of hair at the top

18/This separation of the temporal horn (chipmunk cheeks), is not typically seen in volume loss, where the sylvian fissures remain relatively closed.
So other forms of volume loss will look more like a mushroom & NPH will give you a chipmunk
So other forms of volume loss will look more like a mushroom & NPH will give you a chipmunk

19/In fact, seeing the combo of Scream horror mask & chipmunk face means that there’s a 70-80% the patient will respond to shunting—which is basically the NPH response rate in general!
So now you know to look for the chipmunk so you won’t have to squirrel around w/calling NPH!
So now you know to look for the chipmunk so you won’t have to squirrel around w/calling NPH!

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh






















