OPENING RANGE BREAKOUT STRATEGY EXPLAINED
Opening range breakout trading is an interesting concept. Several traders have asked us how to take advantage of the opening range breakout strategy and if it is a good option. So, we decided it requires a separate discussion.
Opening range breakout trading is an interesting concept. Several traders have asked us how to take advantage of the opening range breakout strategy and if it is a good option. So, we decided it requires a separate discussion.

What Is Opening Price And Why It Is Important?
To understand the opening range breakout strategy, we must clear our understanding of the opening price of the day.
Often the opening sets the mood for trading for the day – uptrend or downtrend.
To understand the opening range breakout strategy, we must clear our understanding of the opening price of the day.
Often the opening sets the mood for trading for the day – uptrend or downtrend.
Key Understanding
🔖 The beginning hour of the trading day is the most active and dynamic period. The opening hours sets the sentiment of the market
🔖 You can make the most money during the opening hour, but it is also volatile
🔖 The beginning hour of the trading day is the most active and dynamic period. The opening hours sets the sentiment of the market
🔖 You can make the most money during the opening hour, but it is also volatile
🔖Without a trading strategy, you run the risk of losing money
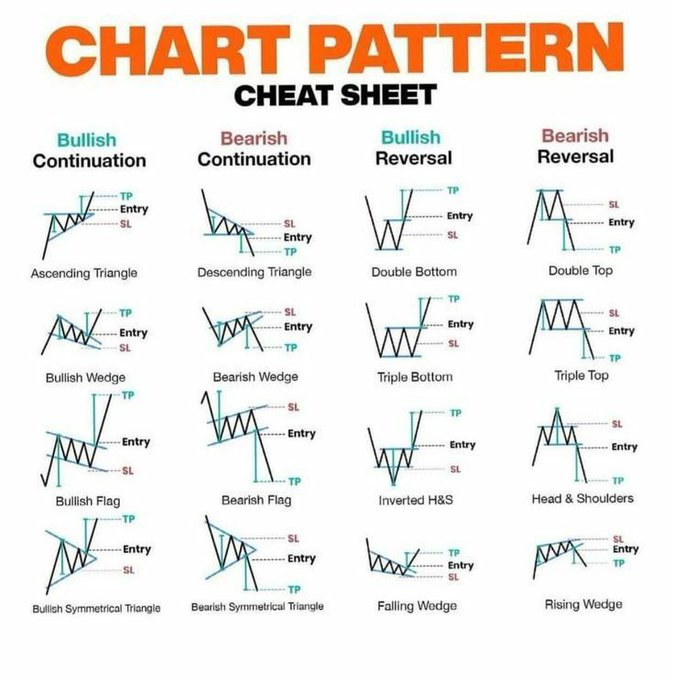
🔖Opening chart breakout is a critical chart pattern that studies the important reversal and continuation patterns
🔖The chart captures move or reversal during the first hour
🔖Opening chart breakout is a critical chart pattern that studies the important reversal and continuation patterns
🔖The chart captures move or reversal during the first hour

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh