
The findings of this one suggest that persistent de novo lipogenesis during fasting may at least partly explain impaired fasting ketogenesis in metabolic syndrome, which appears to be the consequence of reciprocal regulation of DNL and β-oxidation. 

- Forty non-diabetic individuals with and without a history of NAFL were recruited for this study.
- Lipogenesis remained detectable in a subset of individuals after a 24 hour fast, including some subjects without hepatic steatosis or other hallmarks of metabolic syndrome.
- These individuals displayed reduced ketogenesis, but increased acetyl-CoA utilization in the TCA cycle.
- At least three metabolic factors distinguished those who manifested persistent DNL during fasting:
a) They were resistant to the typical physiological effects of fasting, such as attenuation of fasting plasma insulin concentrations, augmentation of fasting plasma NEFA and ketone concentrations,and a diminution of glycogenolysis. 

b) Persistent lipogenesis in these subjects appeared to be a proportionate response to their relative hyperinsulinemia, despite the inability of hyperinsulinemia to suppress hepatic glucose production. 

c) These subjects had lower rates of oxaloacetate utilization for gluconeogenesis compared to its utilization for citrate synthesis. 

Increased utilization of oxaloacetate for citrate synthesis may partially reflect the reliance of DNL on TCA cycle intermediates (e.g., citrate) for the citrate shuttle, simultaneously diminishing ketogenesis.
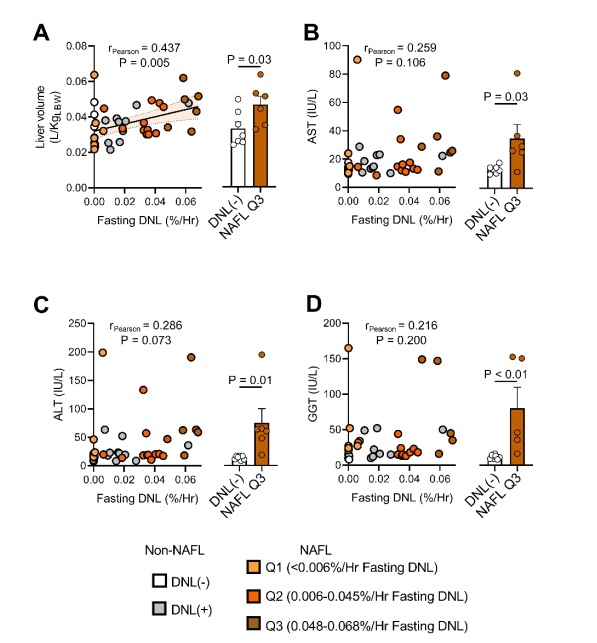
Interestingly, elevated liver volume, but not other indices of liver function (including AST, ALT, and GGT), correlated with fasting DNL. 
Persistent fasting lipogenesis links impaired ketogenesis with citrate synthesis in humans with non-alcoholic fatty liver (open access)
doi.org/10.1172/JCI167…
#MetabolicSyndrome #InsulinResistance #NAFLD #MALFD #Cholesterol #Triglycerides #Diabetes #Obesity
doi.org/10.1172/JCI167…
#MetabolicSyndrome #InsulinResistance #NAFLD #MALFD #Cholesterol #Triglycerides #Diabetes #Obesity
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh










