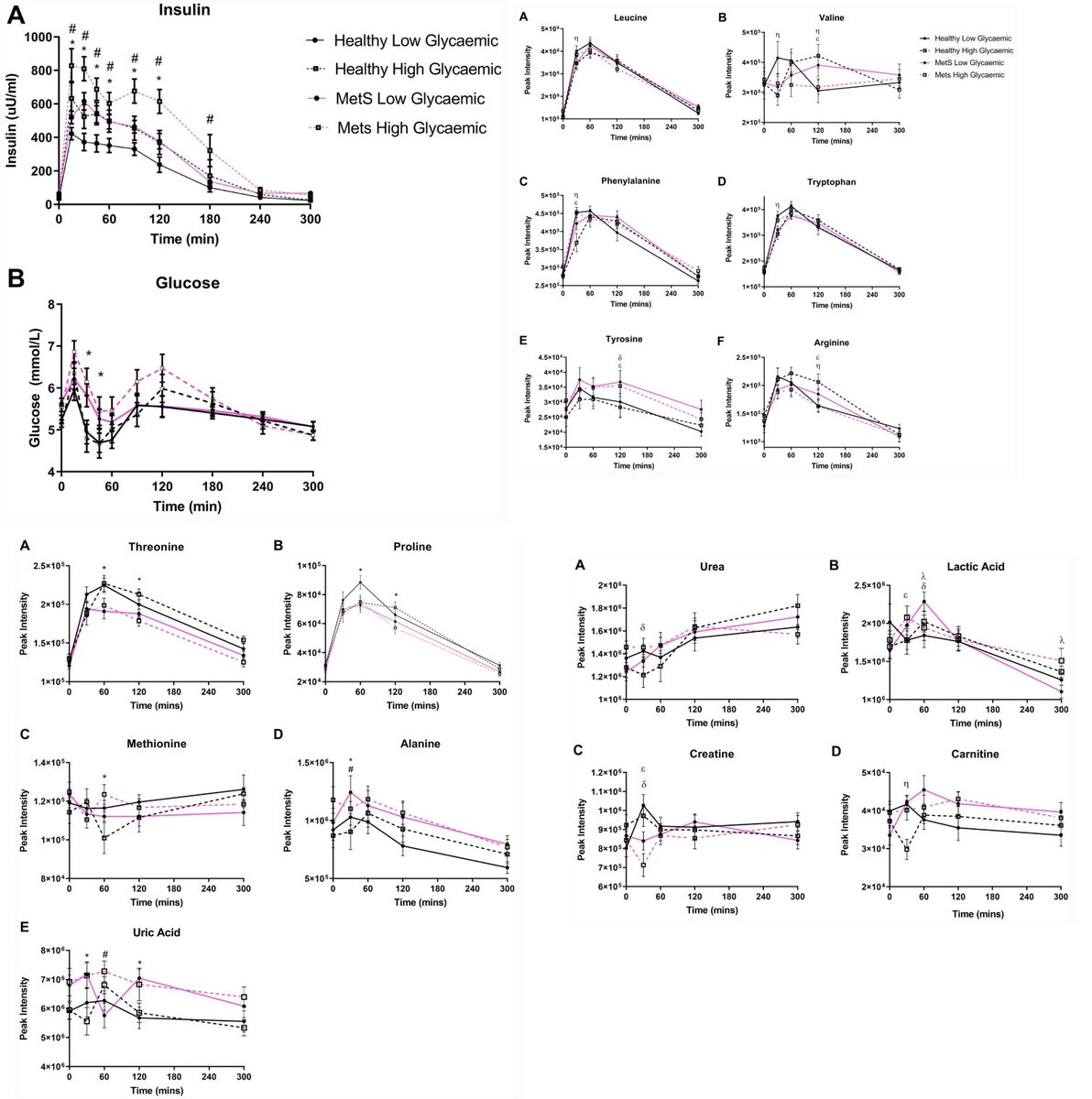
This one failed to find an effect of long-term (24 weeks) daily administration of intranasal insulin at 40IU once daily on food intake, appetite, and weight in older adults with a mean age of 65.5 years, either with or without type 2 diabetes. 

- A null effect of 24 weeks daily administration of 40 I.U. of intranasal insulin once daily on food intake, appetite, and weight in older adults was observed.
- Similarly, there were no differences in the effect of intranasal insulin when comparing men to women, obese to lean participants, and diagnosis of type 2 diabetes.
Daily intranasal insulin at 40IU does not affect food intake and body composition: A placebo-controlled trial in older adults over a 24-week period with 24-weeks of follow-up
doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu…
#nutrition #diet #Obesity #MetabolicSyndrome #appetite
doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu…
#nutrition #diet #Obesity #MetabolicSyndrome #appetite
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter