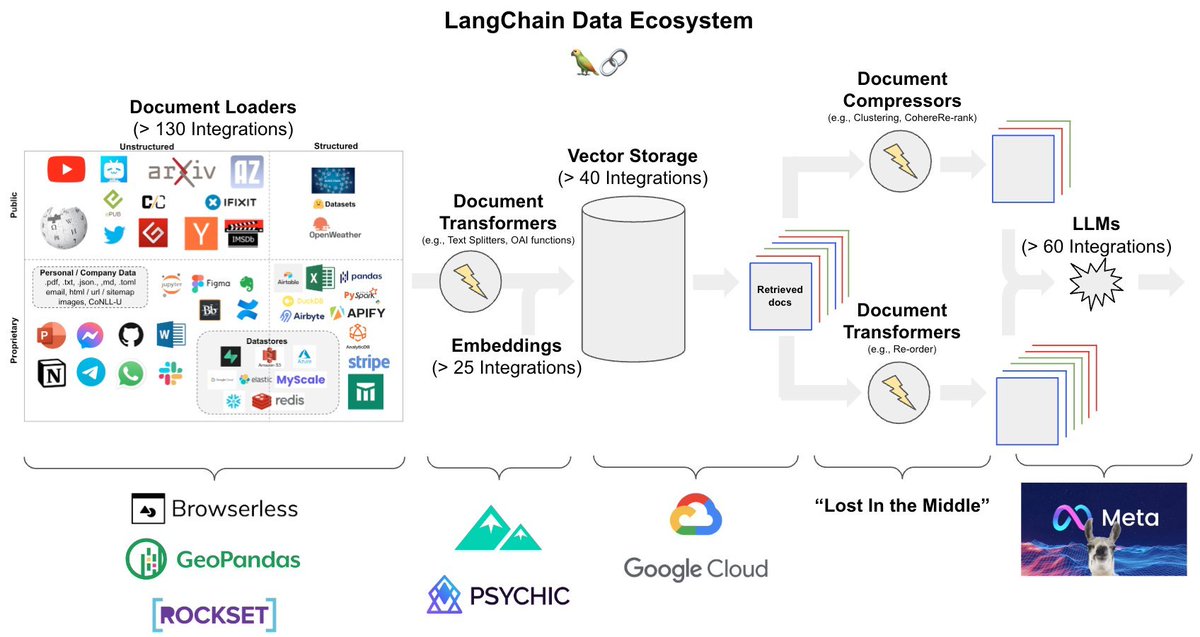
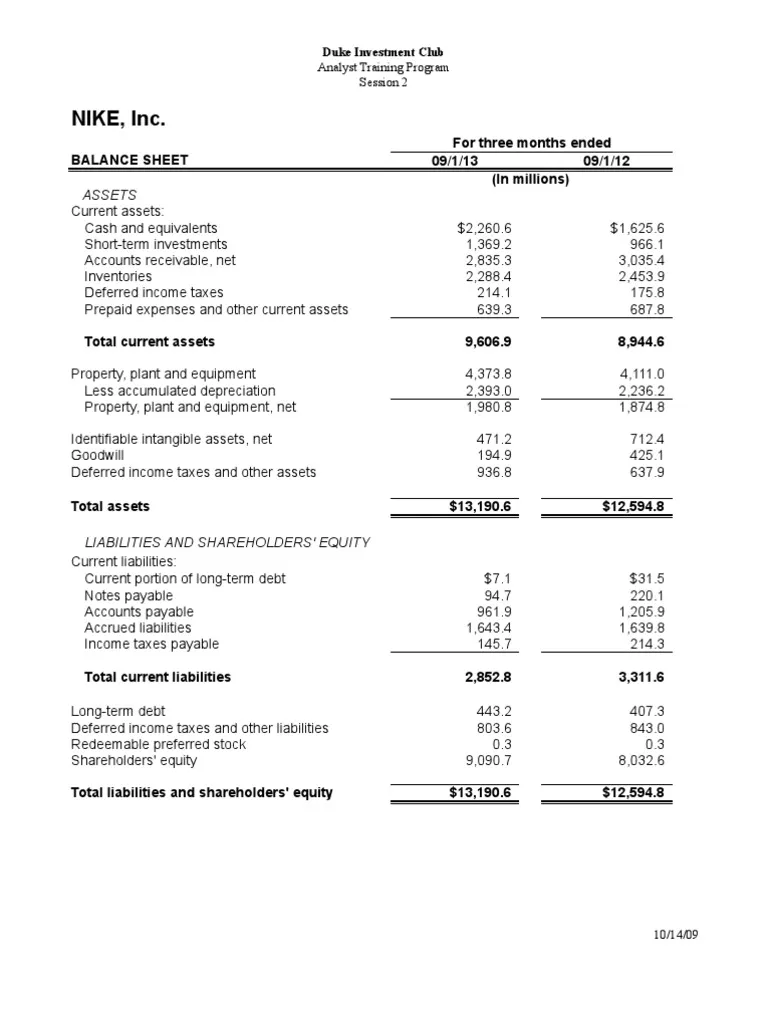
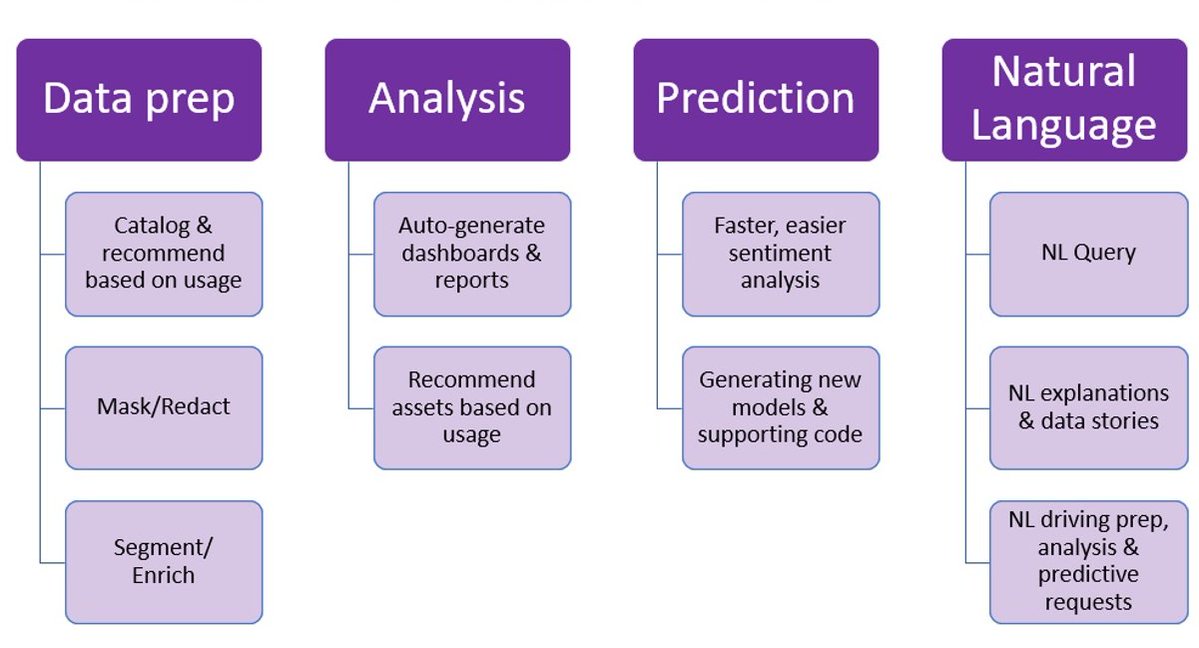
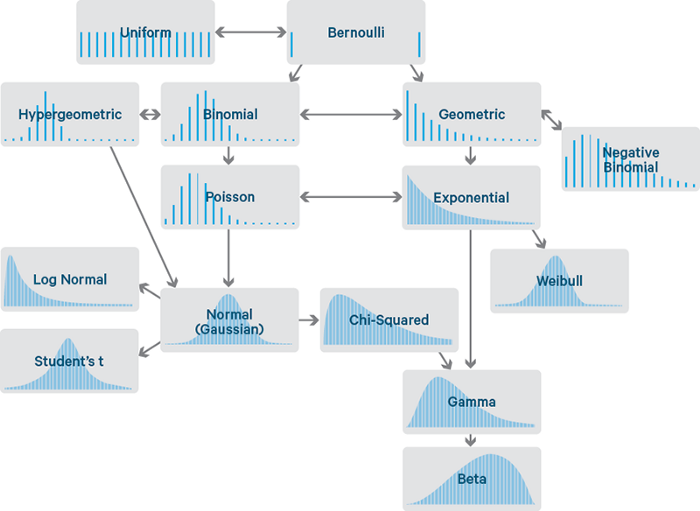
As a data scientist, productivity is a 10X super power.
Here's a short list of AI tools to help data scientists with: 🧵
#ai #datascience #career #skills #tools
Here's a short list of AI tools to help data scientists with: 🧵
#ai #datascience #career #skills #tools

1. Writing code
AI pair programming is a huge benefit.
Tools like #chatgpt & github #copilot can help debug complex code and replace Googling + Stack Overflowing for common scripting.
Key skill: ChatGPT prompting (more on this in my free ChatGPT for Data Scientists)
AI pair programming is a huge benefit.
Tools like #chatgpt & github #copilot can help debug complex code and replace Googling + Stack Overflowing for common scripting.
Key skill: ChatGPT prompting (more on this in my free ChatGPT for Data Scientists)

2. Code Quality & Documentation
Great products have great documentation. AI can help produce documentation, comment code, and replace time-consuming manual documentation with automated AI docs.
Key Skill: Using @mintlify to build your docs: mintlify.com
Great products have great documentation. AI can help produce documentation, comment code, and replace time-consuming manual documentation with automated AI docs.
Key Skill: Using @mintlify to build your docs: mintlify.com

3. Presentations
Great data scientists are storytellers. Use persuasion to your advantage.
Key Skill: Generating images with AI using @midjourney_ai . midjourney.com
Great data scientists are storytellers. Use persuasion to your advantage.
Key Skill: Generating images with AI using @midjourney_ai . midjourney.com

I'm road-testing all of these.
And I've been quietly researching #ChatGPT for Data Scientists (My NUMBER 1 TOOL) for the past 4 months.
I have good news - I'm ready to reveal my chatgpt research!
And I've been quietly researching #ChatGPT for Data Scientists (My NUMBER 1 TOOL) for the past 4 months.
I have good news - I'm ready to reveal my chatgpt research!
If you want to understand how ChatGPT can make you a better data scientist (and mistakes to avoid)...
I'll be sharing my research in a Free WORKSHOP: ChatGPT for Data Scientists (Wednesday, June 7th)!
I'll be sharing my research in a Free WORKSHOP: ChatGPT for Data Scientists (Wednesday, June 7th)!
What's Your Next Step?
Join me and 1,000 data scientists as we crush AI in my LIVE ChatGPT for Data Scientists Workshop.
Seats are limited (1,000 max).
👉Register Here: us02web.zoom.us/webinar/regist…
Join me and 1,000 data scientists as we crush AI in my LIVE ChatGPT for Data Scientists Workshop.
Seats are limited (1,000 max).
👉Register Here: us02web.zoom.us/webinar/regist…

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh