27 yrs old patient, detected to be pregnant when she missed her periods one day back. She has Graves disease on Rx for past 3 years, presently on Carbimazole 5mg daily and not on propranolol. She was euthyroid with Rx for past 1 year. Best strategy ?
Present reports 👇
Present reports 👇

A. Stop carbimazole and monitor by weekly/fortnightly TSH, FT4 levels and follow up.
B. Switch to PTU 50mg bd and do FT4, TSH after 2 weeks and review
C. Switch to PTU 50 mg bd + LT4 50mcg OD. TSH, FT4- 4wkly
D. PTU 50mg BD and Propranolol XL 20mg , Monthly TSH,FT4-followup
B. Switch to PTU 50mg bd and do FT4, TSH after 2 weeks and review
C. Switch to PTU 50 mg bd + LT4 50mcg OD. TSH, FT4- 4wkly
D. PTU 50mg BD and Propranolol XL 20mg , Monthly TSH,FT4-followup
#MedTwitter #MedEd #Endotwitter #Graves #hyperthyroidism #MedicalStudentTwitter #IMGs #IMG #medicaleducation #MedStudentTwitter #medstudent #medicalinternship #medicineresidency #internalmedicine #doctors #madaktari #Medicos #medicina #medical #FOAMed #FOAMim #FOAM4GP 

Graves disease (GD) is an autoimmune condition resulting in thyrotoxicosis (increased production of thyroid hormones) due to hyperthyroidism (hyperactive thyroid gland). The hyperthyroidism of GD is caused by antibodies called thyroid stimulating immunoglobulins (TSIs). 

A hyperthyroid patient who desires future pregnancy may be offered ablative therapy using radioactive iodine, thyroid surgery or medical therapy. It is recommended to go for definitive therapy (ablation/surgery) and wait till becoming euthyroid and clearing of TRAb levels B4 🤰 

MEDICAL THERAPY:-💊💊💊
Prolonged medical therapy ( > =18months) can result in remission of GD and in that situation Antithyroid drugs (ATDs) can be stopped. On an average there is a 50% relapse rate after stoppage of ATDs and 75% of relapses occur in first 3 years of stoppage.

Prolonged medical therapy ( > =18months) can result in remission of GD and in that situation Antithyroid drugs (ATDs) can be stopped. On an average there is a 50% relapse rate after stoppage of ATDs and 75% of relapses occur in first 3 years of stoppage.

The planning of therapy in relation to possible future pregnancy should be discussed with all ♀️ of childbearing age who has GD. The use of contraception until the disease is controlled is strongly recommended. If a GD pt on ATDs become pregnant the Rx of choice is medical mgt.
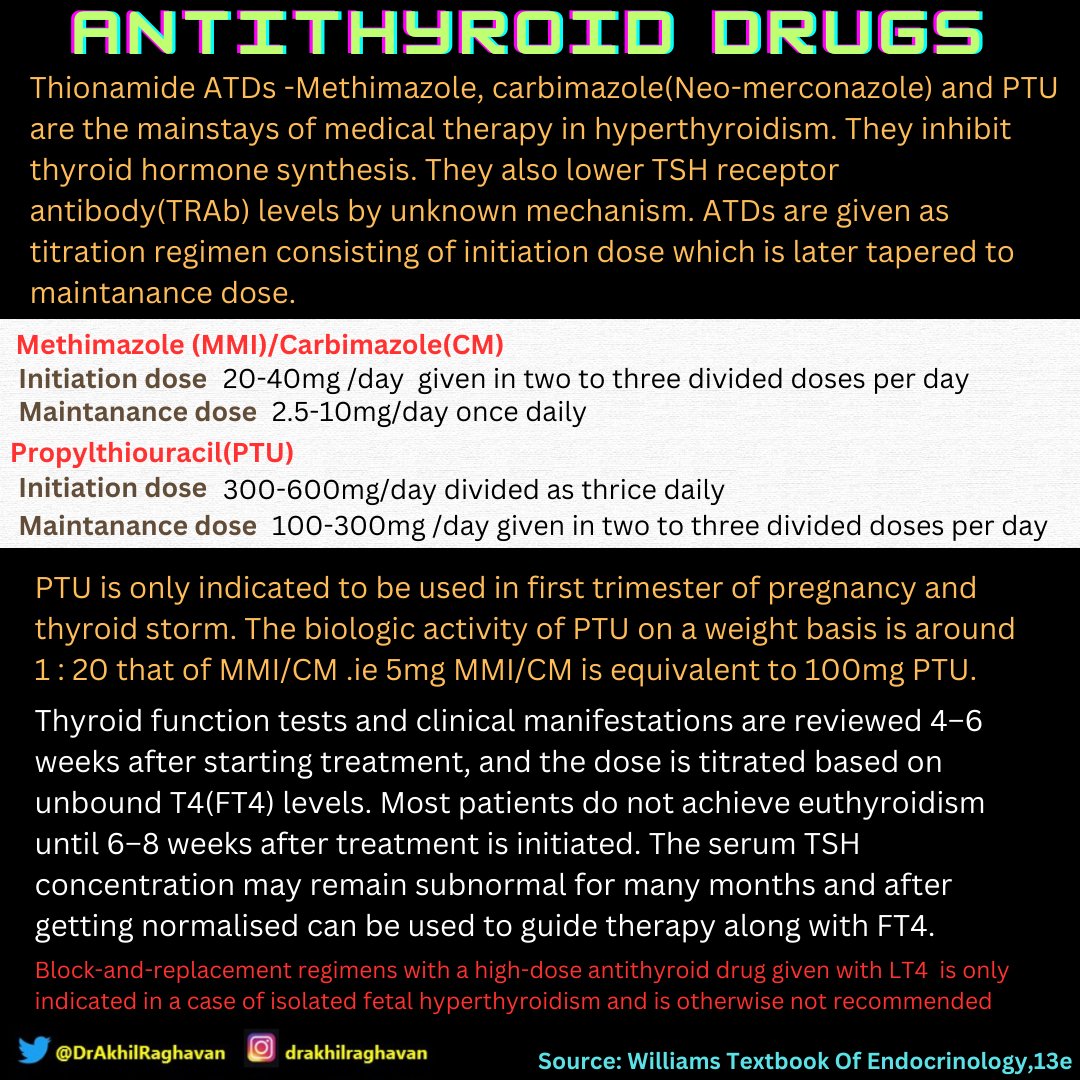
All ATDs are teratogenic and the rationale of preferring PTU over other ATDs in first trimester of pregnancy is that it has lesser incidence of embryopathy and causes less severe embryopathy.
The period of risk when MMI/CM may be teratogenic is especially in weeks 6 to 10 of pregnancy. It should be advised to young ♀️ who are on ATDs , that they test for pregnancy just a few days after a missed period and immediately contact their physician to plan future Rx if 🤰+
When 🤰is diagnosed in ♀️ receiving ATD & is in remission, it is recommended to withdraw ATD and perform weekly or fortnightly assessment and monitoring of FT4 and TSH initially. If euthyroid state is maintained follow up intervals can be extended to 2-4 weeks in 2️⃣&3️⃣trimester 

Patients in whom drug withdrawal is not possible, it is important that MMI/CM be replaced by equivalent doses of PTU preferebly before 6 weeks of pregnancy . When shifting from MMI to PTU, a dose ratio of approximately 1:20 should be used(e.g., MMI 5 mg/d = PTU 50 mg twice daily)
A baseline CBC and LFT is to be done and to be repeated for monitoring. 1-2 weelky clinical assessment and monitoring of FT4 and TSH is done initially and if euthyroid state is maintained follow up intervals can be increased to 2-4 weeks.
TRAb passes the placenta and stimulates the fetal thyroid and can result in fetal hyperthyroidism. Excess maternal thyroxine can cross placenta. ATDs given to the mother also pass through the placenta and thus can treat both the maternal and the fetal hyperthyroidism.
However ATDs may overtreat the fetus compared with the mother resulting in fetal hypothyroidism. So the aim of therapy is to keep the mother in a state of subclinical hyperthyroidism.
FT4 levels should be aimed to be kept just above or equal to upper limit of normal. TSH levels are to be kept just below or equal to lower limit of normal. Minimum dose of ATDs should be used to prevent development of fetal hypothyroidism. 

PTU has higher incidence and severity of ADRs among ATDs. So, it should be replaced by MMI/CM at 14-16 weeks of pregnancy. 2 to 4 weeky FT4 and TSH monitoring and follow up is done till 26weeks.
Owing to general decrease in thyroid autoimmunity and low TRAb levels, discontinuation of all ATDs is feasible in 20%–30% of patients in the last trimester of gestation. At 26 weeks- maternal TRAb,FT4, T3, TSH levels along with an USG to screen fetal hyperthyroidism is to be done
If maternal TRAb levels are undetectable and target FT4,TSH levels are achieved and no signs of fetal hyperthyroidism is seen in USG, then decision to stop ATDs can be taken. 1-2 weekly monitoring of FT4, TSH to be done till delivery. Fetal hypothyroidism should also be ruled out
Fetal surveillance should be
performed in women who have
uncontrolled hyperthyroidism in
the second half of pregnancy, and/or in women with high TRAb. If
hyperthyroidism is not adequately
treated by ATDs or if ATDs cannot
be used, thyroidectomy can be
done in second trimester.
performed in women who have
uncontrolled hyperthyroidism in
the second half of pregnancy, and/or in women with high TRAb. If
hyperthyroidism is not adequately
treated by ATDs or if ATDs cannot
be used, thyroidectomy can be
done in second trimester.

1.Williams Textbook of
Endocrinology,13e
2.Harrisons Principles Of Internal
Medicine,21e
3. 2017 Guidelines of the American
Thyroid Association for the
Diagnosis and Management of
Thyroid Disease During Pregnancy
and the Postpartum
RT&💜the first tweet👇
Endocrinology,13e
2.Harrisons Principles Of Internal
Medicine,21e
3. 2017 Guidelines of the American
Thyroid Association for the
Diagnosis and Management of
Thyroid Disease During Pregnancy
and the Postpartum
RT&💜the first tweet👇
https://twitter.com/DrAkhilRaghavan/status/1661034927188774912?t=kOW5ApwRkCAmQazohedXqw&s=19
Another thyroid problem👇
https://twitter.com/benjy_md/status/1660903651869863936?t=li6VPDJ73Z6UuhJNDPIdxA&s=19
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter