Tips & tricks of DWI to help narrow the differential
Ddx:
Stroke
Abscess
Hypercellular tumor
Hematoma
Epidermoid cyst
Encephalitis
Seizure
Demyelination
Toxic/metabolic disorders
CJD
Other stuff I’m forgetting
#Neurology #neurosurgery #radres #MedTwitter #MedEd @TheASNR



Ddx:
Stroke
Abscess
Hypercellular tumor
Hematoma
Epidermoid cyst
Encephalitis
Seizure
Demyelination
Toxic/metabolic disorders
CJD
Other stuff I’m forgetting
#Neurology #neurosurgery #radres #MedTwitter #MedEd @TheASNR



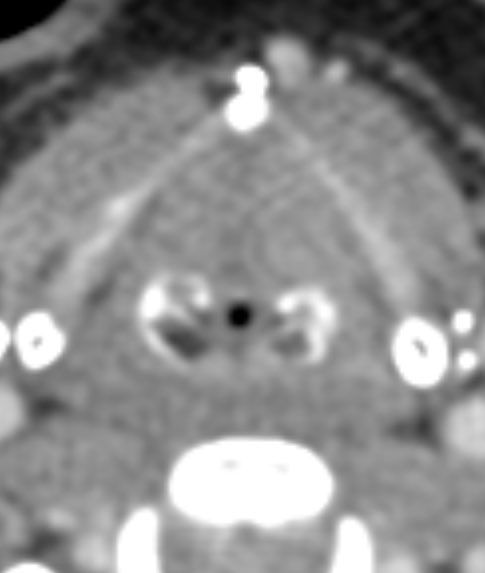
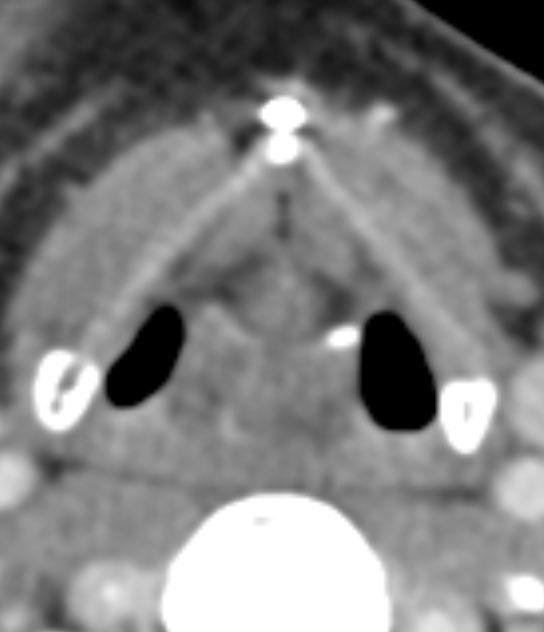
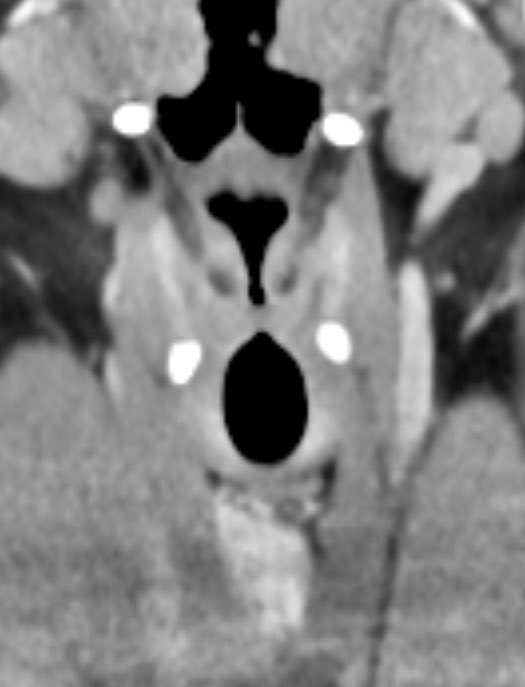
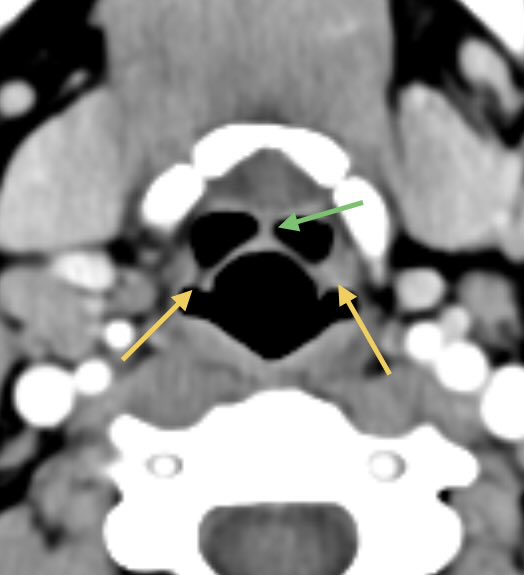
Anything that traps fluid can restrict diffusion! Here are some tricks I use to narrow the ddx
1️⃣STROKE
Cytotoxic edema due to trapped intracellular fluid leads to restriction
Look for wedge shaped restriction in a vascular territory
1️⃣STROKE
Cytotoxic edema due to trapped intracellular fluid leads to restriction
Look for wedge shaped restriction in a vascular territory

2️⃣ABSCESS
Trapped purulent material leads to LIGHT BULB BRIGHT restriction
DWI is excellent for differentiating tumor from pyogenic abscess as the abscess will have CENTRAL restriction
Abscess should also have vasogenic EDEMA, ENHANCEMENT, and possible dual rim sign (T2 & SWI)

Trapped purulent material leads to LIGHT BULB BRIGHT restriction
DWI is excellent for differentiating tumor from pyogenic abscess as the abscess will have CENTRAL restriction
Abscess should also have vasogenic EDEMA, ENHANCEMENT, and possible dual rim sign (T2 & SWI)


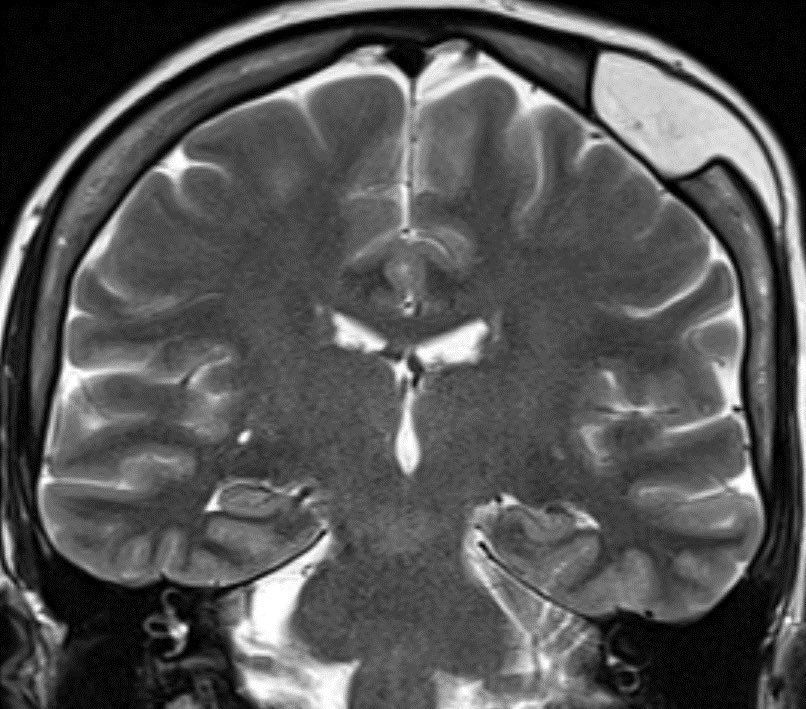
3️⃣HYPERCELLULAR TUMOR (lymphoma, medulloblastoma, embryonal tumor, germinoma, glioblastoma, etc)
Densely packed tumor cells trap fluid in between
Densely packed tumor cells trap fluid in between
Hypercellular tumor continued
Primary CNS Lymphoma
▶️Central diffusion restriction
▶️Homogenous enhancement
▶️Low T2 signal (less cytoplasm and more nucleus so less water in cells and lower T2 signal)
▶️Hyperdensity on CT
▶️Periventricular location

Primary CNS Lymphoma
▶️Central diffusion restriction
▶️Homogenous enhancement
▶️Low T2 signal (less cytoplasm and more nucleus so less water in cells and lower T2 signal)
▶️Hyperdensity on CT
▶️Periventricular location


Hypercellular tumor continued
▶️Glioblastoma or high grade glioma
Variable but may have more eccentric or nodular restriction around areas of necrosis and heterogeneous enhancement
▶️Glioblastoma or high grade glioma
Variable but may have more eccentric or nodular restriction around areas of necrosis and heterogeneous enhancement

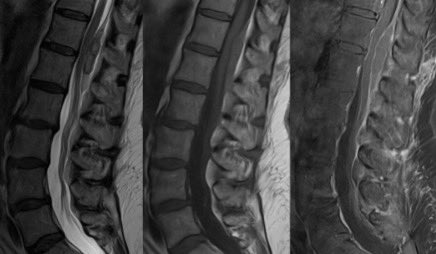
4️⃣HEMATOMA
RBCs trapped in serum and fibrin can restrict on DWI (though blood can also be dark on DWI from susceptibility)
Hyperdensity on CT is a giveaway but this may fade overtime or you may not have a CT
Look for a rim of HYPERINTENSITY ON T1 and HYPOINTENSITY on SWI

RBCs trapped in serum and fibrin can restrict on DWI (though blood can also be dark on DWI from susceptibility)
Hyperdensity on CT is a giveaway but this may fade overtime or you may not have a CT
Look for a rim of HYPERINTENSITY ON T1 and HYPOINTENSITY on SWI


5️⃣DEMYELINATION
High signal on DWI is predominantly due to T2 SHINE THROUGH
True restriction may be seen at the LEADING EDGE (along the margin) in acute demyelination possibly from cytotoxic edema, reduced fiber tract organization, or myelin fragments
(This example is PML)

High signal on DWI is predominantly due to T2 SHINE THROUGH
True restriction may be seen at the LEADING EDGE (along the margin) in acute demyelination possibly from cytotoxic edema, reduced fiber tract organization, or myelin fragments
(This example is PML)


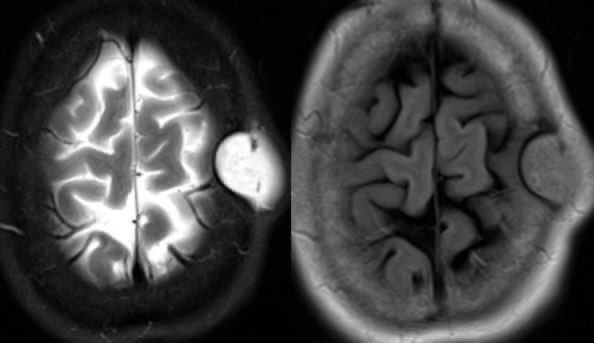
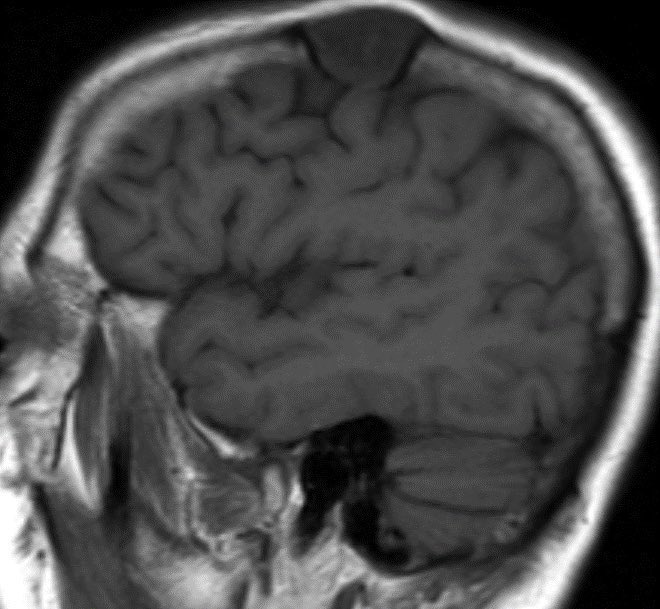
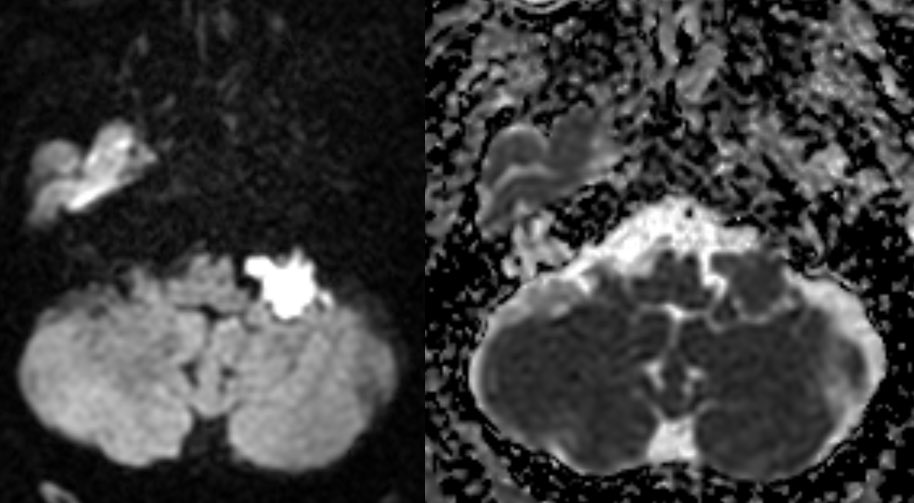
6️⃣EPIDERMOID CYST
Tightly organized epithelial layers cause a light bulb bright restriction
ADC tends to be ISOINTENSE TO BRAIN PARENCHYMA (not super dark), possibly from movement of fluid between layers (at least that’s how I think of it)
Tightly organized epithelial layers cause a light bulb bright restriction
ADC tends to be ISOINTENSE TO BRAIN PARENCHYMA (not super dark), possibly from movement of fluid between layers (at least that’s how I think of it)
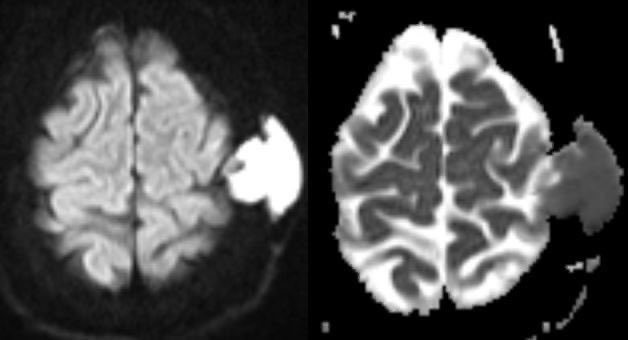
Epidermoid cyst continued
▶️CSF intensity on T1 & T2
▶️Dirty on FLAIR
▶️DO NOT ENHANCE! (May have a tiny rim of enhancement along edge but NO CENTRAL)
▶️CSF intensity on T1 & T2
▶️Dirty on FLAIR
▶️DO NOT ENHANCE! (May have a tiny rim of enhancement along edge but NO CENTRAL)

Bonus cases
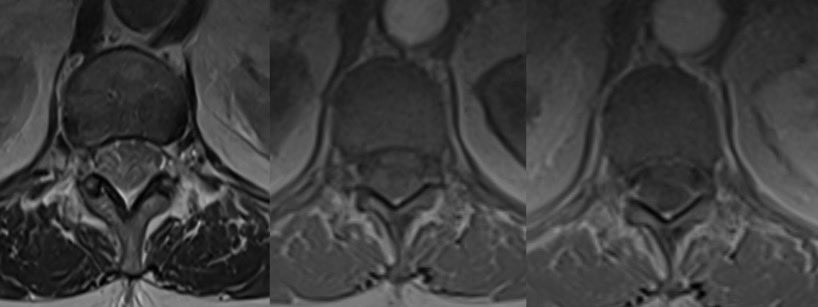
7️⃣SEIZURE
Shows gyriform or cortical restricted diffusion (often in the mesial temporal lobe)
Examples in 2 different patients

7️⃣SEIZURE
Shows gyriform or cortical restricted diffusion (often in the mesial temporal lobe)
Examples in 2 different patients


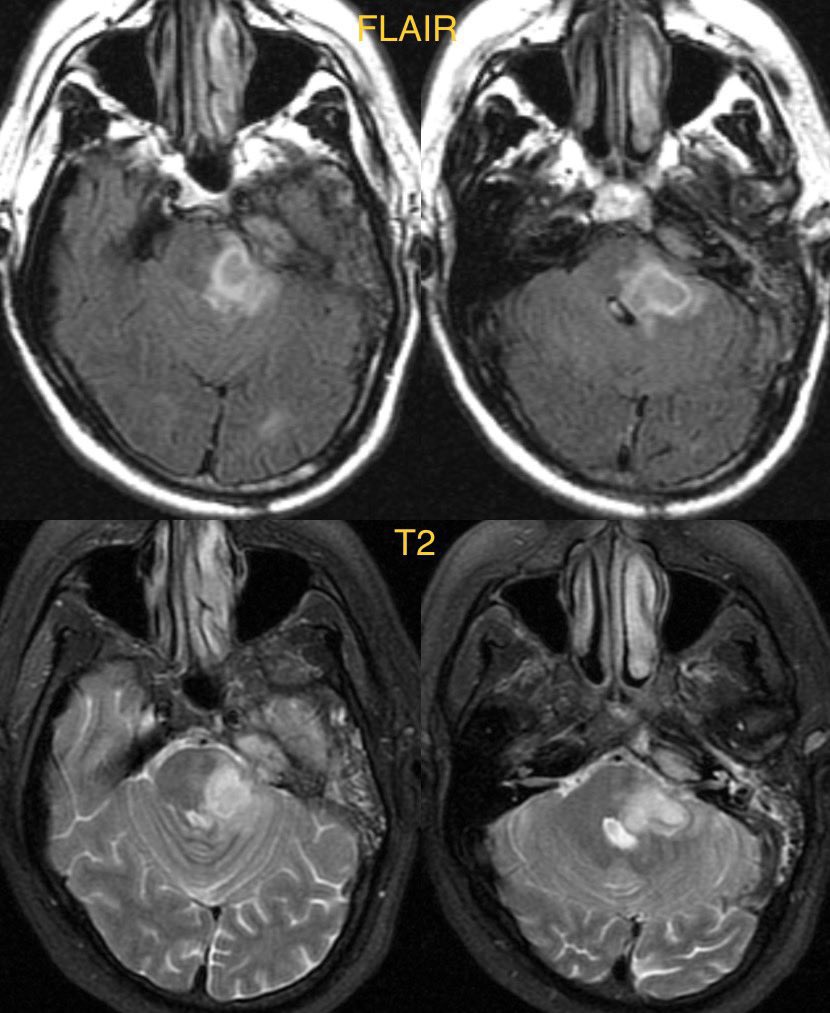
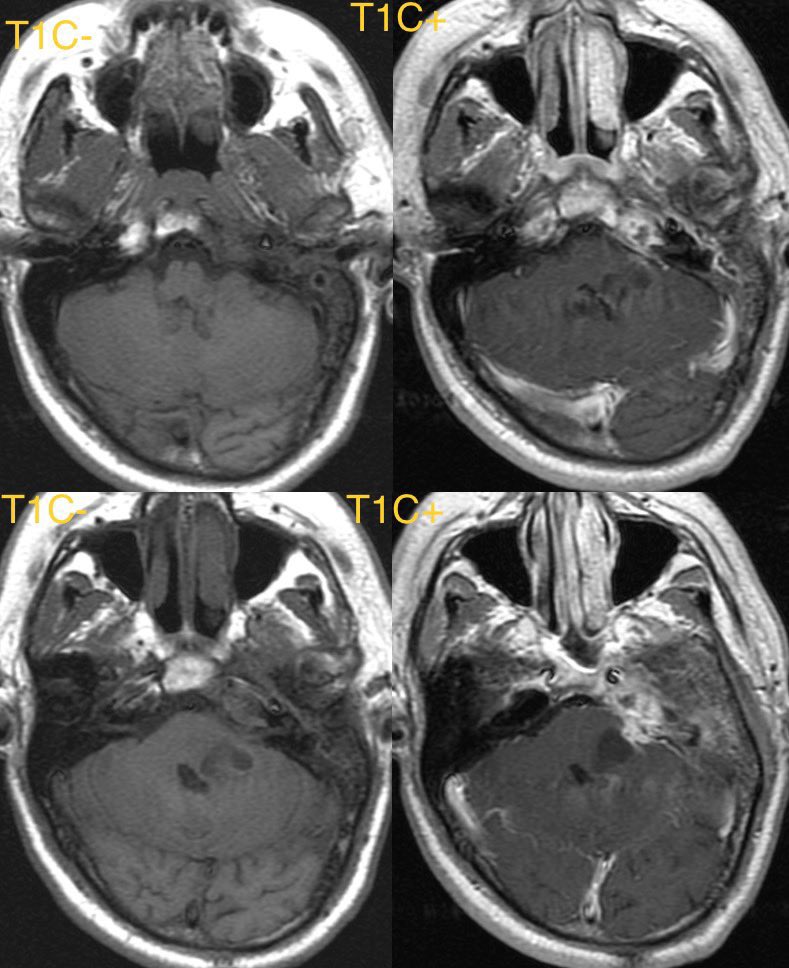
8️⃣ENCEPHALITIS
Diffusion restriction in the insula and temporal lobes favors herpes encephalitis, though any encephalitis can cause restriction
Herpes is usually bilateral but asymmetric and may have patchy enhancement and hemorrhage
Case of herpes
Diffusion restriction in the insula and temporal lobes favors herpes encephalitis, though any encephalitis can cause restriction
Herpes is usually bilateral but asymmetric and may have patchy enhancement and hemorrhage
Case of herpes

9️⃣CJD
Diffusion restriction is seen in the basal ganglia, thalami, and cortex. This can be asymmetric
Diffusion restriction is seen in the basal ganglia, thalami, and cortex. This can be asymmetric

🔟Many Toxic/metabolic disorders
Hepatic encephalopathy
Acute toxic leukoencephalopathy
Hypoxia
Methotrexate toxicity
Drug abuse
CO poisoning
Many more
Hepatic encephalopathy
Acute toxic leukoencephalopathy
Hypoxia
Methotrexate toxicity
Drug abuse
CO poisoning
Many more
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh