1/Does PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA anatomy feel as confusing as its spelling? Does it seem to have as many openings as letters in its name?
Let this #tweetorial on PPF #anatomy help you out
#meded #medtwitter #FOAMed #FOAMrad #neurosurgery #neurology #neurorad #neurotwitter #radres
Let this #tweetorial on PPF #anatomy help you out
#meded #medtwitter #FOAMed #FOAMrad #neurosurgery #neurology #neurorad #neurotwitter #radres
2/The PPF is a crossroads between the skullbase & the extracranial head and neck. There are 4 main regions that meet here. The skullbase itself posteriorly, the nasal cavity medially, the infratemporal fossa laterally, and the orbit anteriorly. 

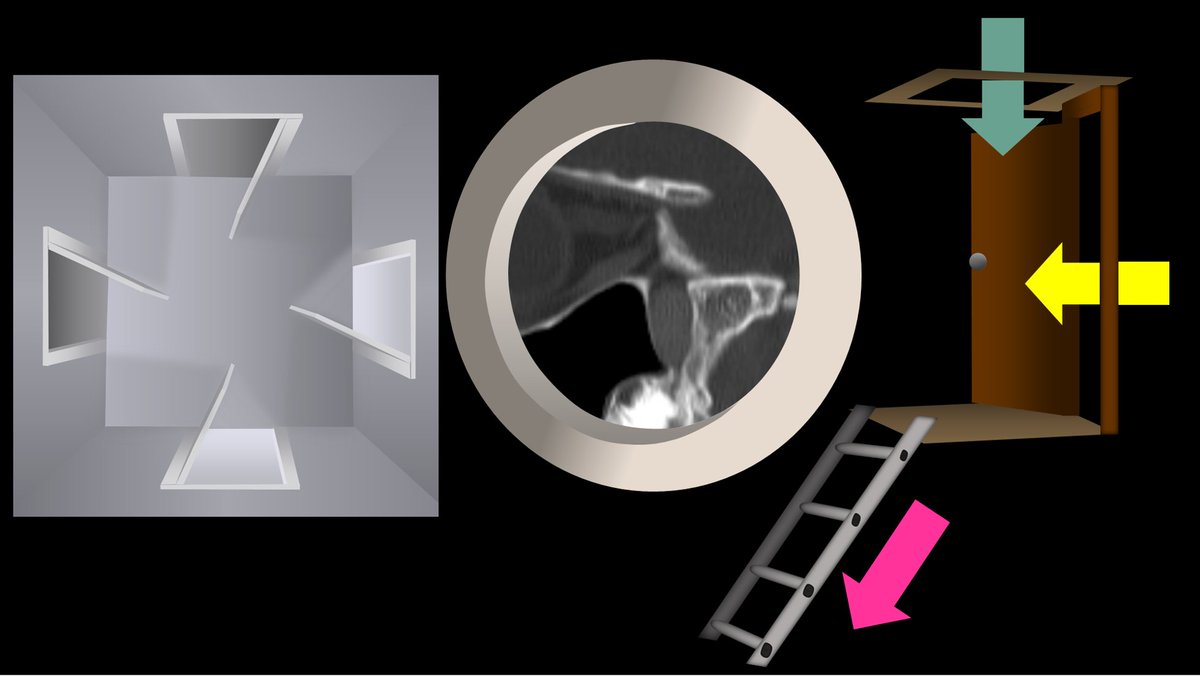
3/At its most basic, you can think of the PPF as a room with 4 doors opening to each of these regions: one posteriorly to the skullbase, one medially to the nasal cavity, one laterally to the infratemporal fossa, and one anteriorly to the orbit 
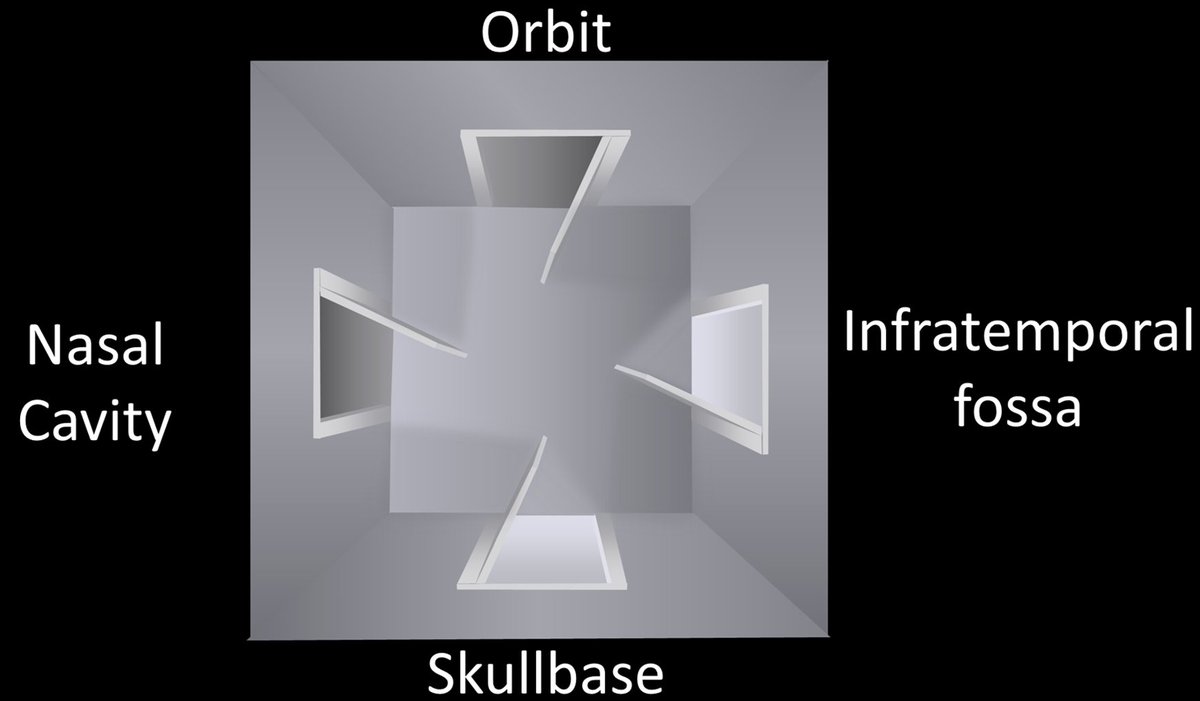
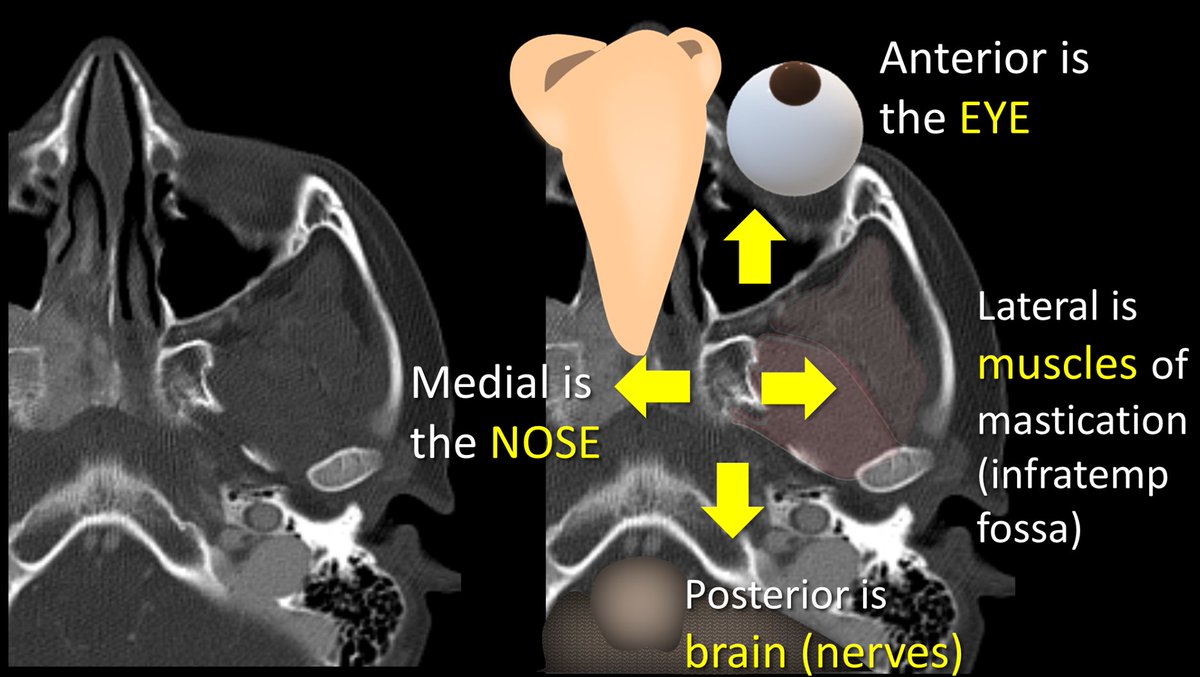
4/You can intuitively remember where each of these doors lead by thinking about what lies around the PPF. Brain is posterior, so post door opens to cranial nerves. Medially is the nose, so med door opens to nasal cavity. Anteriorly is the eye, so ant door goes to orbit & so forth 
5/Name of each door/opening also tells where they go. SPHENOpalatine foramen goes medially towards the SPHENOID sinus. Inferior ORBITAL fissure is to the ORBIT. PterygoMAXILLARY fissure goes laterally like the MAXILLARY sinus. ROTUNDUM is for a cranial nerve, so goes to the brain 

6/Let’s start w/the medial & lat openings. Sphenopalatine foramen (SPF) & pterygomaxillary fissure (PMF) can be seen when the walls of the post max sinus & pterygoid plate are parallel. They look like the two round openings of a cylinder—with the cylinder being the PPF itself. 

7/Their names tell you which side of the cylinder they are on. SPF opens to the sphenoid body/sinus, so it's the medial opening, since these structures are medial. PMF opens towards the maxillary sinus, which goes out laterally towards the zygoma—so PMF is the lateral opening 
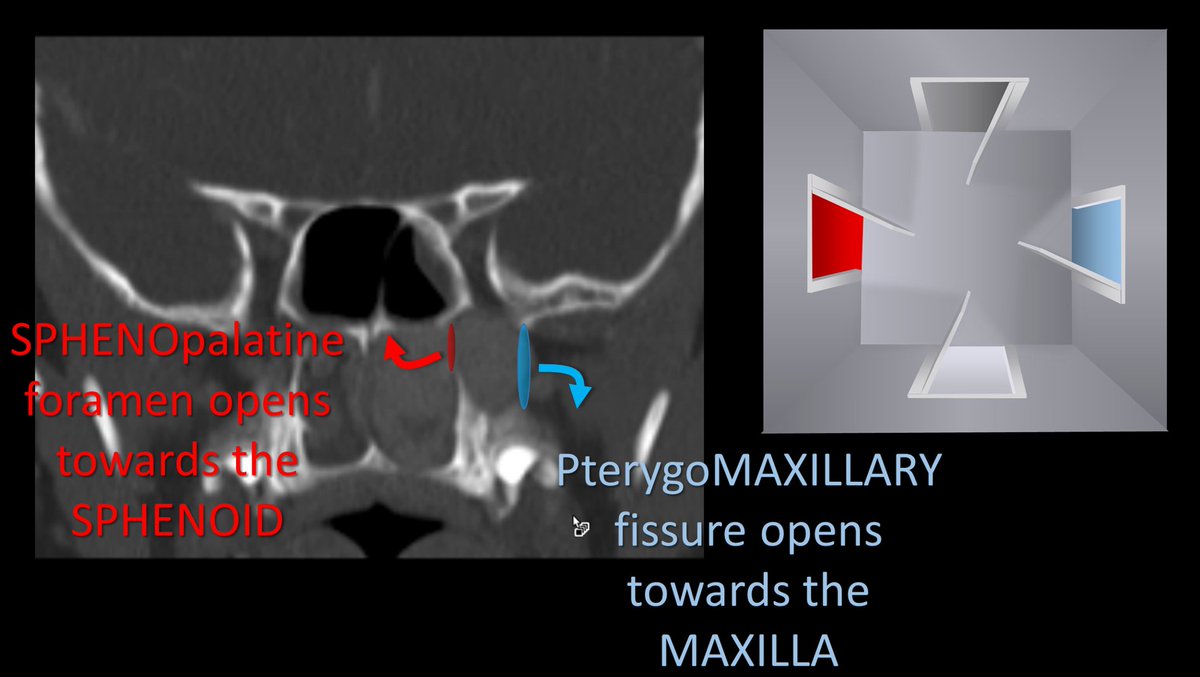
8/There is also an easy mnemonic. In old naval times, the Port side of the ship was the side that docked along the port, so it was the side that dealt w/the outside world. PMF starts w/P, so it is the port side, the side that is towards the world outside the patient (lateral). 

9/Posterior door has 2 parts. More superior part is foramen rotundum. It looks like a cylinder going straight back. I remember Rotundum is the post door bc both Rotundum & Rear start w/R. You can also remember that Rears are Round, if you want to be a little cheeky—literally 

10/The lower half of the posterior door is the pterygoid or vidian canal. I remember that Vidian is the lower opening in the posterior door bc the V almost looks like an arrow pointing down. 

11/Unlike rotundum that looks like a straight cylinder, Vidian has a bit of a curve to it, looking a little bit like the letter L. This helps me to remember that Vidian connects to Foramen Lacerum, bc Vidian looks a little like an L & Lacerum starts w/an L. 

12/Anterior door is the inferior orbital fissure (IOF). You can remember this bc the eye is anterior to the PPF. You can also remember its name (IOF) with the little mnemonic that “I (eye) Opening is Forward.” 

13/But it’s a little bit more complicated than that. While the IOF is anterior, it also superior, more like an anterior skylight than a door. So if you look through the rotundum/vidian door, you will see the SPF medially, the PMF laterally & the IOF in front of you on the ceiling 
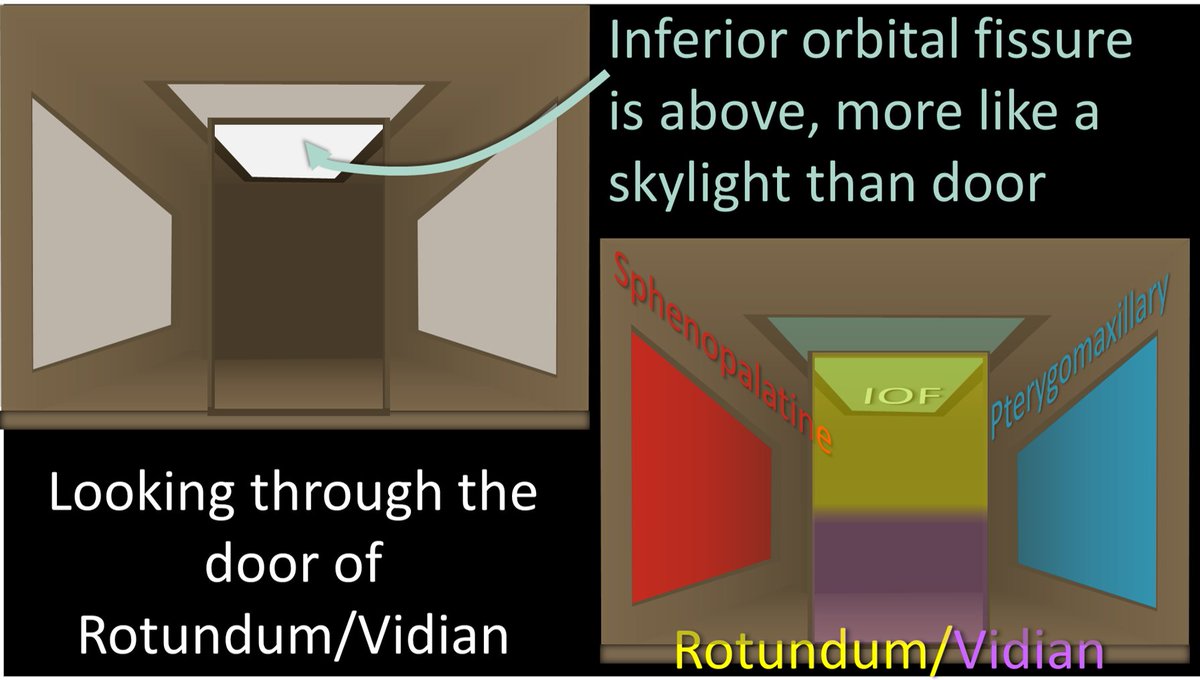
14/But it’s even a little more complicated than that! Turns out there’s a trap door in the floor as well—the palatine canals. You can remember this bc the mouth/palate is below the PPF so you need a hole going down. You can also remember this b/c both Palatine & Pothole start w/P 

15/So looking from above, you will the Rotundum/Vidian rear door, w/the SPF door medially & the PMF door laterally. Up on the anterior ceiling is the IOF skylight, and down on the floor is the trapdoor to the palatine canals. 

16/Here is a view from the side. You can better see how the IOF is like a skylight, rotundum is a rear door, and the palatine canals are the trap door with a ladder leading down to the mouth. 

17/So let’s pretend we are intracranial & peering through the round hole of foramen rotundum. We will see what looks like a loft w/a ladder. The ladder is the palatine canals leading down. The loft itself has a skylight (IOF) & 2 windows—medial window is the SPF & lateral is PMF. 

18/So now you know the basic anatomy of the PPF. As Elizabeth Taylor once said, “There are many doors in this world, don’t be afraid to look through them.” Don’t be afraid of the doors of the PPF—they can open the world of anatomy to you! 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter