NMAT Review
Must Know: Social Science [THREAD]
(Topics: Branches of Social Science, Culture, Socialization, Elements of Culture, Sociological and Anthropological Theories, Religion, Government, Family, School of Thoughts, Biological Psych, Social Psych, Abnormal Psych etc.)
Must Know: Social Science [THREAD]
(Topics: Branches of Social Science, Culture, Socialization, Elements of Culture, Sociological and Anthropological Theories, Religion, Government, Family, School of Thoughts, Biological Psych, Social Psych, Abnormal Psych etc.)
1.Social Science-the scientific study of human society and its origins, development, organizations, and institutions. 
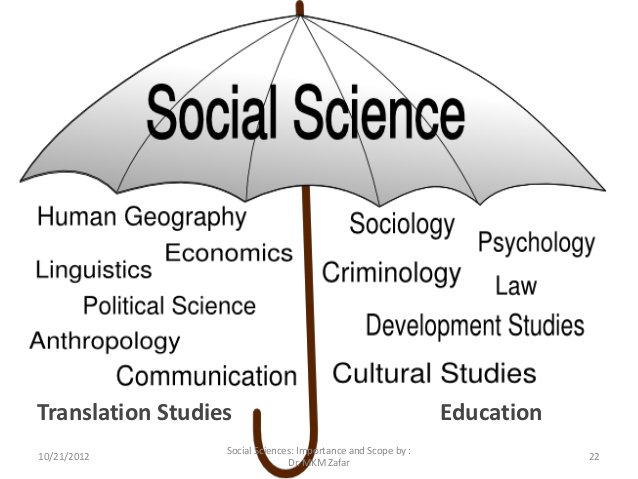
2.Branches of Social Science
-Political Science -study of social arrangements to maintain peace and order in a society.
-Economics -Study and analysis of social behavior of human beings in regards to allocation of resources in order to meet the needs of each individual
-Political Science -study of social arrangements to maintain peace and order in a society.
-Economics -Study and analysis of social behavior of human beings in regards to allocation of resources in order to meet the needs of each individual
3.Branches of Social Science
-Sociology - Systematic study of relationships among people; Assume that behavior is influenced by people’s social, political, occupational and intellectual groupings & by the particular settings in which they find themselves at one time or another
-Sociology - Systematic study of relationships among people; Assume that behavior is influenced by people’s social, political, occupational and intellectual groupings & by the particular settings in which they find themselves at one time or another
4.Branches of Social Science
-Anthropology - Study of the similarities and differences of various cultures; branches are physical anthropology, social anthropology, cultural anthropology, archaeology, and linguistic anthropology
-Anthropology - Study of the similarities and differences of various cultures; branches are physical anthropology, social anthropology, cultural anthropology, archaeology, and linguistic anthropology
5.Branches of Social Science
-Physical Anthropology - Influence of the evolution of natural environment on physical characteristics of humans;
-Archaeology - Study of human culture and activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture.
-Physical Anthropology - Influence of the evolution of natural environment on physical characteristics of humans;
-Archaeology - Study of human culture and activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture.
6.Branches of Social Science
Geography - Study of the natural environment and how it influences social and cultural development
Psychology - study of mental processes and behavior with the goal of describing, explaining, predicting and changing behavior
Geography - Study of the natural environment and how it influences social and cultural development
Psychology - study of mental processes and behavior with the goal of describing, explaining, predicting and changing behavior
7.Branches of Social Science
History - Study of past events; systematic attempt to learn about and verify past events and to relate them to one another and to the present Involves: identifying, classifying, arranging, patterning
History - Study of past events; systematic attempt to learn about and verify past events and to relate them to one another and to the present Involves: identifying, classifying, arranging, patterning
9.Culture-Total pattern of human behavior and its products that are passed on from generation to generation.
Cultural Evolution-gradual accumulative process of how culture is changed.
Cultural Integration-the degree to which a culture is internally consistent and homogeneous.
Cultural Evolution-gradual accumulative process of how culture is changed.
Cultural Integration-the degree to which a culture is internally consistent and homogeneous.
10.Socialization–Lifelong process that shapes personality of individuals to become members of a society
Ascribed Status- status given from birth, and is beyond one’s control (race).
Achieved Status- status that is acquired, which depends on personal accomplishments (profession)
Ascribed Status- status given from birth, and is beyond one’s control (race).
Achieved Status- status that is acquired, which depends on personal accomplishments (profession)
11.Elements of Culture
-Social Norms
-Social institutions
-Material Culture
-Language
-Social Values
-Social Norms
-Social institutions
-Material Culture
-Language
-Social Values
12. Social Norms
Conventions-everyday customs of a group of people that represent usual ways of behaving
Mores-need to be observed by all society members for the culture to survive; Violations are not legally sanctioned but incur social punishment through peer disapproval.
Conventions-everyday customs of a group of people that represent usual ways of behaving
Mores-need to be observed by all society members for the culture to survive; Violations are not legally sanctioned but incur social punishment through peer disapproval.
13.Social Norms
Laws-generally recorded, codified & enforced as a means of securing public obedience; violations are legally sanctioned (fines, imprisonments)
Laws-generally recorded, codified & enforced as a means of securing public obedience; violations are legally sanctioned (fines, imprisonments)
14. Social Norms
Folkways – customary patterns of everyday life that specify what is socially correct and proper in everyday life
Taboos – a norm that society holds so strongly that violating it results in extreme disgust (ex. incest)
Folkways – customary patterns of everyday life that specify what is socially correct and proper in everyday life
Taboos – a norm that society holds so strongly that violating it results in extreme disgust (ex. incest)
15.SOCIAL INSTITUTIONS - An established complex pattern of behavior in which a number of persons participate in order to further important group interests, provide order, coordination & avenue for social change. 

16.MATERIAL CULTURE – Consists of all the physical objects people have borrowed, discovered, or invented, and have attached meaning
LANGUAGE - Body of words and system for usage common to a people of the same community/ nation/geographical location or cultural tradition
LANGUAGE - Body of words and system for usage common to a people of the same community/ nation/geographical location or cultural tradition
17.Social Problems-adversely affect the welfare of large numbers of people and for which it is believed a solution exists to bring about change.
Cultural Lag-the slowness in the rate of change; results in maladjustment within a society
Cultural Lag-the slowness in the rate of change; results in maladjustment within a society
18.Contrasts among cultures
Ethnocentrism-belief of a group that its people and its way of life are superior to all others
Cultural relativism-cultures develop in a way that best suits the population’s needs and the cultural traits within a culture have a specific purpose.
Ethnocentrism-belief of a group that its people and its way of life are superior to all others
Cultural relativism-cultures develop in a way that best suits the population’s needs and the cultural traits within a culture have a specific purpose.
19.Key terms:
Cultural Universals-aspects/traits that are similar among all cultures
Cultural Alternatives-cultural characteristics not necessarily shared by other cultures
Cultural Universals-aspects/traits that are similar among all cultures
Cultural Alternatives-cultural characteristics not necessarily shared by other cultures
20.Key terms:
Enculturation-people learn about their own culture formally and informally
Acculturation-learning about a culture through
Enculturation-people learn about their own culture formally and informally
Acculturation-learning about a culture through
21.Key terms:
Conformity-an individual’s way of adopting attitude and behavior of others because of the pressure to do so
Stereotype-any commonly known public belief about a certain social group or a type of individual (i.e. gender stereotypes)
Conformity-an individual’s way of adopting attitude and behavior of others because of the pressure to do so
Stereotype-any commonly known public belief about a certain social group or a type of individual (i.e. gender stereotypes)
22.FUNCTIONALISM by Emile Durkheim
-Each part of the society contributes to the stability of the society. Durkheim envisioned a society as an organism, wherein each body part has a specific function, but none can function alone.
-Each part of the society contributes to the stability of the society. Durkheim envisioned a society as an organism, wherein each body part has a specific function, but none can function alone.
23.CONFLICT THEORY by Karl Marx
- Conflicts and tensions arise when status, power, and resources are not evenly distributed within social groups. These conflicts become the engine for social change.
- Conflicts and tensions arise when status, power, and resources are not evenly distributed within social groups. These conflicts become the engine for social change.
24.CONFLICT THEORY by Karl Marx
-Marx focused on the causes and effects of class conflict between the bourgeoisie (the owners of the means of production and capitalists) and the proletariat (the working class and the poor). The struggle for power.
-Marx focused on the causes and effects of class conflict between the bourgeoisie (the owners of the means of production and capitalists) and the proletariat (the working class and the poor). The struggle for power.
25.SYMBOLIC INTERACTIONISM by George Mead and Max Weber
-It is a micro-level theory that focuses on the relationships among individuals within a society.
-Views and analyzes society through the subjective meanings people impose on objects, events, and behaviors.
-It is a micro-level theory that focuses on the relationships among individuals within a society.
-Views and analyzes society through the subjective meanings people impose on objects, events, and behaviors.
26.STRUCTURALISM
-Structuralism identifies and analyzes the structures that underlie all cultural phenomena
- Mutual dependency of agency and structure
-Structuralism identifies and analyzes the structures that underlie all cultural phenomena
- Mutual dependency of agency and structure
27.EVOLUTIONISM by E.B. Tylor
-Built from the Charles Darwin’s theory of evolution and natural selection
-Cultural variation is one of the results of different societies at different stages of evolution
-Built from the Charles Darwin’s theory of evolution and natural selection
-Cultural variation is one of the results of different societies at different stages of evolution
28.EVOLUTIONISM by E.B. Tylor
-Tylor believes that cultural degeneration does not occur. Instead, he insisted that culture evolves from simple to complex. Progress is possible for all, as all societies undergo the same stages of development.
-Tylor believes that cultural degeneration does not occur. Instead, he insisted that culture evolves from simple to complex. Progress is possible for all, as all societies undergo the same stages of development.
29. GEMEINSCHAFT AND GESELLSCHAFT by Ferdinand Tonnies
Gemeinschaft-individuals of a society are more inclined towards social community
Gesselschaft-society in which individuals of a society give more importance to their personal needs and wants than the social community.
Gemeinschaft-individuals of a society are more inclined towards social community
Gesselschaft-society in which individuals of a society give more importance to their personal needs and wants than the social community.

30.GEOGRAPHY - Focuses on spatial interaction of human beings with each other with their physical environment.
DEMOGRAPHY - Study of the number and characteristics of a population; Concerned with factors that may be causing the population to increase or decrease
DEMOGRAPHY - Study of the number and characteristics of a population; Concerned with factors that may be causing the population to increase or decrease
31.MALTHUSIAN THEORY by Thomas Robert Malthus
-Belief that population tends to outrun the means of subsistence
-Population growth would necessarily tend to outrun means of subsistence
based on the LAW OF DIMINISHING RETURNS
-Belief that population tends to outrun the means of subsistence
-Population growth would necessarily tend to outrun means of subsistence
based on the LAW OF DIMINISHING RETURNS
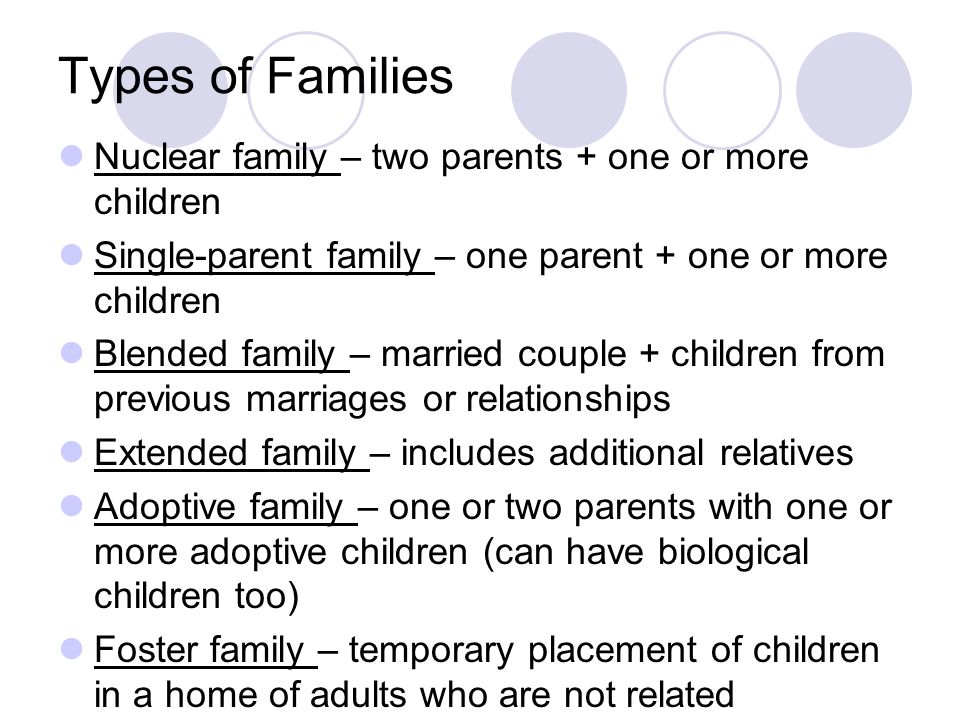
33.Number of mates
Monogamy-one husband and one wife
Polygamy-multiple marriage; two or more nuclear family
Cenogamy-group marriage
Monogamy-one husband and one wife
Polygamy-multiple marriage; two or more nuclear family
Cenogamy-group marriage
34.Family based on residency
Patrilocal/virolocal-the family resides with the husband’s family and place of residency
Matrilocal/uxorilocal-the family resides with the wife’s family and place of residency
Neolocal- a married couple, or the family resides separately
Patrilocal/virolocal-the family resides with the husband’s family and place of residency
Matrilocal/uxorilocal-the family resides with the wife’s family and place of residency
Neolocal- a married couple, or the family resides separately
35.Lineage
Patrilineal-identified through the male lineage; children get the father’s last name.
Matrilineal-descent is traced through the female line; do not use family names at all.
Patrilineal-identified through the male lineage; children get the father’s last name.
Matrilineal-descent is traced through the female line; do not use family names at all.
36.Family Control
-Patriarchy-father is supreme authority
-Matriarchy-mother is the supreme authority
-Egalitarian/partnership
-Patriarchy-father is supreme authority
-Matriarchy-mother is the supreme authority
-Egalitarian/partnership
37.Hinduism
-believes that the soul inhabits successive bodies in its journey through the universe
-all beings even gods must die and be reborn in an endless cycle
-believes that the soul inhabits successive bodies in its journey through the universe
-all beings even gods must die and be reborn in an endless cycle
39.Buddhism
-developed out from Hinduism
-to free people from endless cycle of reincarnations
-Shakyamuni Gautama/Siddharta Gautama (the completed one, the perfected)
-developed out from Hinduism
-to free people from endless cycle of reincarnations
-Shakyamuni Gautama/Siddharta Gautama (the completed one, the perfected)
40.Judaism
-developed out of the religion of ancient Hebrew tribe
-waits for the coming of the Messiah (descendant of King David)
Brands of Judaism
-Orthodox: resist change of beliefs and rituals
-Reformed: reject much of Jewish traditionalism
-Conservatives
-developed out of the religion of ancient Hebrew tribe
-waits for the coming of the Messiah (descendant of King David)
Brands of Judaism
-Orthodox: resist change of beliefs and rituals
-Reformed: reject much of Jewish traditionalism
-Conservatives
41.Christianity
-believes in Jesus Christ
-believe in God, to do His will, to believe in Jesus as the son of God.
-believes in the Bible
*Reformation-urge that religion revert to its source
-protestants gained freedom from the control of Rome
-believes in Jesus Christ
-believe in God, to do His will, to believe in Jesus as the son of God.
-believes in the Bible
*Reformation-urge that religion revert to its source
-protestants gained freedom from the control of Rome
42.Islam
-submission; submitters to the will of God
-Muhammad: believed he was chosen by God/Allah to be the messenger of the divine revelation
-Abu Bakr: first successor who wrote down the messages after Muhammad’s death
-submission; submitters to the will of God
-Muhammad: believed he was chosen by God/Allah to be the messenger of the divine revelation
-Abu Bakr: first successor who wrote down the messages after Muhammad’s death
43.Islam
Major denomination
Shiites(sectarians)-followers of Ali and follow a system of Imamah(true leader of Muslim)
Sunnis(traditionalists)-followers of Abu Bakr
Major denomination
Shiites(sectarians)-followers of Ali and follow a system of Imamah(true leader of Muslim)
Sunnis(traditionalists)-followers of Abu Bakr
45.Schools of thought
Structuralism(Wilhelm Wundth)-study of the elements that compromise the mind
Functionalism(William James)-study how the mind works to adapt to the environment
Gestalt(Wertheimer, Koffka, Kohler)-the whole is greater than the sum of it’s parts
Structuralism(Wilhelm Wundth)-study of the elements that compromise the mind
Functionalism(William James)-study how the mind works to adapt to the environment
Gestalt(Wertheimer, Koffka, Kohler)-the whole is greater than the sum of it’s parts
46.Schools of thought
Psychanalysis(Sigmund Freud)-the unconscious mind is the primary source of human behavious
Behaviorism(John Watson)-observable behaviors
Cognitive Theory
Self Concept(Carl Rogers)
Humanism-free will and human potential
Psychanalysis(Sigmund Freud)-the unconscious mind is the primary source of human behavious
Behaviorism(John Watson)-observable behaviors
Cognitive Theory
Self Concept(Carl Rogers)
Humanism-free will and human potential
47.Iceberg Theory- Freud used the metaphor of an iceberg to describe his theory that there are three levels of consciousness. 

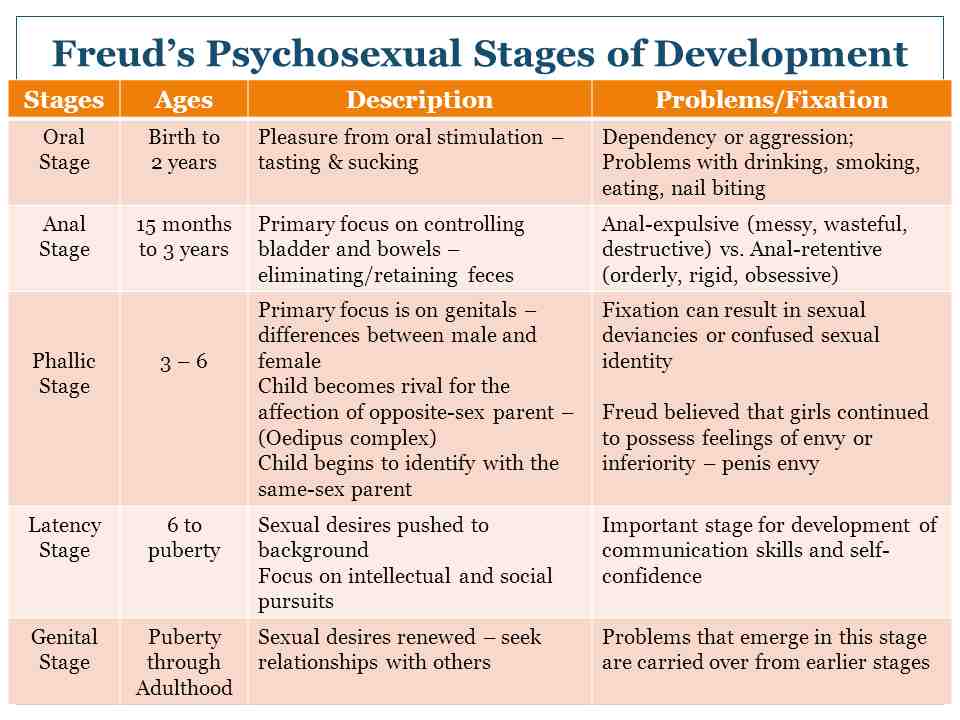
49.Psychosexual Stages-if these stages are completed successfully, the results is a healthy personality, and if issues occurred and not resolved at a specific stage, fixation may occur. 
53.BF Skinner’s Operant Conditioning 

55.Social-Cognitive Learning/Observational Learning
-Albert Bandura
-people not only learn from receiving punishments and rewards, they can also learn while watching other people being rewarded or punished.
-Albert Bandura
-people not only learn from receiving punishments and rewards, they can also learn while watching other people being rewarded or punished.
57.Self Concept(Carl Rogers)
-he believes that a person can reach self actualization if the person’s ideal self(who they want to be) is congruent with their self image(actual behavior)
-he believes that a person can reach self actualization if the person’s ideal self(who they want to be) is congruent with their self image(actual behavior)
60.Parts of a Neuron 



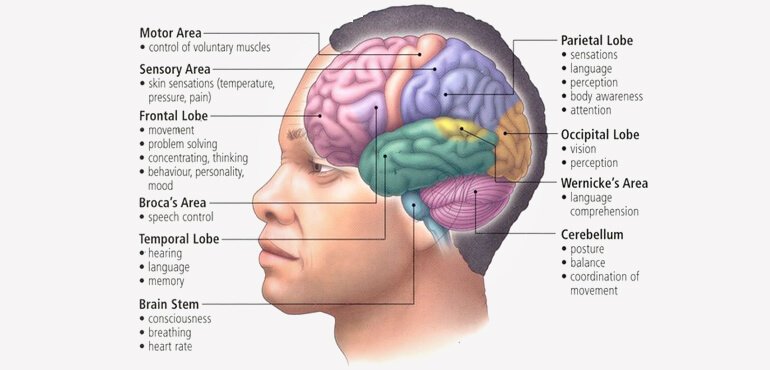
61.Parts of Brain 
67.Schizophrenia-psychotic disorder characterized by inability to dram the line between reality and fantasy. Severely disordered thinking, bizarre behavior. 

68.Personality disorders-persistent, rigid, and maladaptive patterns of behaviors that interfere with normal social interaction 

70.Social Influence-how the presence of others affects one’s thoughts.
Conformity-change in behavior to match other’s
Compliance-change in behavior as a response to a request to change
Obedience-compliance to request of an authority figure
Conformity-change in behavior to match other’s
Compliance-change in behavior as a response to a request to change
Obedience-compliance to request of an authority figure
Click entry 29 for continuation.
@threadreaderapp unroll
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh