Must Know: Physics [Thread]
(Topics: Motion, Force, Energy, Work, Power, Thermodynamics, Electricity, Fluids, Optics etc.)

Derived Quantities-depend on other quantities.
Scalar- Quantity having a magnitude only (ie. Distance, time, temperature)
Vector- a quantity having both magnitude and direction (ie. Displacement, velocity, acceleration)
acceleration due to gravity (g) – the constant acceleration of a freely falling body
Note: almost the same with UARM equations with minor changes.

Inertia-tendency of things to resist change in motion.
F=ma
Note: Unit-Newton (N)
Note: Even though action and reaction forces are equal and oppositely directed, they don’t cancel each other when they are acting on different objects.
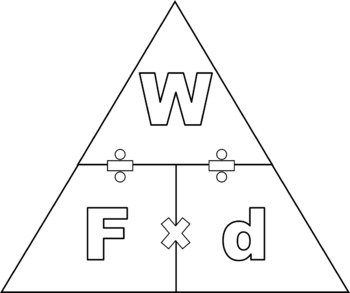
Note: work= positive if the F has the same direction with the d
Work=negative if the F has an opposite direction with the d
Work is 0 if the F is perpendicular to d
Symbol and Formula: PE = mgh
Kinetic Energy- Is the energy associated to particles and systems that are moving.
Symbol and Formula: KE = ½ mv2
Conservation of ME
ME=KE+PE
ME(initial)=ME(Final)
Formula: p=mv
Where:
P=momentum(Kg - m/s)
M=mass (Kg)
V=velocity (m/s)
-the product of the force and the time. It is the interval during which it acts; change in momentum.
I=FΔt
Conservation of Momentum
-if the net force acting on a system is zero, the total momentum of the system remains the same.
Note: In any collisions, the total momentum of the system is always conserved. The total momentum equals total momentum after collision.
KE(total)=KE(final) – KE(initial)
*When the colliding bodies stick together and move as one body after the collision is called completely inelastic collision.
Formula: KE(initial)=KE(final)
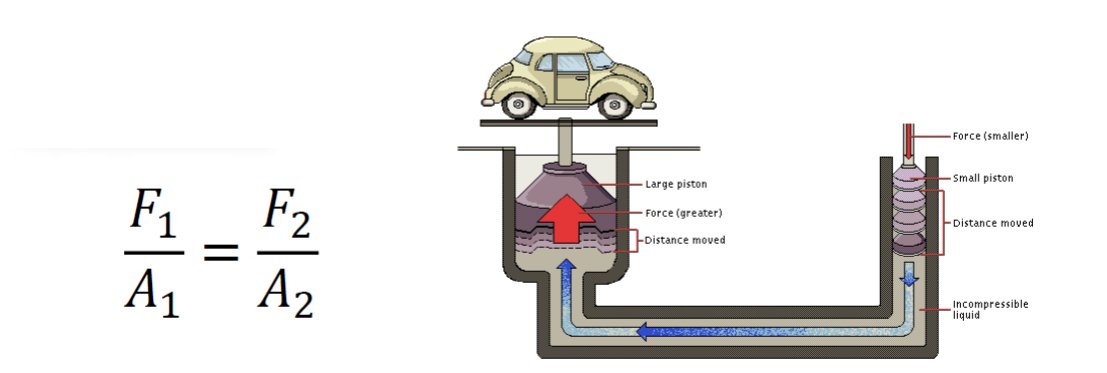
- any substance that does not have definite shape and exhibits the phenomenon of flow.
Gases- expand to fill their container’s shape
Liquid- flow under the influence of gravity until they occupy the lowest possible regions of their containers
Ferrofluid- liquid which becomes strongly polarized in the presence of magnetic field
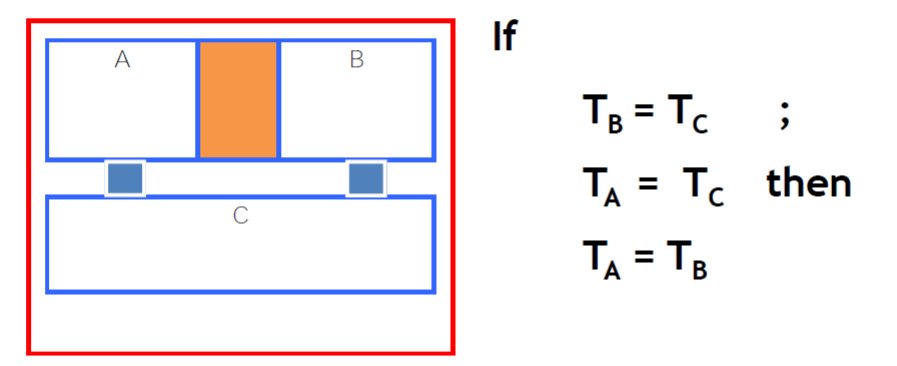
Zeroth Law- If body A is in thermal equilibrium with body B, and B is in thermal equilibrium with C, then A is in Thermal equilibrium with C.
1st law- states that energy can be converted from one form to another with the interaction of heat, work and internal energy, but it cannot be created nor destroyed, under any circumstances.

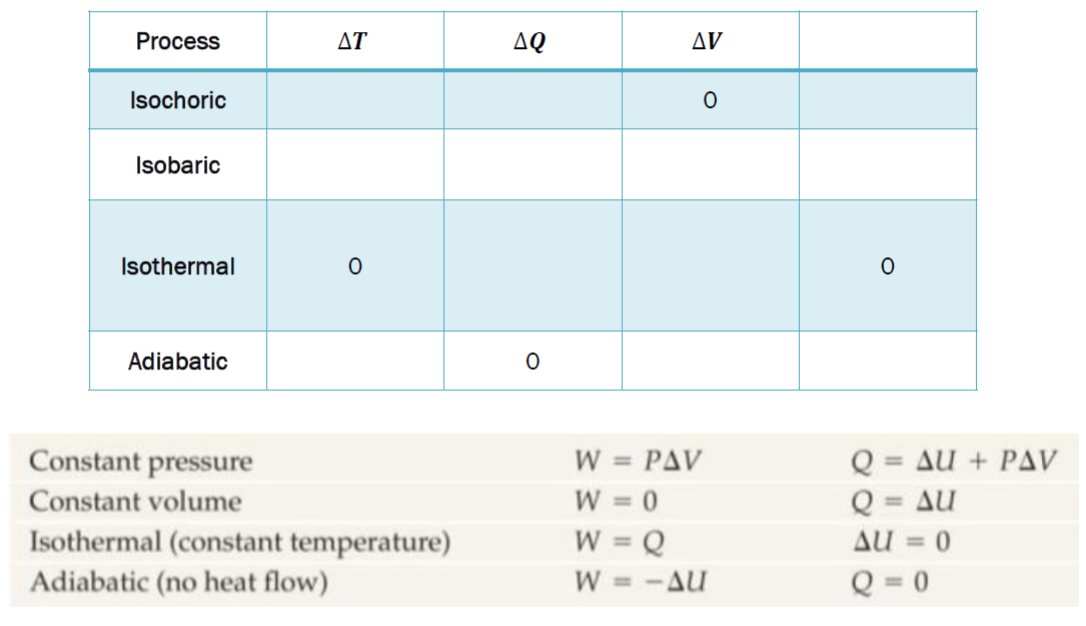
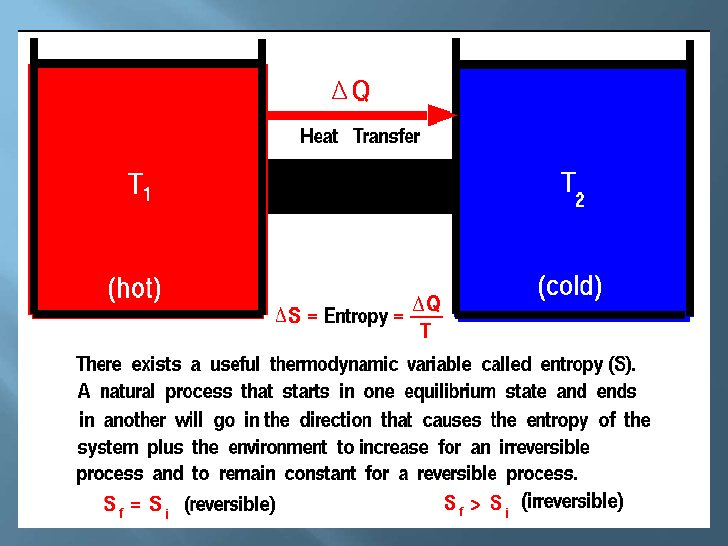
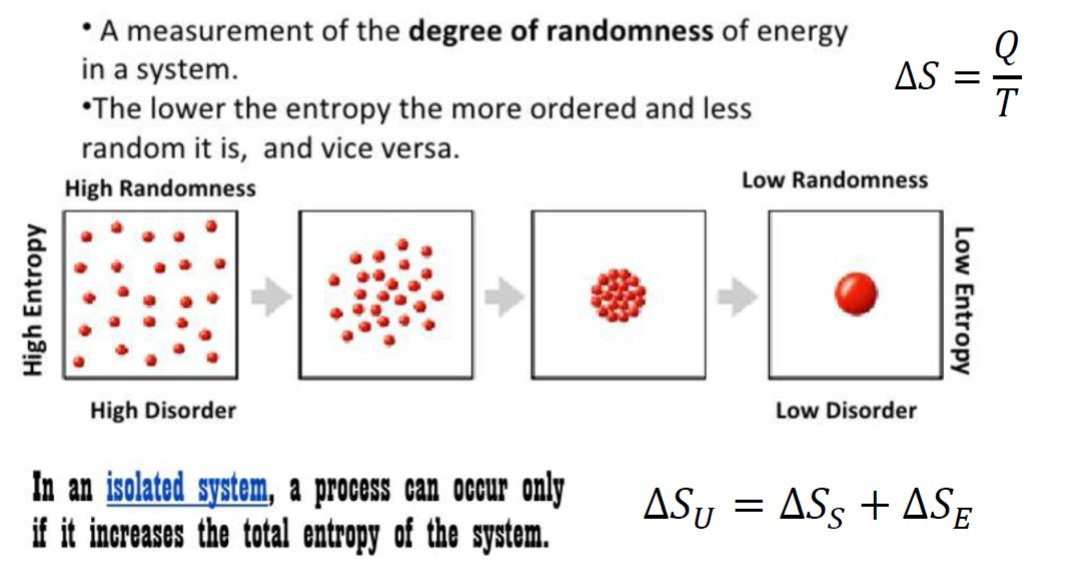
2nd Law-in any cyclic process the netropy will either increase or remain the same.
Entropy-measure of disorderliness of a system.