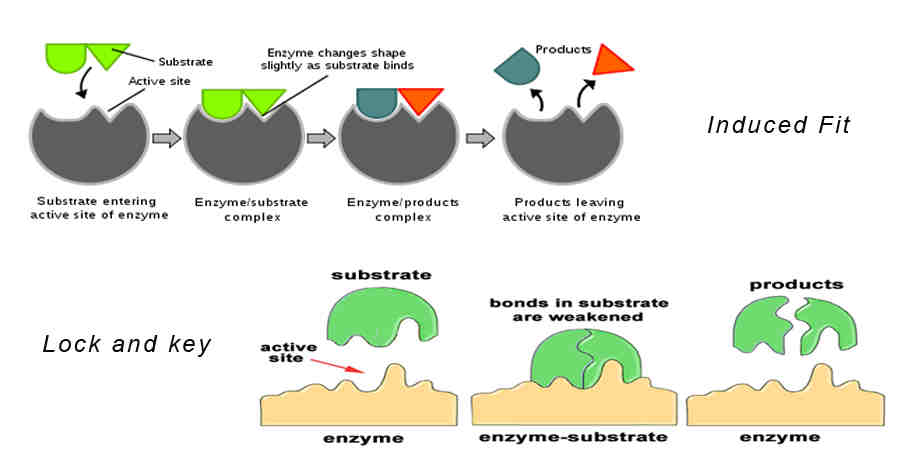
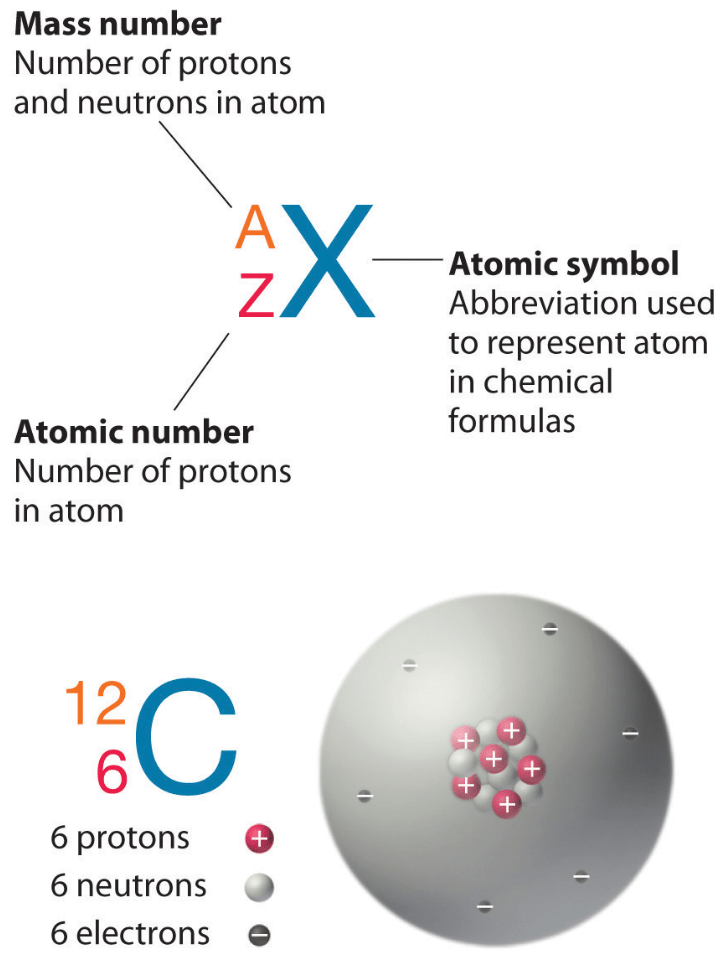Must Know: Chemistry [THREAD]
(Topics: Matter, Solubility, Concentration, Colligative Properties, Gas Laws, Atom, Compounds, Acids & Bases, Chemical Tests, Thermochemistry, Quantum numbers etc.)
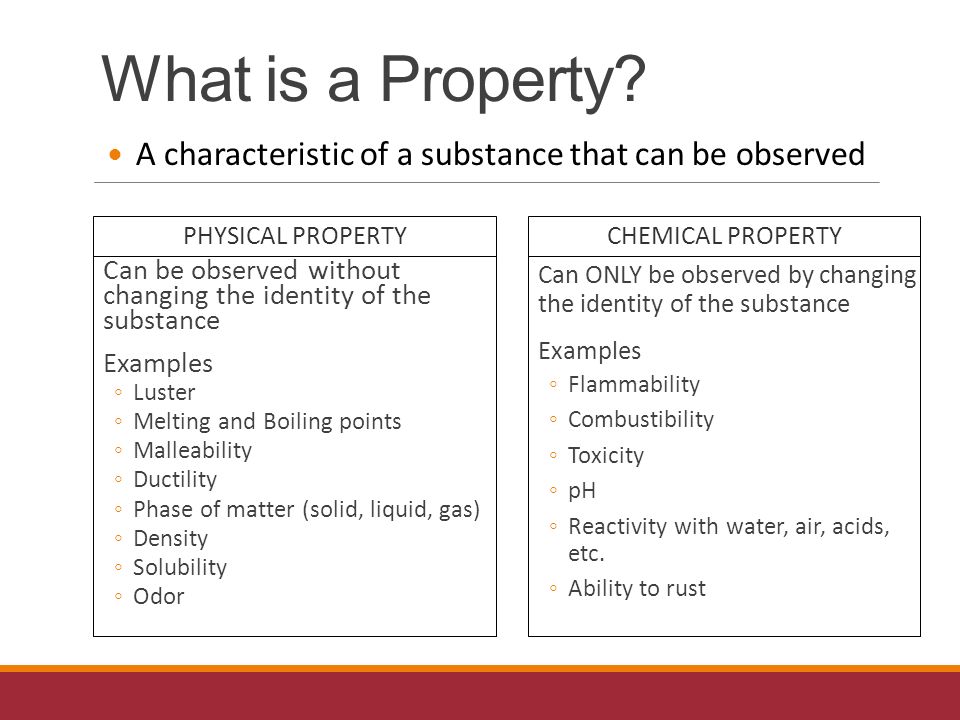
-science that deals with the properties and composition of various forms of matter
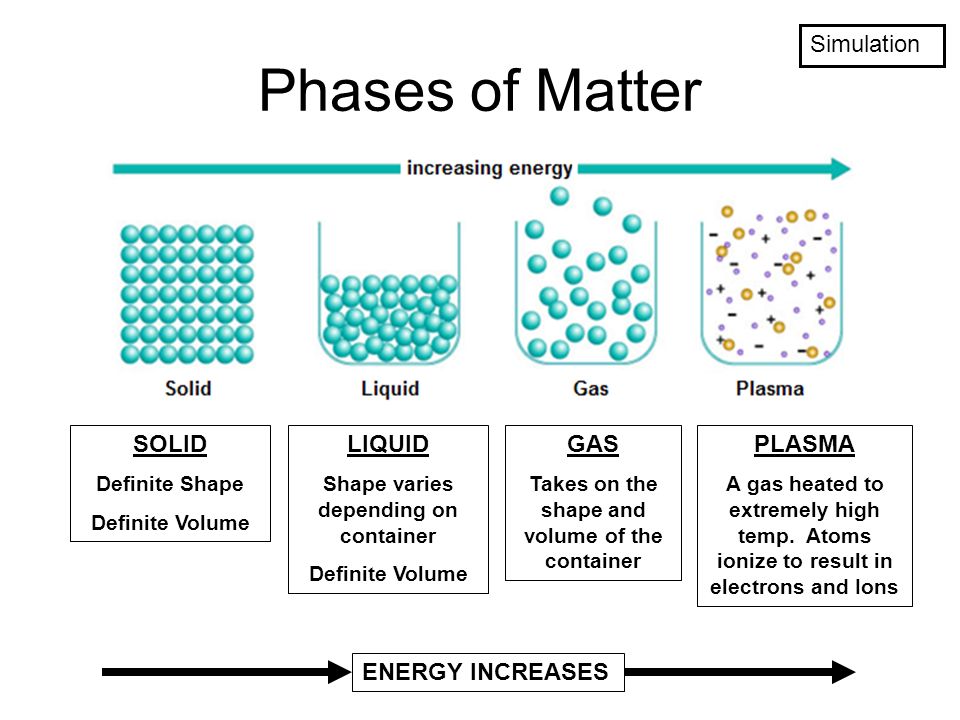
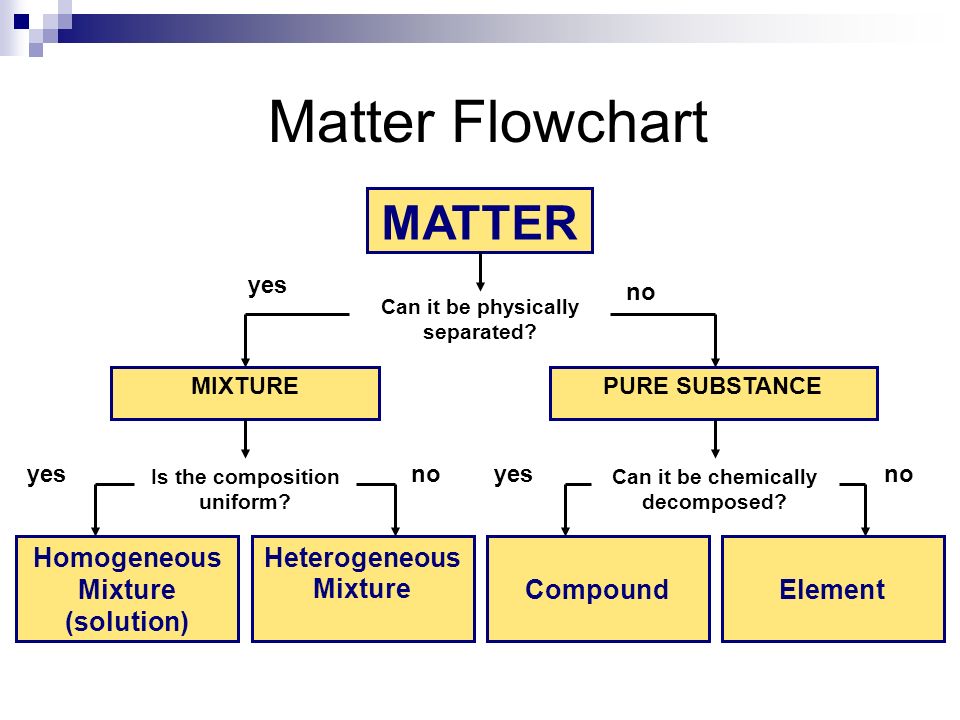
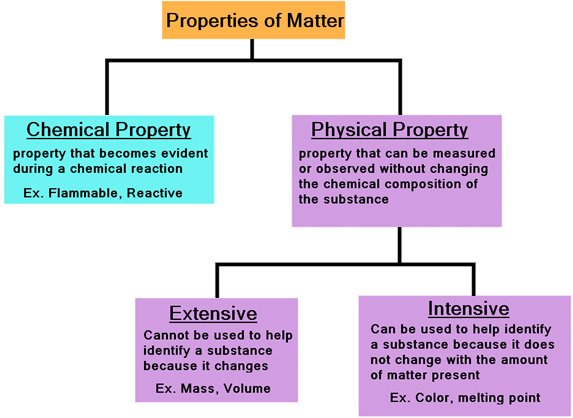
Matter
-anything that has mass and occupies space
Mass
-amount of matter in an object
Volume
-amount of space occupied by matter
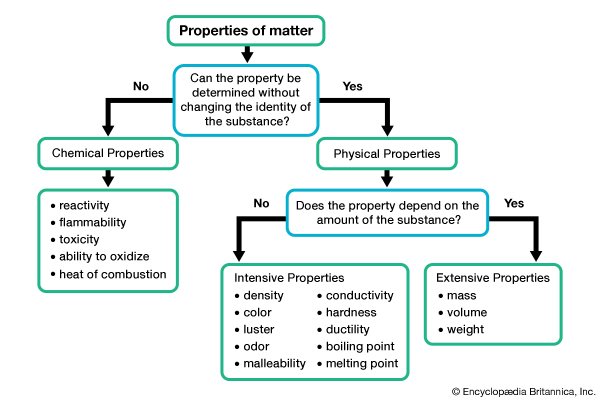
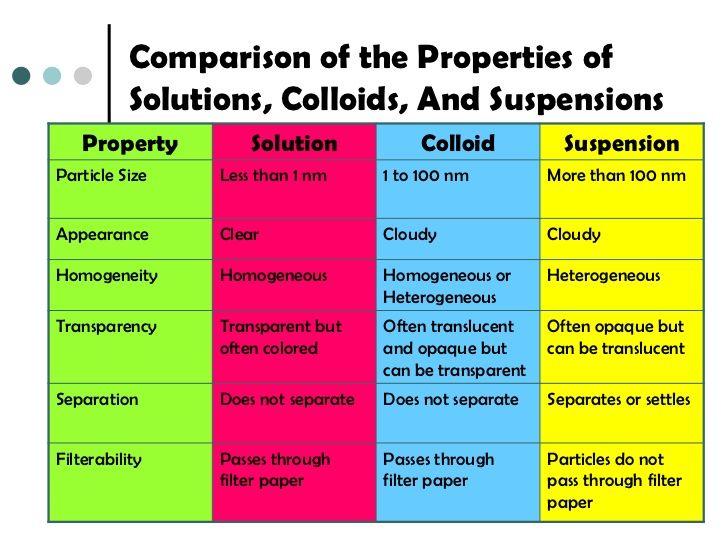
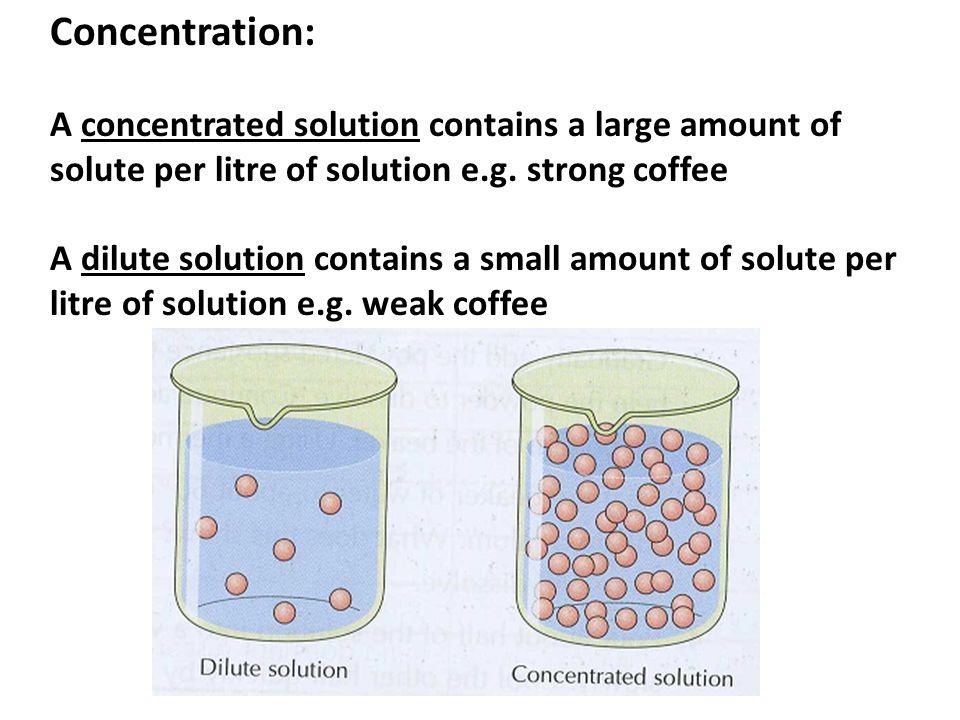
-properties of solutions that depends on the ratio of the no. of solutes to the no. of solvent molecules present in a solution
-they do not depend on the nature of the chemical species present
Isomers-Same formula but different structures
Isotopes-Same atomic numbers different mass number
Isobars-Same mass number different atomic number
Isotones-Same number of neutrons
Isoelectronic-Same number of electrons
a.Electrostatic interactions-attractions between the opposing poles of dipole molecules
-dipole-dipole
-ion-dipole
-ion-induced dipole
-hydrogen bonding
b.Van Der Waal’s-sum of all attractive and repulsive forces between and within molecules


-highest oxidation state of organic compounds
-contains one or more carboxyl group