Must Know: Biology Part 2 [THREAD]
(Topics: Circulatory System, Nervous System, Digestive System, Endocrine System, Immune System, Blood Typing, DNA & RNA, Genetics etc.)
Autotrophs
-“self-feeders” harvest the energy of sunlight through photosynthesis, converting radiant energy in to chemical energy (i.e. plants, algae, and some bacteria)
Heterotrophs
-“fed by others” used energy/food produced by others/autotrophs (i.e. humans etc.)
Digestion
-breakdown of large molecules into smaller ones.
Metabolism
-the sum of all chemical processes occurring within a living cell.
Catabolism
-Destructive Metabolism
Anabolism
-Constructive Metabolism
Arteries
-away from the heart (thicker walls because of the high pressure of blood from the heart)
Veins
-towards the heart
Capillaries
-where exchange of gases & waste materials happen; only single file of RBC can pass through.
Arteries
-Oxygenated Blood
Veins
-Deoxygenated Blood
Exception:
Pulmonary Arteries
-Deoxygenated Blood
Pulmonary Vein
-Oxygenated Blood
Pulmonary Circulation
- From heart, to the lungs and back to the heart.
Systemic Circulation
-From heart to the rest of the body & vice versa.
Autonomic NS
-facilitates most of the involuntary actions
Sympathetic System
-Fight-or-Flight-or-Freeze
Parasympathetic system
-Rest-and-digest
Somatic NS
-all voluntary activities
Afferent Neurons
-transmitting impulses from the area where you received the stimulus
Efferent Neurons
-conductance of motor reflexes from the CNS to the area where the impulse where received.
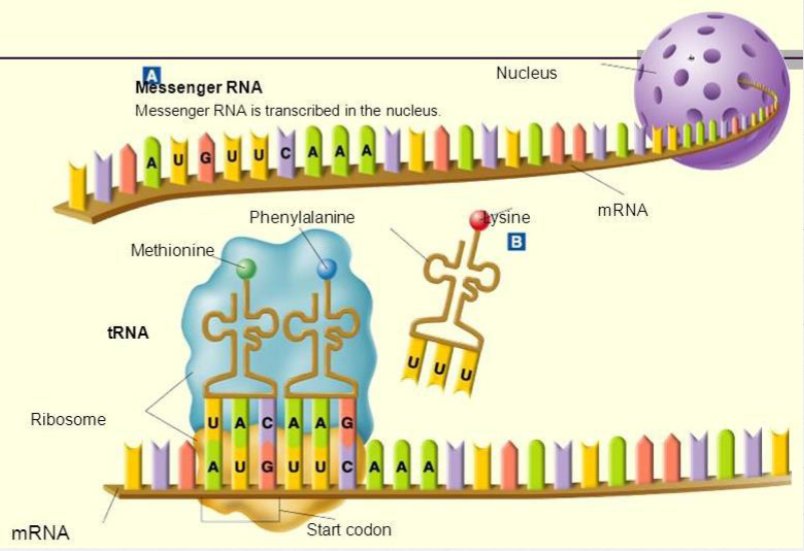
DNA-RNA-Protein
Initiation: AUG
Termination: UAA, UGA, UAG
Pyrimidines: Cytosine and Thymine/Uracil
Purines: Adenine and Guanine
(Adenine is to Thymine; Cytosine is to Guanine)
Helicase
-Unzips the DNA
Primase
-Provides RNA primers
DNA Polymerase III
-synthesizes in the lagging strand (3’ to 5’)
DNA Polymerase I
-synthesizes in the leading strand (5’ to 3’)
Ligase
-connects the areas of the Okazaki fragments
Topoisomerase-
relieves the tension and stress on the unzipped DNA; prevents super-coiling
Single Strand Binding Protein
-Prevents the unzipped strand of DNA from reattaching again
Initiation
-occurs when the RNA polymerase meets the start codon
Elongation
-the synthesis of RNA from DNA template via the addition of nucleotides
Termination
-occurs when the RNA polymerase meets the stop codon forming mRNA
-Presence of -OH
-Single-stranded
-less stable
-Contains Purines (Adenine and Guanine) and
-Pyrimidines (Uracil and Cytosine)
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
-carries amino acids to the ribosomes
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
-binds proteins in order to form ribosomes
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
-serves as template for the formation of proteins
Law of Dominance
-states that one of the factors for a pair of inherited traits will be dominant and the other recessive, unless both factors are recessive.
-dominant allele completely masks the recessive allele
Law of Segregation
-states that two members of a single gene pair separate from each other during gamete formation.
-ensures that each gamete contains one of the genes of a gene pair
Law of Independent Assortment
- states that genes on different chromosomes independently behave in the production of gametes.
-genes are randomly assigned; characteristics are totally independent
Dominant-trait that is manifested
Recessive-trait that is masked
Genotype-Genetic Makeup
Phenotype-Morphological manifestation of genotype
Homozygous-trait that is pure bred; has the same type of trait
Heterozygous-combination of a dominant and a recessive traits
Incomplete Dominance
-blending of characteristics
-a type of inheritance that neither traits from the parents is dominant to the other.
Codominance
-no blending of characteristics
-a type of inheritance that both traits from the parents are manifested
Multiple Alleles
- Characteristics have more than two alleles
-a type of inheritance where-in multiple alleles affect a certain trait.
Polygenes
- Characteristics are determined by two or more genes
-a type of inheritance where in multiple number of genes affect a certain trait