Challenging Case @IDweek2019
63M B cell lymphoma
RCHOP, RICE —> CD19-CAR-T
ACV, Levo, Fluco Prophy
SIRS —> cytokine release syndrome
Rx tocilizumab —> anakinra
Mental status change —> CART-related encephalopathy
Rx: dexamethasone
Now coma / anisocoria
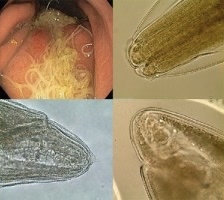
MRI / path (photo)
63M B cell lymphoma
RCHOP, RICE —> CD19-CAR-T
ACV, Levo, Fluco Prophy
SIRS —> cytokine release syndrome
Rx tocilizumab —> anakinra
Mental status change —> CART-related encephalopathy
Rx: dexamethasone
Now coma / anisocoria
MRI / path (photo)

Presented by Dr Pearlie Chong @UTSWNews at @IDWeek2019 what is the diagnosis of this neurologic complication following CD19-targeted CAR T cell Rx, followed by use of tocilizumab, anakinra and dexamethasone to manage cytokine release and encephalopathy syndrome?
Case diagnosis: cerebral angioinvasive #mucormycosis due to #Rhizopus
CD19-targeted CAR-T #immunotherapy for B cell cancers —> #lymphodepletion
Other immunodeficiencies:
1. conditioning Rx
2. hypogammaglobulinemia
3. IL-6 deficiency (tocilizumab)
4. IL-1 inhibition (anakinra)
CD19-targeted CAR-T #immunotherapy for B cell cancers —> #lymphodepletion
Other immunodeficiencies:
1. conditioning Rx
2. hypogammaglobulinemia
3. IL-6 deficiency (tocilizumab)
4. IL-1 inhibition (anakinra)
Infections post #CART
1. Incidence: 1.19 / 100 days (=salvage chemoRx)
2. Onset: median 6d
3. Causes: bacteria most common; virus (mostly respiratory, few herpes); fungus 5%
4. Risk: ALL, >4 prior chemoRx, high-dose CAR-T, cytokine release syndrome
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
1. Incidence: 1.19 / 100 days (=salvage chemoRx)
2. Onset: median 6d
3. Causes: bacteria most common; virus (mostly respiratory, few herpes); fungus 5%
4. Risk: ALL, >4 prior chemoRx, high-dose CAR-T, cytokine release syndrome
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
Cytokine release syndrome and risk of infection after CAR-T infusion
Severe (grade 4–5) cytokine release syndrome is the primary risk factor - associated with a >3-fold increased hazard for infection.
doi.org/10.1093/ofid/o…
Severe (grade 4–5) cytokine release syndrome is the primary risk factor - associated with a >3-fold increased hazard for infection.
doi.org/10.1093/ofid/o…
#CART in children and young adults
1. Incidence: 30%
2. Most common during first month after CAR-T infusion
3. Etiology: bacteria (most common, 18%), viruses (mostly respiratory, 12%). One case of IFI.
doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt…
1. Incidence: 30%
2. Most common during first month after CAR-T infusion
3. Etiology: bacteria (most common, 18%), viruses (mostly respiratory, 12%). One case of IFI.
doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt…
Infections after CAR-T for B cell cancers
1. CRS grade 3 or higher - independent correlation with infection
2. Incidence: 42%
3. Most common - month 1
4. Causes: Bacteria; then virus and fungus
5. Late infections (>1 month) - respiratory viruses
doi.org/10.1093/cid/ci…
1. CRS grade 3 or higher - independent correlation with infection
2. Incidence: 42%
3. Most common - month 1
4. Causes: Bacteria; then virus and fungus
5. Late infections (>1 month) - respiratory viruses
doi.org/10.1093/cid/ci…
#CART #IDDailyPearls
1. CD19-targeted CAR-T cell causes severe lymphodepletion (note additional deficiencies from conditioning agents)
2. Infection: bacteria > virus (mostly respiratory, few herpes) > fungus
3. Cytokine release syndrome - independent predictor of infection
1. CD19-targeted CAR-T cell causes severe lymphodepletion (note additional deficiencies from conditioning agents)
2. Infection: bacteria > virus (mostly respiratory, few herpes) > fungus
3. Cytokine release syndrome - independent predictor of infection
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh