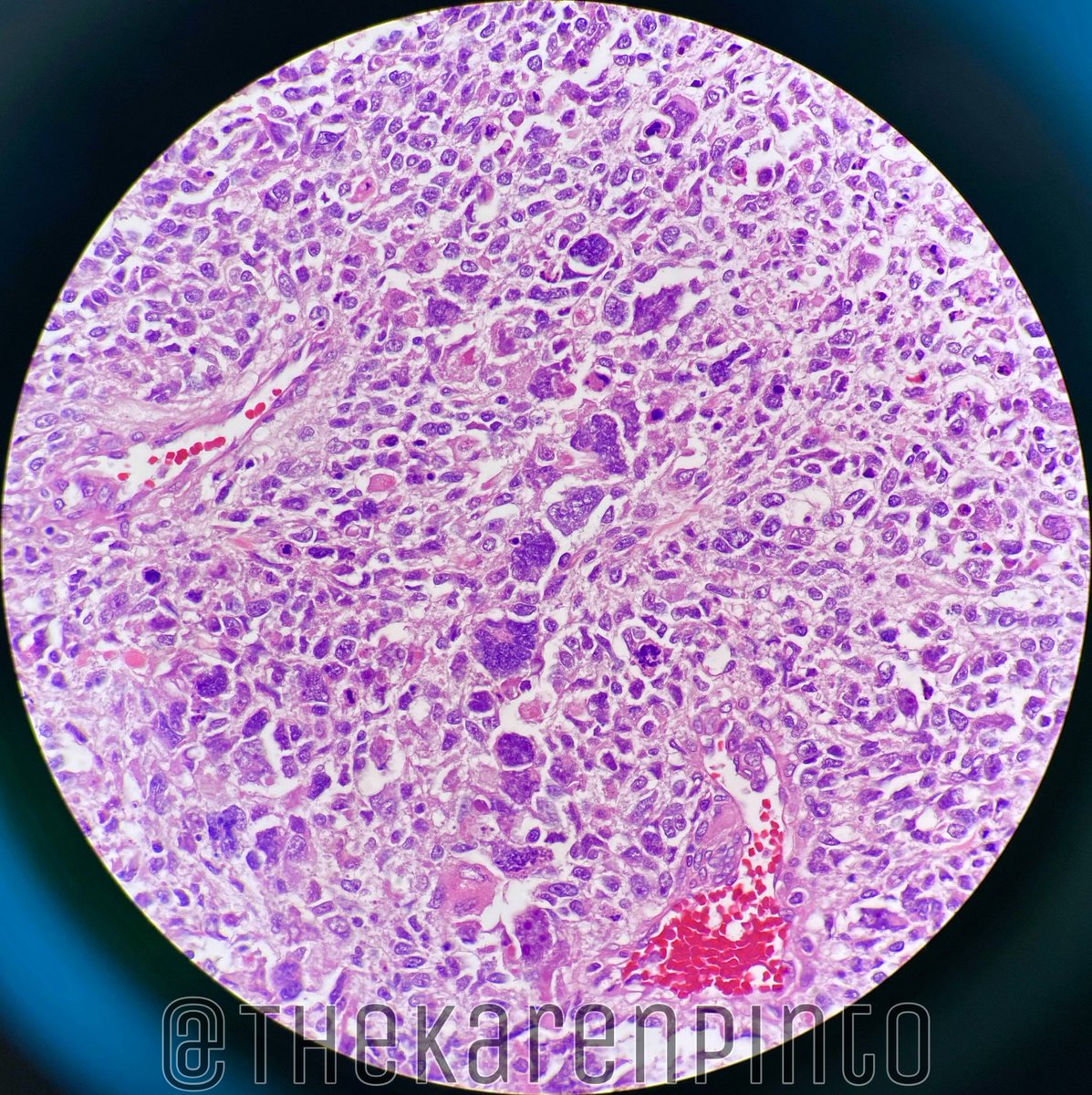
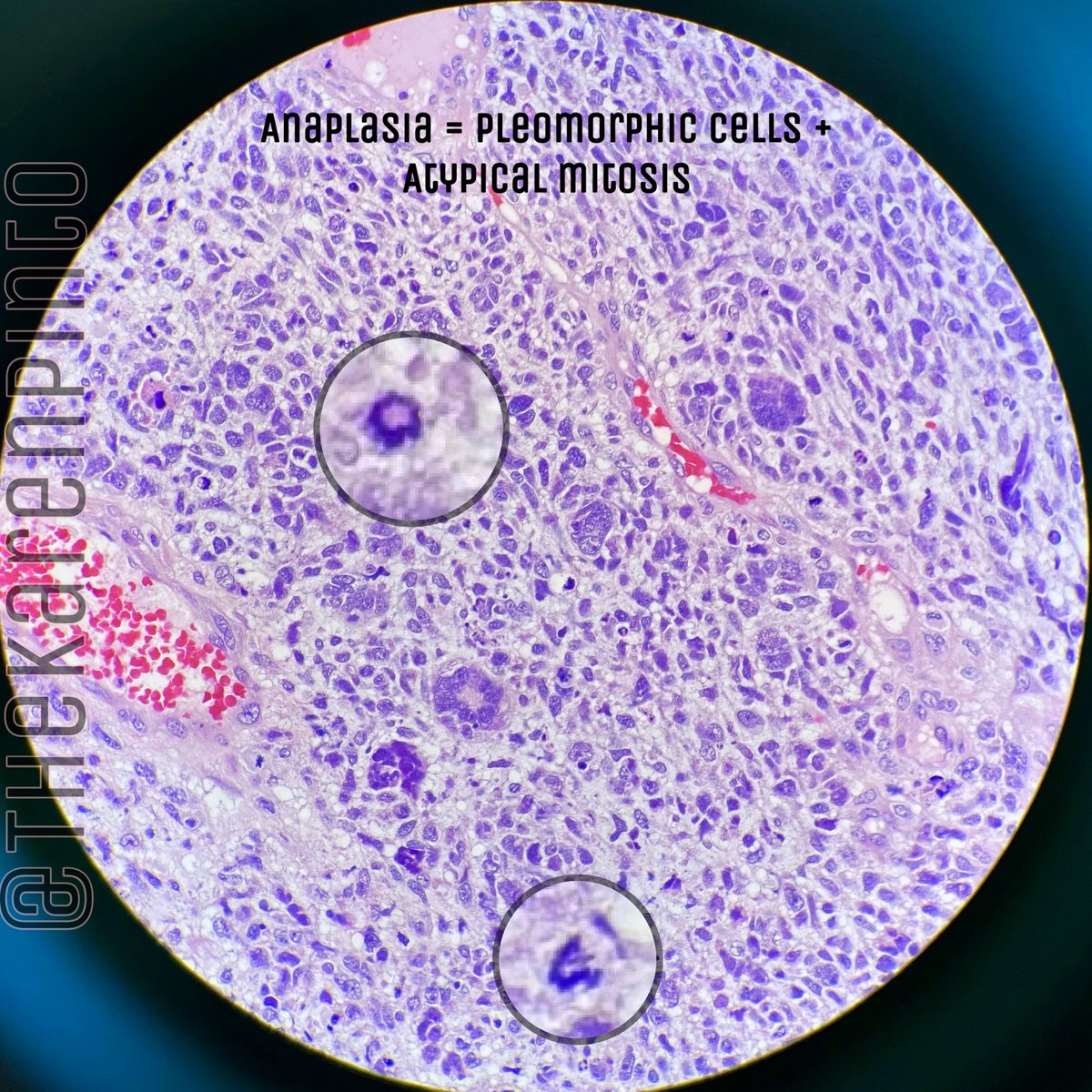
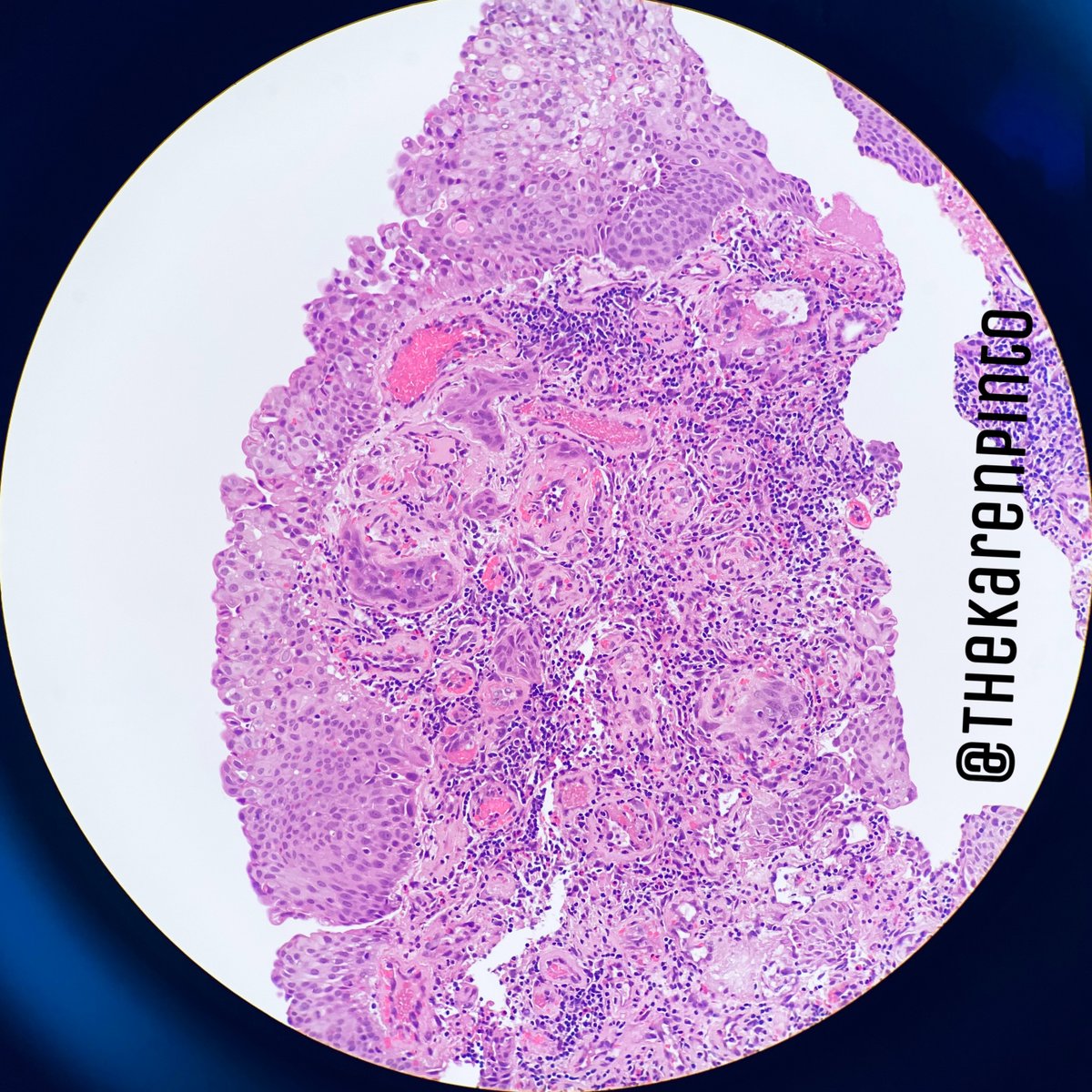
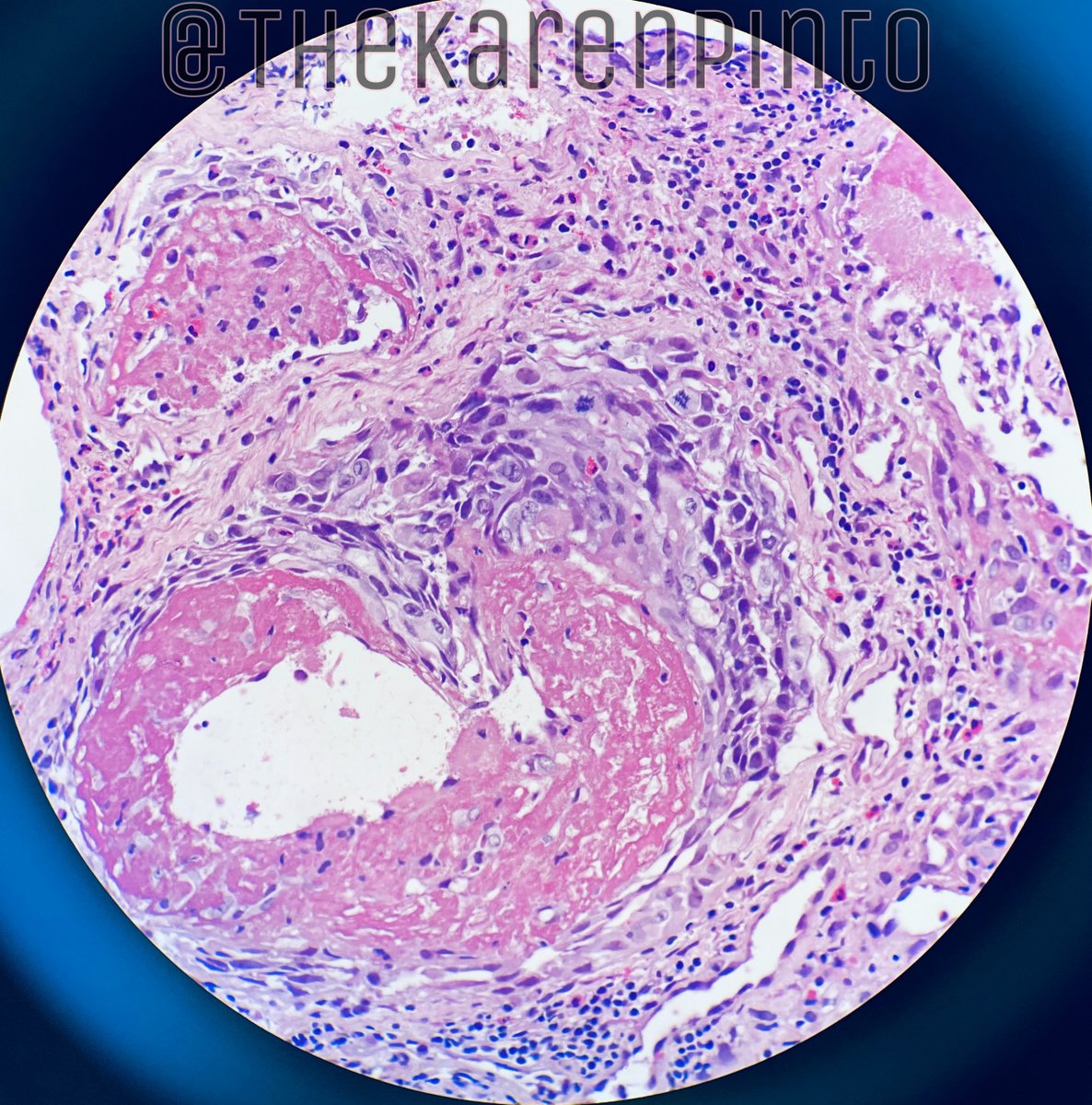
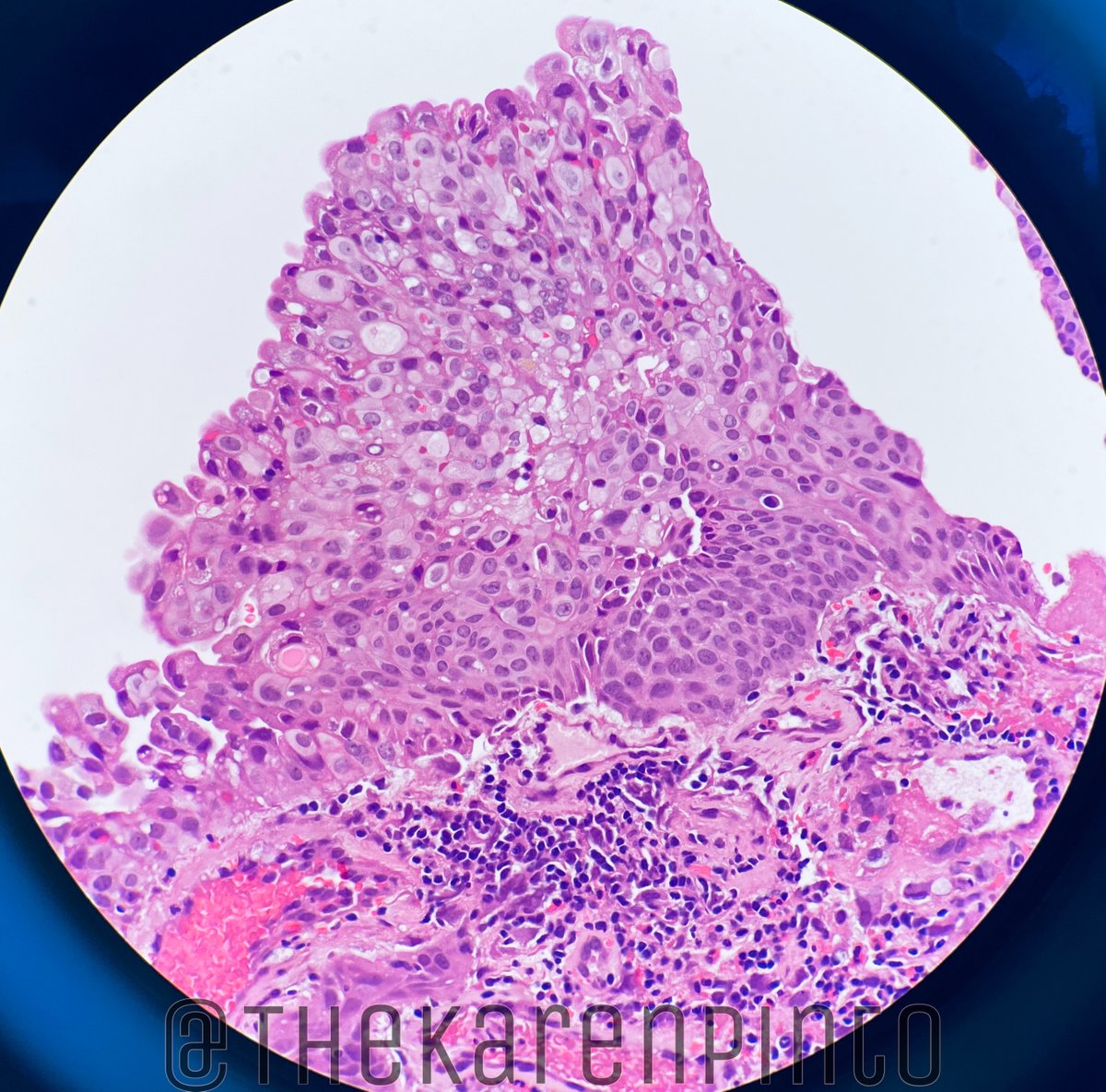
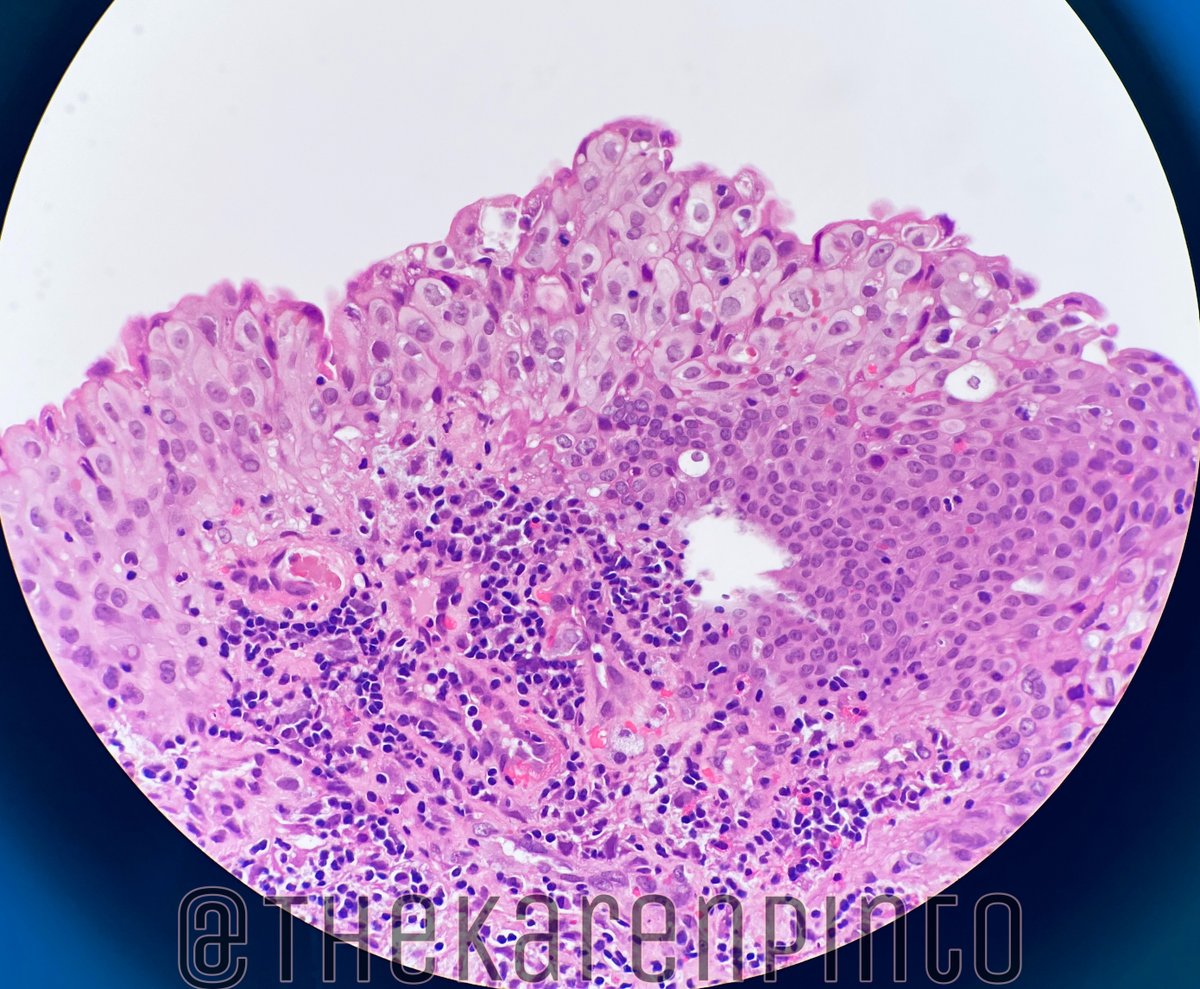
History: Proptosis & pain
Specimen: Exenteration
#pathology #PediPath #BSTPath #orbit
(*Image courtesy: Dr. Sayed Hashim)
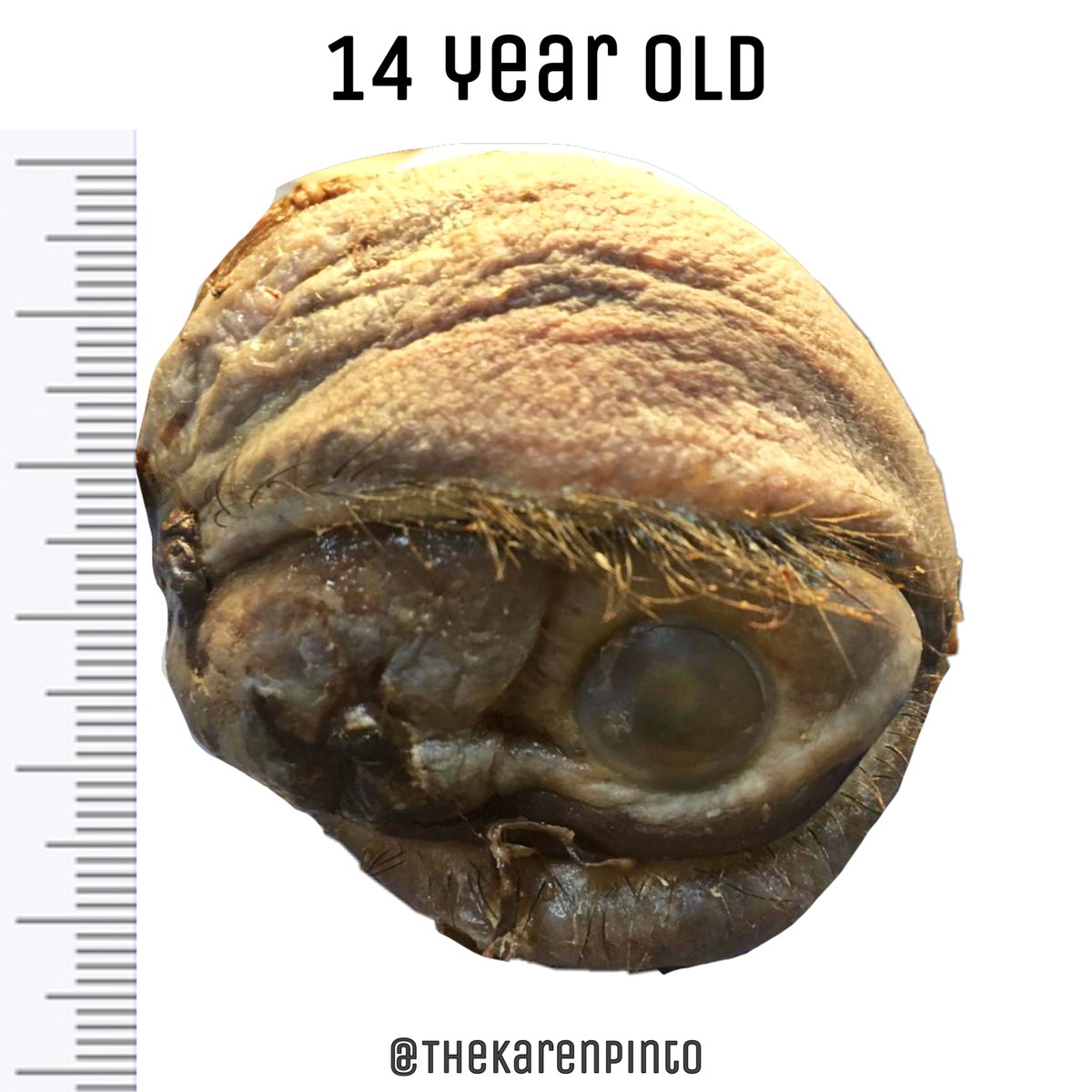
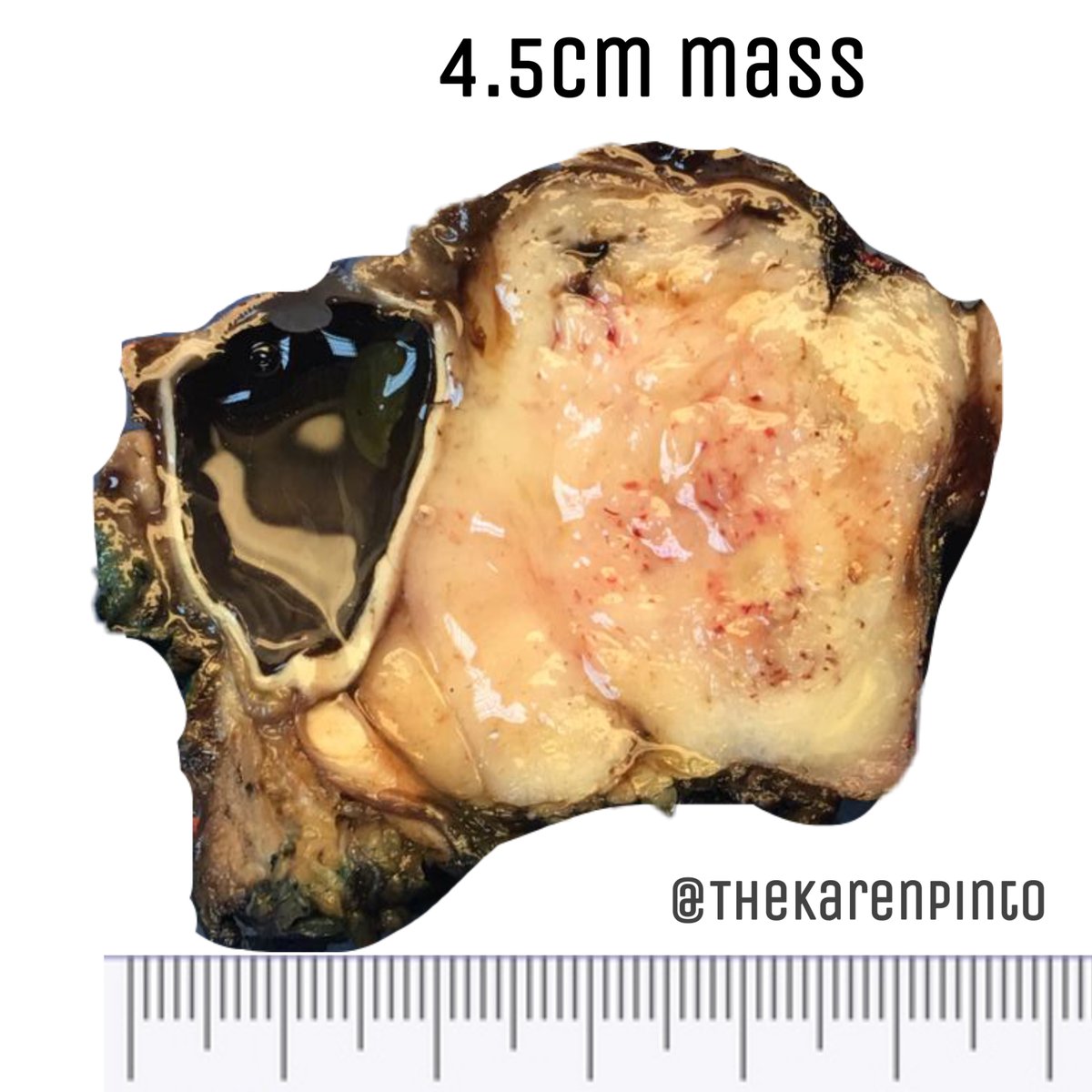
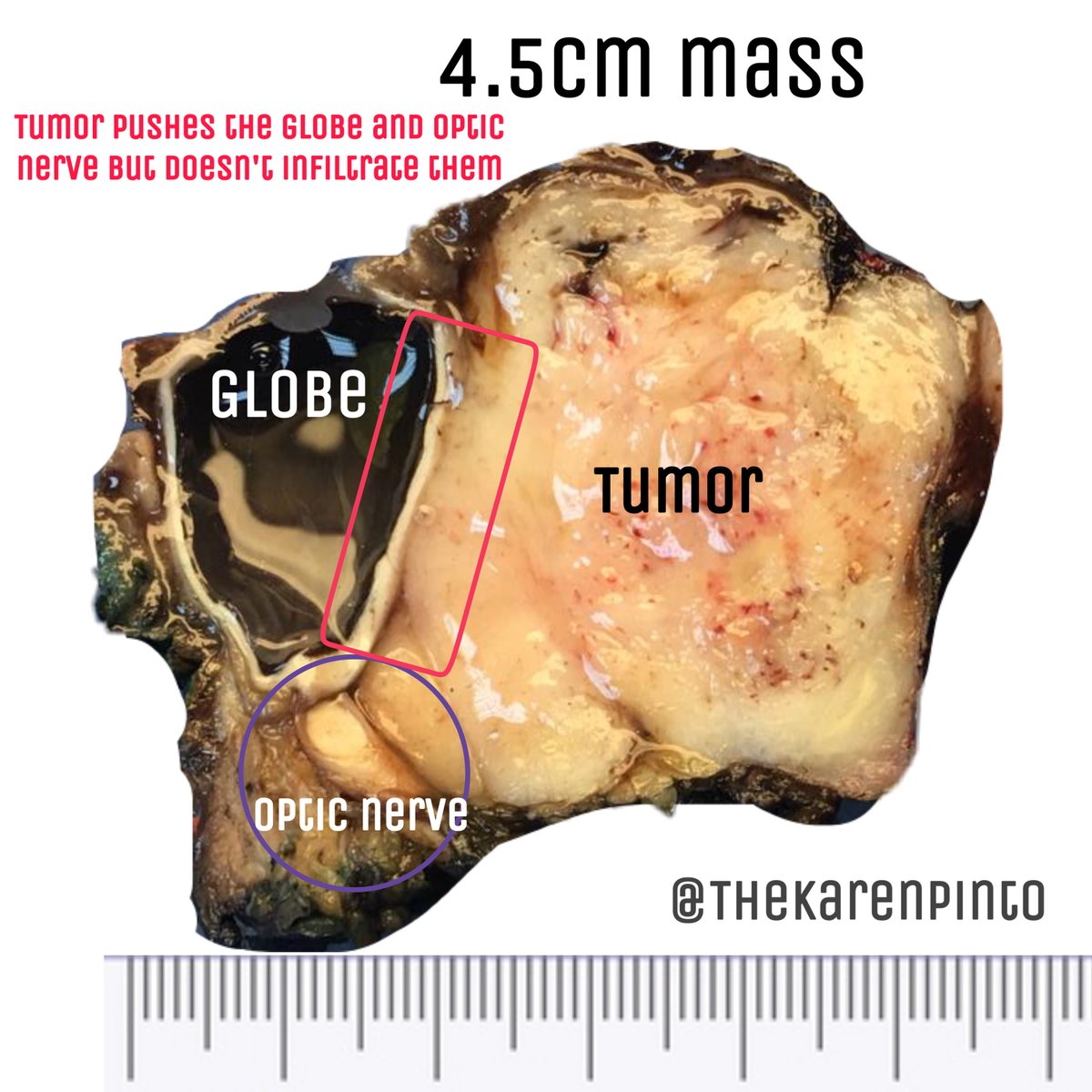
Q1. Is it benign or malignant?
DDx of orbital tumors in children:
1. Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS)
2. Neuroblastoma
3. Synovial sarcoma
4. Chloroma
& so on
Most common orbital malignancy in children
(*Also seen as a second malignancy, post-radiation, for treated cases of
-squamous cell carcinoma (eyelid)
-retinoblastoma)
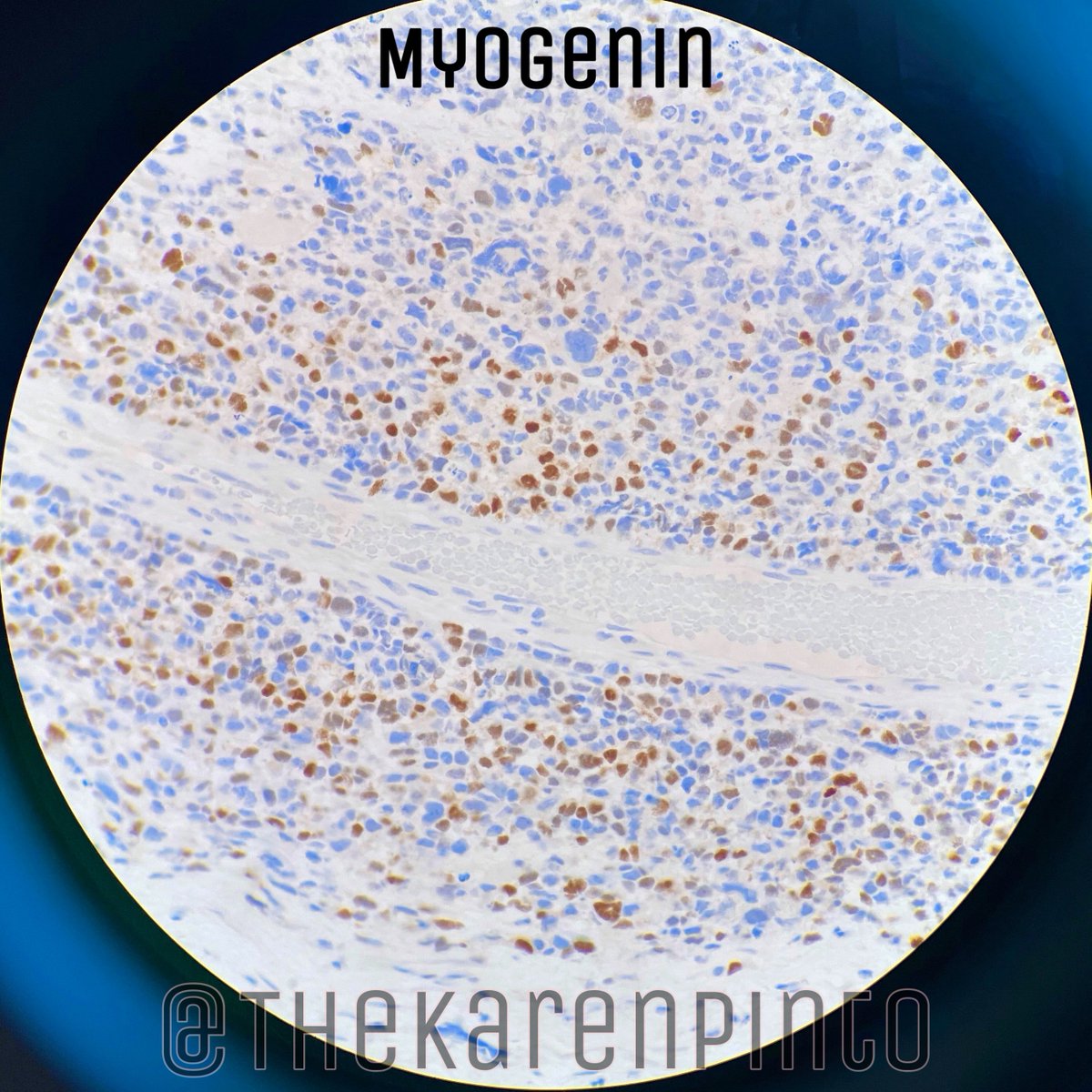
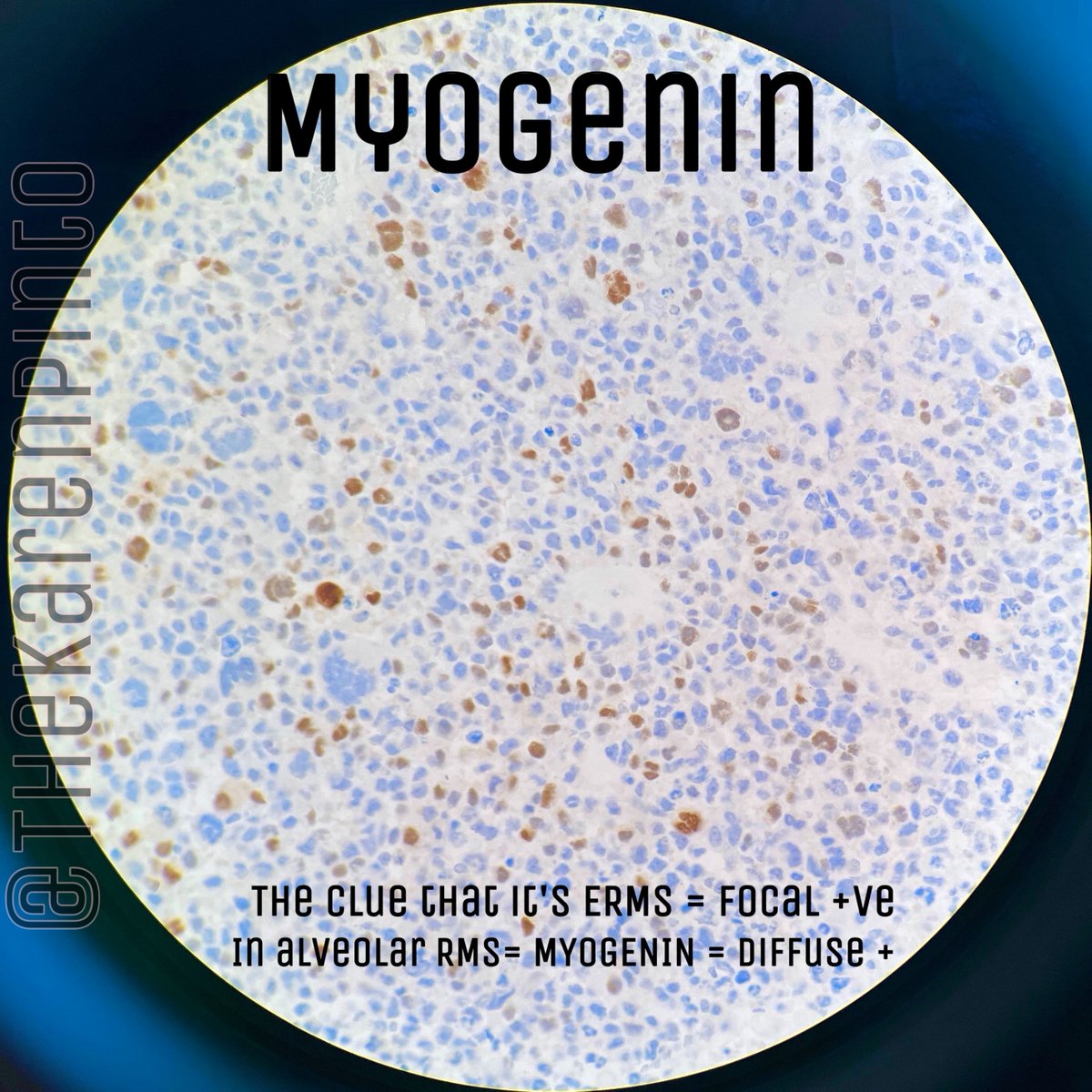
Q. Myogenin staining helps differentiate embryonal RMS from it’s mimic: solid variant of alveolar RMS
Myogenin- “focal” / “patchy” staining in ERMS while it is DIFFUSELY positive in alveolar RMS
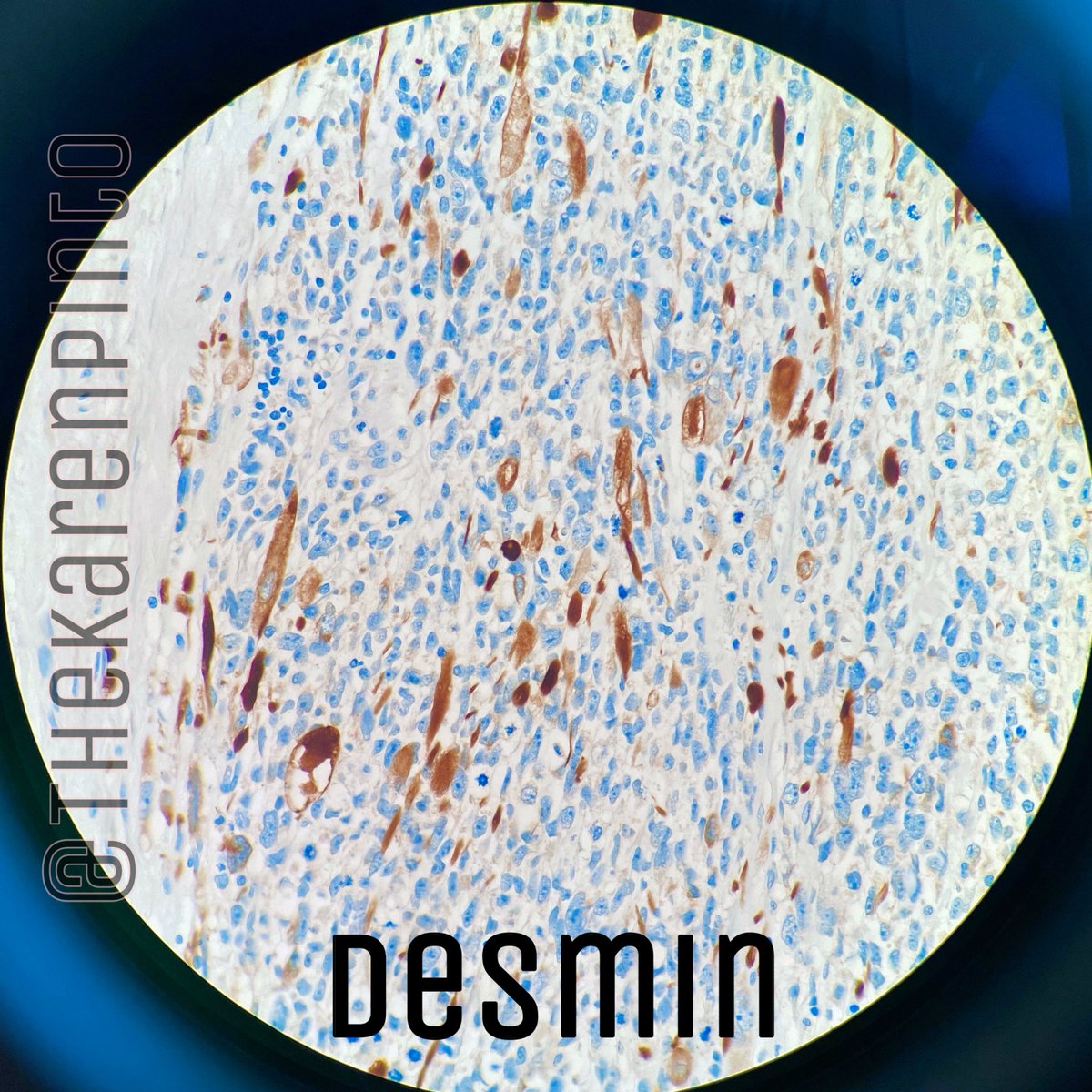
Desmin-positive
#IHCPath
(LOH-loss of heterozygosity)
As well as chromosomal aneuploidies with gains of chromosome 8 (seen in 90% of patients)
All the others are seen with “alveolar” rhabdomyosarcomas
Depends on 3 things:
1. Clinical Stage
2. Clinical Group
3. Clinical Risk group
Unlike other organ systems, there is NO AJCC stage given for head and neck ERMS or ARMS.
All the above staging systems, need clinical information
*If the child is LESS THAN 10 years, in spite of having ‘Clinical Stage 4’ disease, they will be assigned ‘INTERMEDIATE’ risk group
-orbit
-eyelid
-conjunctive
-uveal tract
1. Embryonal (including botyroid)
2. Alveolar (worst prognosis)
3. Spindle/sclerosing
4. Pleomorphic
-Li-Fraumeni syndrome
-Dicer1 syndrome
-Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1)
-Costello syndrome
-Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
-Noonan syndrome
Combined therapy
Chemo-radiation with surgery
1. Immunotherapy
-vaccine therapy
-immune checkpoint inhibitor - Ipilimumab
-PD-1 inhibitor: Nivolumab / Pembrolizumab
2. Targeted therapy
-mTOR inhibitors (Sirolimus) for recurrent RMS
-tyrosine kinase inhibitors
(PS: The patient age, sex and history have been changed to protect the patient's identity & it’s not a recent case)
(Hope most of you survived reading it till then end)